Mastering The Pareto Chart: A Complete Information To Studying And Decoding Information
By admin / September 30, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Mastering the Pareto Chart: A Complete Information to Studying and Decoding Information
Associated Articles: Mastering the Pareto Chart: A Complete Information to Studying and Decoding Information
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing subject associated to Mastering the Pareto Chart: A Complete Information to Studying and Decoding Information. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Mastering the Pareto Chart: A Complete Information to Studying and Decoding Information

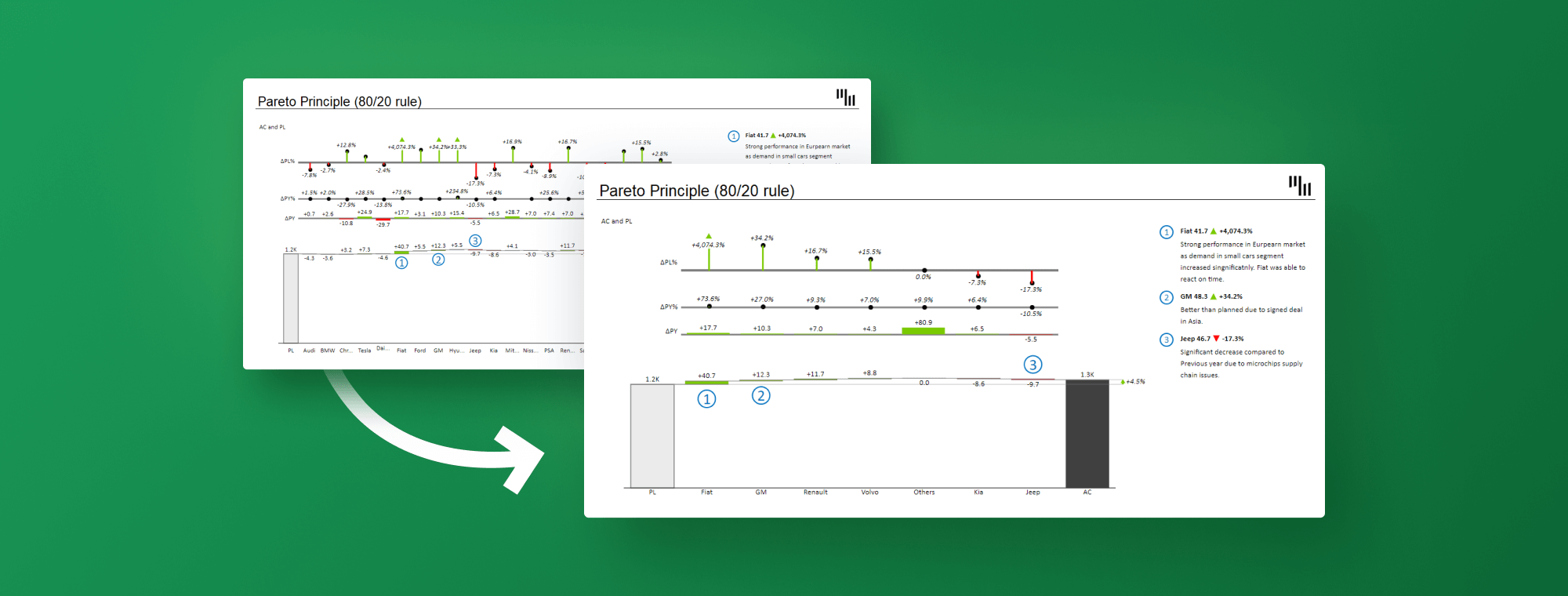
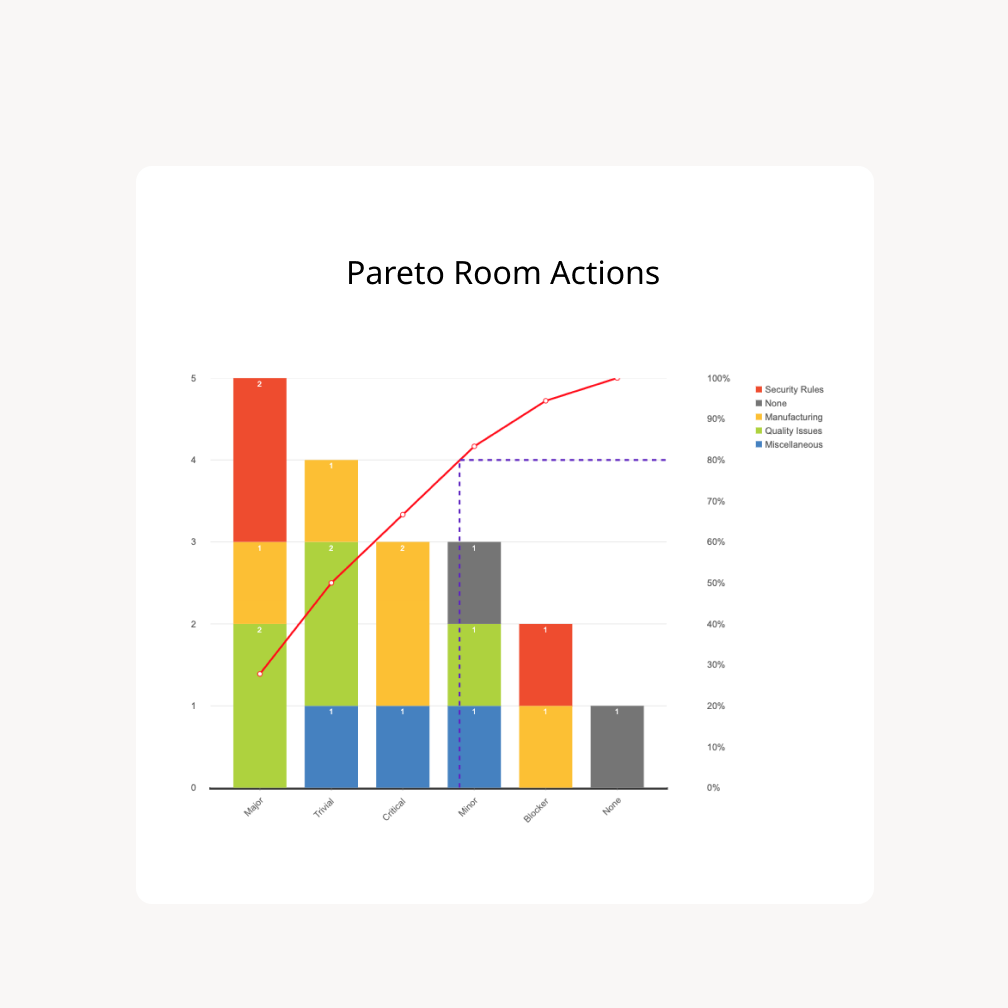
The Pareto chart, a robust visualization software named after the Italian economist Vilfredo Pareto, is a hybrid graph combining a bar chart and a line graph. It’s uniquely designed to spotlight the "very important few" contributing to the "trivial many," a precept also known as the Pareto precept or the 80/20 rule. Whereas the 80/20 rule is a common commentary, the Pareto chart’s power lies in its capability to visually characterize the relative contribution of various elements inside a dataset, permitting for centered problem-solving and useful resource allocation. This text supplies a complete information to understanding and decoding Pareto charts, protecting their development, key parts, and software throughout numerous fields.
Understanding the Building of a Pareto Chart:
A Pareto chart successfully combines two distinct graphical representations:
-
Bar Chart: This part shows the frequency or magnitude of various classes contributing to a particular downside or final result. The bars are sometimes organized in descending order, from essentially the most frequent/important class to the least.
-
Line Graph: Superimposed on the bar chart is a cumulative frequency line graph. This line represents the working complete of frequencies or magnitudes as you progress from left to proper throughout the classes. It visually demonstrates the cumulative proportion contribution of every class.
Key Parts of a Pareto Chart:
-
X-axis (Horizontal Axis): This axis lists the classes being analyzed, normally ordered from the most important to the smallest contribution. These classes might characterize something from defects in a producing course of to causes for buyer complaints. Readability in labeling is essential for correct interpretation.
-
Y-axis (Left Vertical Axis): This axis represents the frequency or magnitude of every class. This may very well be the variety of defects, the fee related to every class, or some other quantifiable measure related to the evaluation. The dimensions needs to be clearly outlined and constant.
-
Y-axis (Proper Vertical Axis): This axis shows the cumulative proportion of the whole. This axis is essential for understanding the Pareto precept’s software to the info.
