Decoding The Tides: A Deep Dive Into The Tide Chart For [Your Location] On [Your Date]
By admin / September 4, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Decoding the Tides: A Deep Dive into the Tide Chart for [Your Location] on [Your Date]
Associated Articles: Decoding the Tides: A Deep Dive into the Tide Chart for [Your Location] on [Your Date]
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we are going to discover the intriguing matter associated to Decoding the Tides: A Deep Dive into the Tide Chart for [Your Location] on [Your Date]. Let’s weave fascinating info and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the Tides: A Deep Dive into the Tide Chart for [Your Location] on [Your Date]

This text gives a complete evaluation of the tide chart for [Your Location] on [Your Date], explaining the knowledge introduced, its implications for varied actions, and the scientific ideas governing the ebb and circulate of the ocean. Bear in mind to exchange "[Your Location]" and "[Your Date]" along with your particular location and date. For correct info, you will have to seek the advice of a dependable tide prediction service particular to your chosen location (e.g., NOAA Tides & Currents, a neighborhood harbormaster, or a devoted nautical charting app). This text will use hypothetical knowledge for illustrative functions.
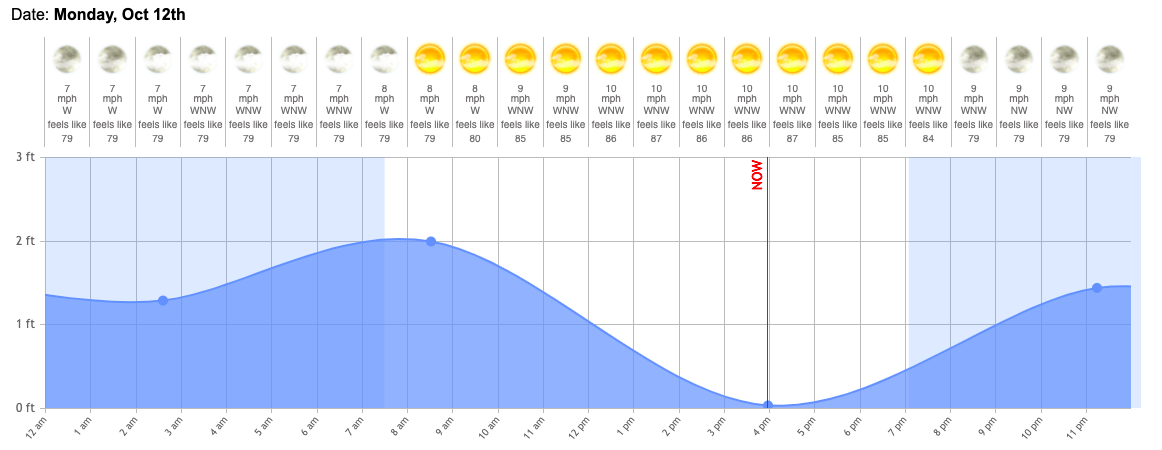
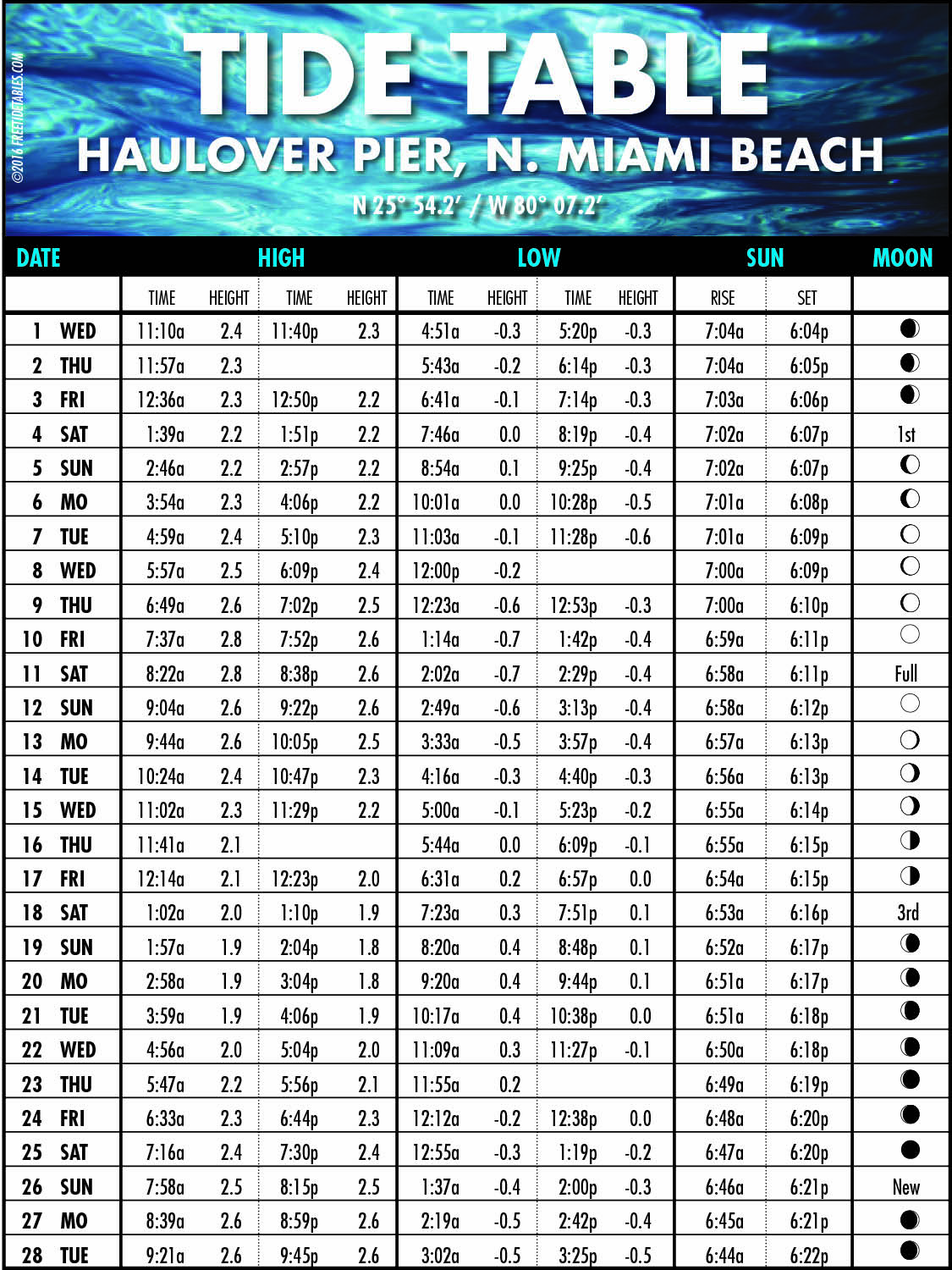
Hypothetical Tide Chart Information for [Your Location] on [Your Date]:
Let’s assume the next tide predictions for [Your Location] on [Your Date]:
| Time | Tide Peak (ft) | Tide Kind |
|---|---|---|
| 02:00 AM | 1.2 | Low |
| 08:30 AM | 7.8 | Excessive |
| 15:00 PM | 1.5 | Low |
| 21:15 PM | 7.5 | Excessive |
Understanding the Chart:
The desk above presents a simplified tide chart. An actual tide chart would probably present extra knowledge factors, providing a smoother curve representing the continual change in water degree. Let’s break down the weather:
-
Time: This means the time of day (in 24-hour format) when the required tide peak is predicted to happen. The time zone is essential and needs to be clearly acknowledged on the official chart.
-
Tide Peak (ft): This represents the vertical distance (in ft, or meters relying on the chart) between the imply low water (MLW) degree and the anticipated water degree on the given time. MLW is a reference level representing the typical of the bottom low tides over an extended interval. Different reference factors, similar to imply sea degree (MSL), may additionally be used.
-
Tide Kind: This means whether or not the anticipated tide is a excessive tide (excessive water) or a low tide (low water).
