Navigating The AI Mission Lifecycle: A Chart-Pushed Information
By admin / November 15, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Navigating the AI Mission Lifecycle: A Chart-Pushed Information
Associated Articles: Navigating the AI Mission Lifecycle: A Chart-Pushed Information
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by the intriguing matter associated to Navigating the AI Mission Lifecycle: A Chart-Pushed Information. Let’s weave fascinating data and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Navigating the AI Mission Lifecycle: A Chart-Pushed Information

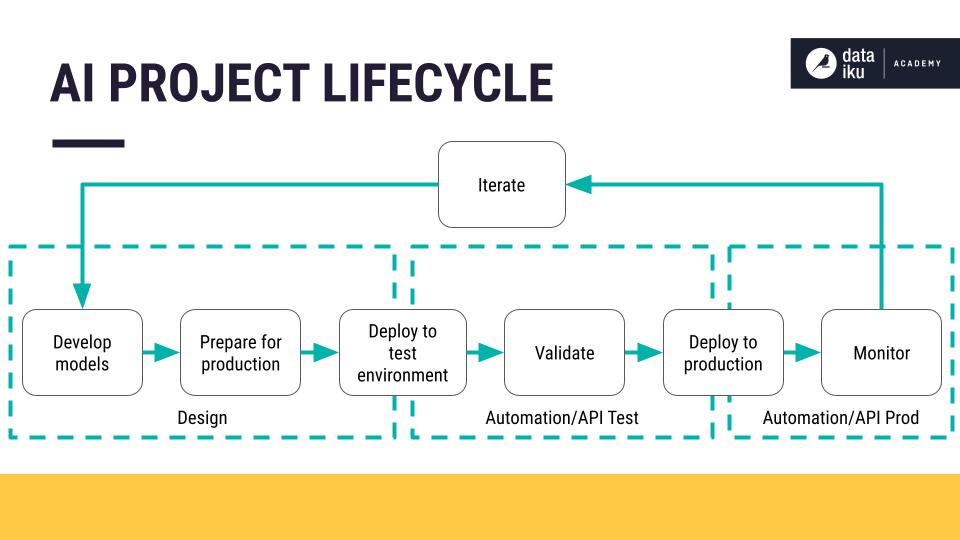
Synthetic intelligence (AI) tasks, whereas promising transformative outcomes, are notoriously complicated. Efficiently navigating their lifecycle requires a structured strategy, meticulous planning, and a deep understanding of the varied phases concerned. This text delves into the AI undertaking cycle, utilizing a complete chart as a visible information to interrupt down the important thing phases and their related actions. We’ll discover every stage intimately, highlighting potential challenges and providing greatest practices for profitable implementation.
(Insert Chart Right here: The chart ought to visually symbolize the AI undertaking lifecycle. Instructed phases embody: 1. Drawback Definition & Scoping, 2. Information Acquisition & Preparation, 3. Mannequin Choice & Coaching, 4. Mannequin Analysis & Validation, 5. Deployment & Integration, 6. Monitoring & Upkeep. Every stage may have sub-stages or key actions listed. Think about using totally different shapes and colours to symbolize totally different features, making it visually interesting and simple to know.)
1. Drawback Definition & Scoping:
This preliminary part is arguably probably the most essential. A poorly outlined downside results in wasted assets and finally, undertaking failure. This stage entails:
- Figuring out the Enterprise Drawback: Clearly articulate the enterprise problem that AI goals to handle. What particular ache level are you attempting to unravel? Quantify the issue’s impression – what are the prices related to the present scenario?
- Defining Measurable Goals: Set up clear, particular, measurable, achievable, related, and time-bound (SMART) objectives. How will you measure the success of your AI answer? Will it’s improved accuracy, decreased prices, elevated effectivity, or one thing else?
- Feasibility Evaluation: Consider the technical feasibility of the undertaking. Do you could have entry to the mandatory knowledge? Are the required AI methods mature sufficient to unravel the issue? Are there moral issues to handle?
- Useful resource Allocation: Decide the required assets – finances, personnel, infrastructure, and timeline. This entails estimating the prices related to every stage of the undertaking.
- Stakeholder Administration: Determine and interact all related stakeholders – enterprise leaders, knowledge scientists, engineers, and end-users. Guarantee alignment on objectives and expectations.
Challenges: Ambiguous downside statements, unrealistic expectations, and inadequate stakeholder buy-in are frequent pitfalls at this stage.
2. Information Acquisition & Preparation:
AI fashions are solely nearly as good as the information they’re skilled on. This part focuses on gathering, cleansing, and getting ready the information vital for mannequin improvement:
- Information Assortment: Determine and purchase the related knowledge sources. This may contain inner databases, exterior APIs, internet scraping, or different strategies. Guarantee knowledge high quality and compliance with privateness rules.
- Information Cleansing: Handle lacking values, outliers, inconsistencies, and errors within the knowledge. This typically entails knowledge imputation, normalization, and transformation methods.
- Information Exploration & Evaluation: Perceive the traits of the information – distributions, correlations, and potential biases. This helps inform mannequin choice and have engineering.