-
Bars: Every bar represents a single class, with its peak comparable to its frequency or magnitude on the left Y-axis. The bars are sometimes coloured for visible emphasis.
-
Cumulative Proportion Line: This line connects the cumulative percentages calculated for every class. It reveals the share of the whole contributed by the classes as much as that time. As an illustration, if the primary three classes characterize 75% of the whole, the road will present 75% on the finish of the third bar.
Studying and Decoding a Pareto Chart:
The first objective of a Pareto chart is to determine the "very important few" classes that contribute most importantly to the general downside. That is performed by specializing in the next:
-
Class Contribution: The peak of every bar instantly reveals the person contribution of every class. The tallest bars characterize essentially the most important elements.
-
Cumulative Proportion: The cumulative proportion line reveals the cumulative contribution of the classes. This helps determine the purpose the place a small variety of classes account for a big proportion of the whole. For instance, the primary few classes would possibly account for 80% of the whole, highlighting the "very important few."
-
80/20 Rule (Pareto Precept): Whereas not all the time exactly 80/20, the chart helps visualize whether or not a small proportion of classes disproportionately contribute to the general downside. Figuring out this permits for focused interventions.
-
Prioritization: The Pareto chart facilitates prioritization by clearly exhibiting which classes require fast consideration. Assets will be centered on addressing essentially the most important contributors, resulting in higher effectivity and influence.
Purposes of Pareto Charts:
Pareto charts discover purposes throughout various fields, together with:
-
Manufacturing: Figuring out essentially the most frequent sorts of defects in a manufacturing course of, permitting for focused high quality enchancment efforts.
-
High quality Management: Analyzing buyer complaints to pinpoint the commonest points and enhance buyer satisfaction.
-
Healthcare: Figuring out essentially the most frequent causes of hospital readmissions or affected person falls, resulting in improved affected person security protocols.
-
Venture Administration: Figuring out essentially the most time-consuming duties in a undertaking, permitting for higher useful resource allocation and scheduling.
-
Enterprise Course of Enchancment: Figuring out bottlenecks in a enterprise course of, resulting in streamlining and effectivity positive factors.
-
Gross sales and Advertising and marketing: Analyzing gross sales information to determine essentially the most worthwhile merchandise or buyer segments, permitting for centered advertising campaigns.
-
Human Assets: Analyzing worker turnover information to determine frequent causes for workers leaving, permitting for improved retention methods.
Limitations of Pareto Charts:
Whereas highly effective, Pareto charts have some limitations:
-
Oversimplification: The chart would possibly oversimplify complicated issues with a number of interacting elements. Additional evaluation could be wanted to totally perceive the basis causes.
-
Information Dependency: The chart’s effectiveness relies upon closely on the accuracy and completeness of the underlying information. Inaccurate information results in deceptive conclusions.
-
Subjectivity in Class Definition: The selection of classes can affect the chart’s interpretation. Cautious consideration is required in defining classes to make sure significant evaluation.
-
Ignoring Correlation: The chart does not explicitly present correlations between classes. Additional evaluation could also be obligatory to know the relationships between contributing elements.
Superior Purposes and Issues:
-
Weighted Pareto Charts: These charts incorporate weights to mirror the relative significance of various classes, offering a extra nuanced evaluation when classes have various impacts.
-
Stratification: Making use of Pareto evaluation to totally different subgroups (strata) of information can reveal patterns that could be masked in general information. For instance, analyzing buyer complaints individually by product sort or area.
-
Root Trigger Evaluation: Pareto charts typically function a place to begin for extra in-depth root trigger evaluation strategies just like the "5 Whys" or fishbone diagrams. The chart identifies the issue areas, and additional investigation delves into the underlying causes.
Conclusion:
The Pareto chart is a beneficial software for visualizing and analyzing information, significantly when figuring out essentially the most important contributors to an issue. Its capability to spotlight the "very important few" permits for centered problem-solving and useful resource allocation, resulting in important enhancements in numerous fields. Whereas not a standalone answer, its use along with different analytical strategies supplies a robust method to data-driven decision-making. By understanding its development, key parts, and limitations, one can successfully make the most of the Pareto chart to achieve beneficial insights and obtain significant enhancements. Do not forget that the important thing to success lies not solely in creating the chart however in decoding its message and utilizing it to information efficient motion.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied beneficial insights into Mastering the Pareto Chart: A Complete Information to Studying and Decoding Information. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!