Components Influencing Tides:
The rhythmic rise and fall of ocean tides are primarily pushed by the gravitational forces exerted by the moon and the solar. The moon’s proximity to the Earth makes its gravitational pull the dominant issue. The solar additionally performs a big function, although its affect is weaker attributable to its higher distance.
-
Gravitational Pull: The moon’s gravity attracts the water on the aspect of the Earth dealing with it, making a bulge of water – a excessive tide. Concurrently, a second bulge happens on the alternative aspect of the Earth attributable to inertia. Because of this the water lags behind the Earth’s rotation, leading to two excessive tides and two low tides per day.
-
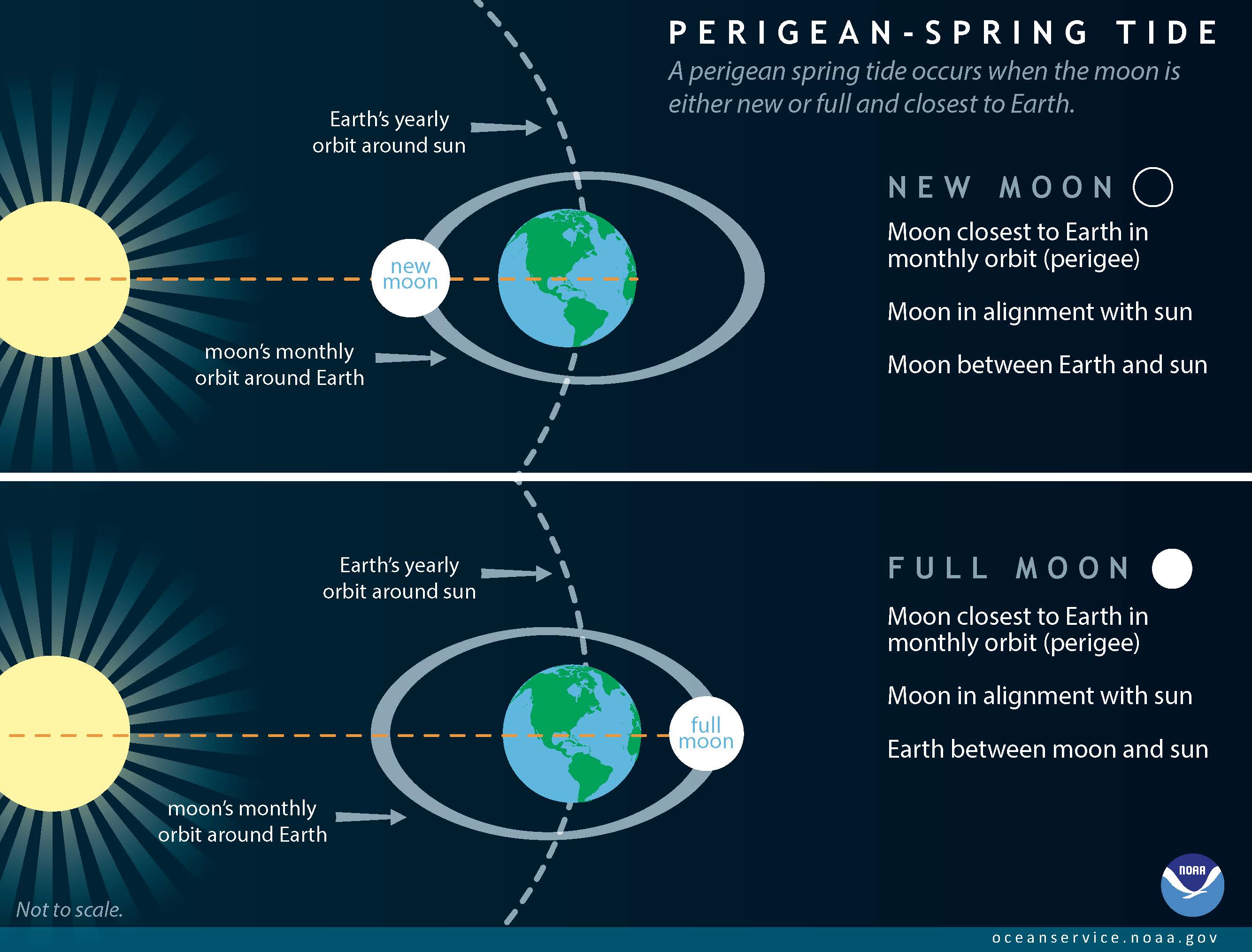
Tidal Bulges: The positions of the solar and moon relative to the Earth have an effect on the dimensions of those tidal bulges. When the solar, moon, and Earth are aligned (throughout new and full moons), their gravitational forces mix, producing bigger tidal ranges – referred to as spring tides. Conversely, when the solar and moon are at proper angles to one another (throughout first and third quarter moons), their gravitational forces partially cancel one another out, leading to smaller tidal ranges – referred to as neap tides.
