Decoding The 30-12 months Treasury Yield: A 20-12 months Retrospective And Future Outlook
By admin / July 27, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Decoding the 30-12 months Treasury Yield: A 20-12 months Retrospective and Future Outlook
Associated Articles: Decoding the 30-12 months Treasury Yield: A 20-12 months Retrospective and Future Outlook
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to Decoding the 30-12 months Treasury Yield: A 20-12 months Retrospective and Future Outlook. Let’s weave fascinating data and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the 30-12 months Treasury Yield: A 20-12 months Retrospective and Future Outlook

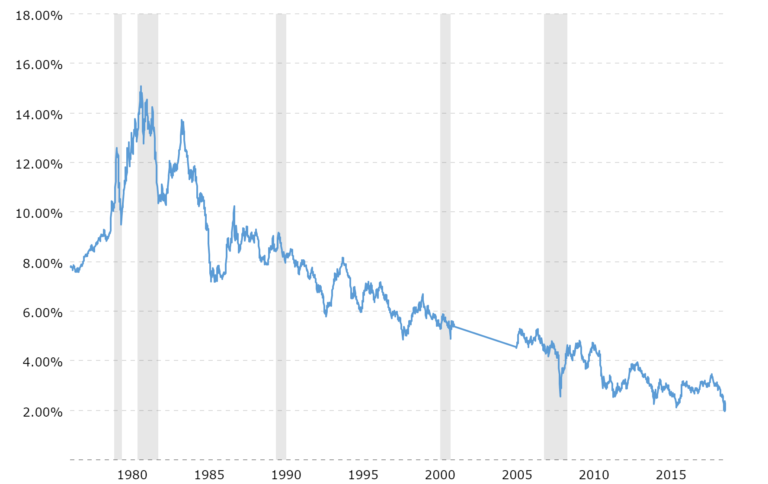
The 30-year Treasury yield, a benchmark for long-term rates of interest in the USA, holds important sway over the economic system and monetary markets. Its actions mirror investor sentiment, inflation expectations, financial development prospects, and central financial institution insurance policies. Analyzing its trajectory over the previous 20 years reveals worthwhile insights into its habits and potential future route. This text delves into the historic efficiency of the 30-year Treasury yield because the 12 months 2000, exploring the important thing elements which have pushed its fluctuations and providing a perspective on what the longer term may maintain.
The 2000s: A Decade of Decline and Volatility
The beginning of the millennium noticed the 30-year Treasury yield hovering round 6%, a mirrored image of comparatively sturdy financial development and reasonable inflation. Nevertheless, the last decade was marked by important volatility and a persistent downward pattern. The dot-com bubble burst in 2000 triggered a recession, prompting the Federal Reserve to aggressively minimize rates of interest. This led to a decline within the 30-year yield, reaching lows beneath 4% by 2003.
The mid-2000s witnessed a interval of relative stability, with the yield steadily rising because the economic system recovered. Nevertheless, the seeds of the 2008 monetary disaster have been already sown. The housing bubble, fueled by straightforward credit score circumstances, in the end burst, triggering a worldwide monetary meltdown. This disaster despatched shockwaves by way of the monetary system, resulting in a dramatic flight to security and a plunge within the 30-year Treasury yield. It fell to historic lows, briefly dipping beneath 3% in late 2008.
The Federal Reserve’s response to the disaster concerned unprecedented quantitative easing (QE), a program designed to inject liquidity into the monetary system by buying long-term Treasury securities, together with 30-year bonds. This large intervention additional suppressed long-term rates of interest, retaining the 30-year yield exceptionally low all through the rest of the last decade.
The 2010s: A Sluggish Ascent and the Taper Tantrum
The 2010s have been characterised by a sluggish and uneven ascent within the 30-year Treasury yield. The economic system steadily recovered from the Nice Recession, however the restoration was sluggish and uneven. The Federal Reserve maintained its accommodative financial coverage, retaining rates of interest close to zero for an prolonged interval. Nevertheless, because the economic system confirmed indicators of enchancment, the prospect of the Fed finally tapering its QE program started to weigh available on the market.
The "taper tantrum" of 2013 highlighted the market’s sensitivity to modifications within the Fed’s financial coverage. The mere suggestion of a discount in QE led to a pointy rise in Treasury yields, together with the 30-year yield, as buyers anticipated increased rates of interest sooner or later. This episode underscored the highly effective affect of central financial institution actions on long-term rates of interest.
Regardless of the taper tantrum, the 30-year Treasury yield remained comparatively low all through many of the 2010s, reflecting persistent low inflation and sluggish financial development in lots of components of the world. The yield steadily climbed, however it by no means reached the degrees seen within the early 2000s.