- Function Engineering: Choose and remodel related options from the uncooked knowledge to enhance mannequin efficiency. This can be a essential step that always requires area experience.
- Information Splitting: Divide the information into coaching, validation, and testing units. This ensures unbiased analysis of the mannequin’s efficiency.
Challenges: Information shortage, poor knowledge high quality, knowledge silos, and knowledge bias are frequent obstacles at this stage. Addressing these challenges requires cautious planning and doubtlessly important funding in knowledge engineering.
3. Mannequin Choice & Coaching:
This part entails selecting the suitable AI mannequin and coaching it on the ready knowledge:
- Mannequin Choice: Choose probably the most appropriate AI algorithm primarily based on the issue sort (classification, regression, clustering, and so on.) and the traits of the information. Contemplate elements like mannequin complexity, interpretability, and computational assets.
- Mannequin Coaching: Practice the chosen mannequin on the coaching knowledge. This entails iteratively adjusting the mannequin’s parameters to attenuate its error on the coaching set.
- Hyperparameter Tuning: Optimize the mannequin’s hyperparameters to enhance its efficiency. This typically entails methods like grid search, random search, or Bayesian optimization.
- Mannequin Validation: Consider the mannequin’s efficiency on the validation set to forestall overfitting. Monitor metrics like accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, and AUC.
Challenges: Choosing the proper mannequin, coping with overfitting or underfitting, and reaching passable efficiency are frequent challenges.
4. Mannequin Analysis & Validation:
Rigorous analysis is essential to make sure the mannequin meets the outlined aims:
- Efficiency Metrics: Assess the mannequin’s efficiency utilizing acceptable metrics. The selection of metrics is determined by the particular downside and enterprise objectives.
- Error Evaluation: Analyze the mannequin’s errors to establish areas for enchancment. This may contain inspecting misclassified cases or analyzing prediction errors.
- Bias Detection: Determine and mitigate potential biases within the mannequin. That is essential for guaranteeing equity and avoiding discriminatory outcomes.
- Explainability & Interpretability: Relying on the applying, it could be vital to know how the mannequin arrives at its predictions. That is notably necessary in high-stakes purposes the place transparency is essential.
- A/B Testing: Evaluate the efficiency of the AI mannequin in opposition to current strategies or various fashions.
Challenges: Deciphering efficiency metrics, coping with sudden outcomes, and guaranteeing equity and transparency are key challenges.
5. Deployment & Integration:
This part entails deploying the skilled mannequin right into a manufacturing setting:
- Mannequin Deployment: Combine the skilled mannequin into the prevailing methods or create a brand new system to host the mannequin. This may contain deploying the mannequin to a cloud platform, on-premise servers, or edge units.
- API Improvement: Create APIs to permit different methods to work together with the deployed mannequin.
- System Integration: Guarantee seamless integration of the AI mannequin with different enterprise processes and workflows.
- Person Interface (UI) Design: Develop a user-friendly interface for interacting with the AI system.
Challenges: Scalability, maintainability, safety, and integration with current methods are frequent challenges.
6. Monitoring & Upkeep:
Steady monitoring and upkeep are important for guaranteeing the long-term success of the AI system:
- Efficiency Monitoring: Observe the mannequin’s efficiency over time. This helps establish potential points and make sure the mannequin continues to satisfy the outlined aims.
- Mannequin Retraining: Retrain the mannequin periodically with new knowledge to keep up its accuracy and relevance.
- Mannequin Drift Detection: Monitor for mannequin drift – modifications within the mannequin’s efficiency as a consequence of modifications within the knowledge distribution.
- Bug Fixing: Handle any bugs or errors which will come up within the system.
- Safety Updates: Implement safety updates and patches to guard the system from vulnerabilities.
Challenges: Sustaining mannequin accuracy, detecting and addressing mannequin drift, and guaranteeing system safety are ongoing challenges.
By following a structured strategy and punctiliously contemplating the challenges at every stage, organizations can considerably improve their probabilities of efficiently deploying and sustaining high-performing AI methods. The chart offered serves as a roadmap, guiding groups by the complexities of the AI undertaking lifecycle and fostering a extra environment friendly and efficient improvement course of. Do not forget that profitable AI tasks are iterative, requiring steady monitoring, analysis, and adaptation.


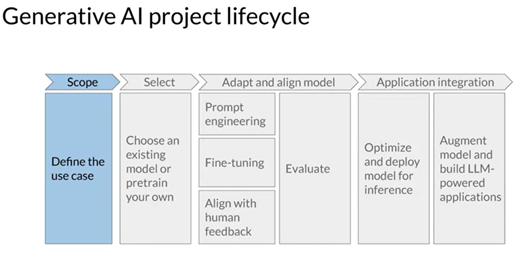
.jpg?width=933u0026name=ifographic-The%20Data%20Science%20Lifecycle-01%20(1).jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered useful insights into Navigating the AI Mission Lifecycle: A Chart-Pushed Information. We hope you discover this text informative and helpful. See you in our subsequent article!