-
Earth’s Rotation: The Earth’s rotation on its axis causes the tidal bulges to maneuver throughout the globe, resulting in the cyclical sample of excessive and low tides at any given location.
-
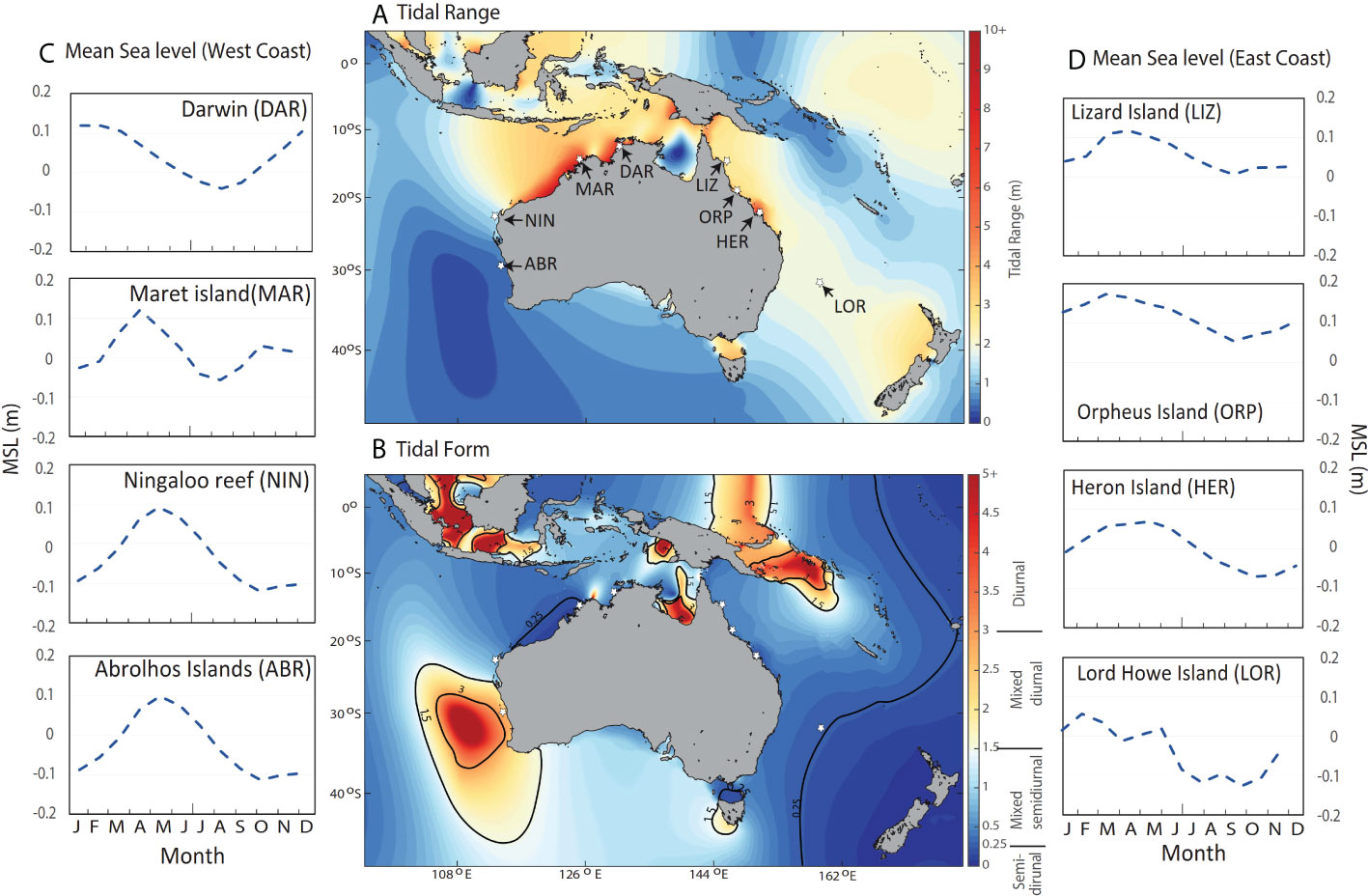
Ocean Basin Form and Depth: The form and depth of the ocean basin considerably affect the timing and amplitude of tides. Coastal options like bays, inlets, and estuaries can amplify or dampen tidal results, creating distinctive tidal patterns in several places.