The 2020s: Inflation, Pandemic, and Rising Yields
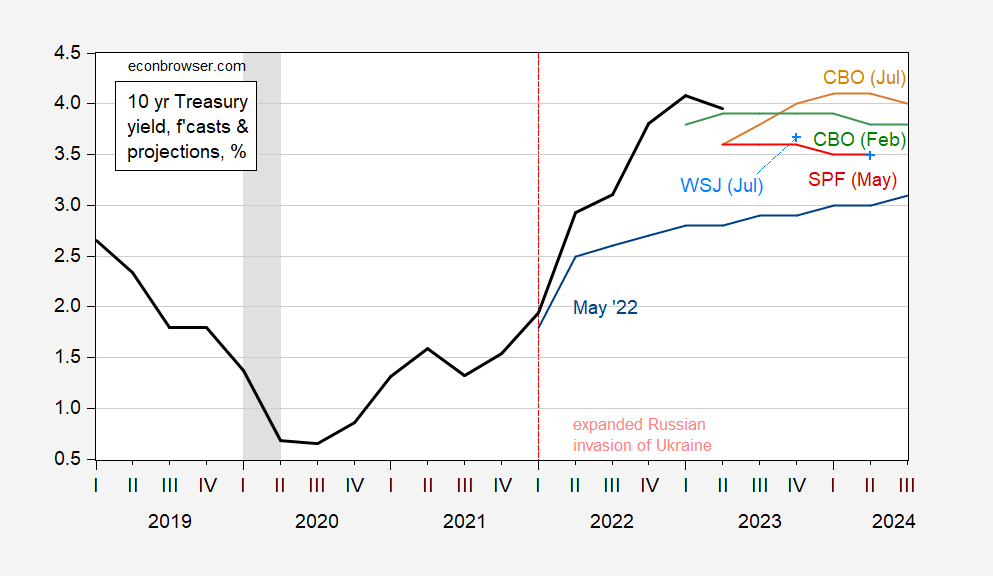
The 2020s have witnessed a dramatic shift within the trajectory of the 30-year Treasury yield. The COVID-19 pandemic triggered an unprecedented financial shock, resulting in large authorities spending and additional quantitative easing by the Federal Reserve. This, mixed with provide chain disruptions and pent-up demand, fueled a surge in inflation, the likes of which hadn’t been seen in a long time.
The rise in inflation compelled the Federal Reserve to reverse course and embark on an aggressive financial tightening marketing campaign, elevating rates of interest sharply to fight inflation. This led to a big enhance within the 30-year Treasury yield, as buyers anticipated increased rates of interest for an prolonged interval. The yield surged to ranges not seen in over a decade, reflecting the market’s expectation of a sustained interval of upper rates of interest to regulate inflation.
The conflict in Ukraine additional exacerbated inflationary pressures, including to the upward stress on the 30-year Treasury yield. Geopolitical uncertainty and provide chain disruptions contributed to the persistent rise in inflation and rates of interest.
Components Influencing the 30-12 months Treasury Yield
A number of key elements work together to affect the 30-year Treasury yield:
- Inflation Expectations: Increased inflation expectations typically result in increased Treasury yields, as buyers demand increased returns to compensate for the erosion of buying energy.
- Financial Progress: Sturdy financial development usually results in increased Treasury yields, as buyers anticipate increased future rates of interest from the central financial institution.
- Federal Reserve Coverage: The Federal Reserve’s financial coverage selections considerably impression Treasury yields. Elevating rates of interest usually results in increased yields, whereas reducing charges results in decrease yields.
- World Financial Circumstances: World financial circumstances can even affect Treasury yields. A world financial slowdown can result in decrease yields, whereas robust world development can result in increased yields.
- Provide and Demand: The availability and demand for Treasury securities play a vital function in figuring out their yields. Elevated demand results in decrease yields, whereas elevated provide results in increased yields.
- Geopolitical Occasions: Geopolitical occasions, resembling wars or political instability, can considerably impression Treasury yields, as buyers search secure haven belongings throughout occasions of uncertainty.
Future Outlook: Uncertainty and Potential Eventualities
Predicting the longer term trajectory of the 30-year Treasury yield is inherently difficult, given the complicated interaction of things influencing it. Nevertheless, a number of potential eventualities will be thought of:
- Situation 1: Sustained Excessive Inflation: If inflation stays stubbornly excessive, the Federal Reserve might have to keep up a restrictive financial coverage for an extended interval, doubtlessly retaining the 30-year Treasury yield elevated.
- Situation 2: Inflation Moderation: If inflation moderates as anticipated, the Federal Reserve might finally pause or reverse its charge hikes, doubtlessly resulting in a decline within the 30-year Treasury yield.
- Situation 3: Recession: A major financial slowdown or recession might result in a decline within the 30-year Treasury yield, as buyers search secure haven belongings and the Federal Reserve cuts rates of interest.
The precise path of the 30-year Treasury yield will depend upon the evolution of those elements and the effectiveness of the Federal Reserve’s insurance policies in managing inflation and fostering sustainable financial development. Shut monitoring of inflation knowledge, financial development indicators, and Federal Reserve communications can be essential in assessing the doubtless future route of this necessary benchmark. Moreover, world financial occasions and geopolitical dangers will proceed to play a big function in shaping investor sentiment and influencing the yield on the 30-year Treasury. Understanding these dynamics is significant for buyers, policymakers, and anybody within the well being of the worldwide economic system.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied worthwhile insights into Decoding the 30-12 months Treasury Yield: A 20-12 months Retrospective and Future Outlook. We hope you discover this text informative and helpful. See you in our subsequent article!