-
Climate Circumstances: Meteorological elements similar to wind and atmospheric stress may have an effect on tide heights. Sturdy winds can push water in direction of or away from the coast, modifying the anticipated tide ranges. Equally, modifications in atmospheric stress could cause minor variations in sea degree.
Implications for Coastal Actions:
Understanding tide charts is essential for a variety of coastal actions:
-
Boating and Navigation: Figuring out the tide heights is crucial for secure navigation, particularly in shallow waters or estuaries. Low tides can expose shallow areas, whereas excessive tides can have an effect on boat entry to docks and harbors.
-
Fishing: Tidal currents and water ranges affect fish conduct and their distribution. Skilled anglers use tide charts to foretell the very best instances and places for fishing.
-
Browsing: The scale and high quality of surf are immediately associated to the tidal patterns. Totally different tides create completely different wave circumstances, making tide charts invaluable for surfers.
-
Coastal Development and Engineering: Understanding tidal patterns is important for designing and establishing coastal infrastructure, similar to seawalls, harbors, and bridges. Correct tide predictions are essential for making certain the structural integrity and longevity of those tasks.
-
Shellfishing and Beachcombing: Low tides expose intertidal zones, offering alternatives for shellfishing and beachcombing. Tide charts assist people plan these actions to maximise their time within the uncovered areas.
-
Coastal Ecology and Analysis: Scientists use tide charts to check coastal ecosystems, monitor modifications in sea degree, and perceive the affect of local weather change on coastal environments.
Deciphering the Hypothetical Tide Chart:
Primarily based on our hypothetical tide chart for [Your Location] on [Your Date], we are able to see that:
-
The best excessive tide happens at 08:30 AM and 21:15 PM, reaching roughly 7.8 ft and seven.5 ft respectively. The distinction between these excessive tides highlights the affect of things past the easy lunar gravitational mannequin.
-
The bottom low tide happens at 02:00 AM, reaching roughly 1.2 ft.
-
The tidal vary (the distinction between excessive and low tide) is roughly 6.6 ft (7.8 ft – 1.2 ft) on the first excessive tide and 6.0 ft (7.5 ft – 1.5 ft) on the second. This distinction additional emphasizes the complicated interaction of assorted elements influencing the tides.
Conclusion:
Tide charts present important info for understanding and predicting the cyclical modifications in sea degree. By understanding the elements influencing tides and appropriately deciphering the information introduced in a tide chart, people and organizations could make knowledgeable choices for a variety of coastal actions, making certain security, effectivity, and environmental duty. Bear in mind to all the time seek the advice of a dependable and up-to-date tide prediction service particular to your location and date for correct and secure planning. This text serves as an introduction to the topic; additional analysis into particular tidal phenomena and native circumstances will improve your understanding and software of this priceless info.



Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered priceless insights into Decoding the Tides: A Deep Dive into the Tide Chart for [Your Location] on [Your Date]. We recognize your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!