Mastering The Artwork Of The Bar Chart: A Complete Information To DIY Information Visualization
By admin / August 21, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Mastering the Artwork of the Bar Chart: A Complete Information to DIY Information Visualization
Associated Articles: Mastering the Artwork of the Bar Chart: A Complete Information to DIY Information Visualization
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by way of the intriguing matter associated to Mastering the Artwork of the Bar Chart: A Complete Information to DIY Information Visualization. Let’s weave fascinating info and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Mastering the Artwork of the Bar Chart: A Complete Information to DIY Information Visualization

Bar charts, these ubiquitous pillars of knowledge illustration, are way more versatile and highly effective than their easy look suggests. They successfully talk comparisons between classes of knowledge, making them indispensable instruments for every little thing from enterprise shows to educational analysis. Whereas available software program packages supply straightforward bar chart creation, understanding the underlying rules and mastering the artwork of crafting them your self supplies invaluable perception into information evaluation and efficient communication. This complete information will stroll you thru the method of making your individual bar chart, protecting every little thing from information preparation to stylistic issues.
I. The Basis: Information Preparation and Planning
Earlier than even fascinated about aesthetics, the bedrock of a profitable bar chart is meticulously ready information. This part entails a number of vital steps:
-
Defining your query: What story are you making an attempt to inform together with your information? What comparisons do you need to spotlight? A clearly outlined goal guides your information choice and chart design. For instance, are you evaluating gross sales figures throughout totally different areas, or the efficiency of assorted advertising and marketing campaigns?
-
Information assortment and cleansing: Collect your uncooked information from dependable sources. This would possibly contain spreadsheets, databases, or surveys. Crucially, clear your information rigorously. This consists of dealing with lacking values (imputation or exclusion), figuring out and correcting outliers, and guaranteeing information consistency (e.g., utilizing constant models). Inaccurate information will result in deceptive and in the end ineffective charts.
-
Categorizing your information: Bar charts are inherently categorical. Establish the classes you need to signify on the horizontal (x) axis (e.g., months, product varieties, areas). The vertical (y) axis will signify the quantitative values related to every class (e.g., gross sales income, models bought, buyer satisfaction scores).
-
Selecting the best chart sort: Whereas the essential bar chart is appropriate for a lot of conditions, variations exist:
- Vertical bar chart: The most typical sort, ultimate for evaluating classes with comparatively few information factors.
- Horizontal bar chart: Higher fitted to longer class labels or when evaluating a lot of classes. They’re additionally helpful when specializing in the rating of classes.
- Grouped bar chart: Used to match a number of variables inside every class (e.g., gross sales of various merchandise in every area).
- Stacked bar chart: Reveals the contribution of various sub-categories to a complete worth inside every essential class. Helpful for displaying proportions.
- 100% stacked bar chart: A variation of the stacked bar chart the place every bar represents 100%, displaying the proportion of every sub-category inside every essential class.
The selection relies upon totally on the character of your information and the message you purpose to convey.
II. Handbook Building: A Step-by-Step Information
Whereas software program affords ease and precision, manually developing a bar chart supplies a deeper understanding of the method. This may be finished utilizing graph paper, rulers, pencils, and coloured pencils or markers.
-
Selecting the size: Decide the suitable scale in your y-axis. The vary ought to embody your highest and lowest values, whereas permitting for clear visible illustration. Think about using increments which are straightforward to interpret (e.g., multiples of 5, 10, or 100).
-
Drawing the axes: Draw two perpendicular traces, one horizontal (x-axis) and one vertical (y-axis). Label the axes clearly with the class names (x-axis) and the quantitative measure (y-axis), together with models (e.g., "Gross sales Income ($)", "Variety of Prospects").
-
Plotting the bars: For every class, draw an oblong bar whose top corresponds to its worth on the y-axis. Keep constant spacing between the bars for readability.
-
Including labels and titles: Add labels to every bar indicating its worth. Embody a transparent and concise title that summarizes the chart’s content material. A subtitle can present extra context.
-
Including a legend (if mandatory): If utilizing a grouped or stacked bar chart, embody a legend explaining the totally different colours or patterns used.
-
Evaluation and refine: Earlier than finalizing, critically evaluate your chart. Is the size acceptable? Are the labels clear and correct? Does the chart successfully talk your message?
III. Leveraging Software program: Ease and Precision
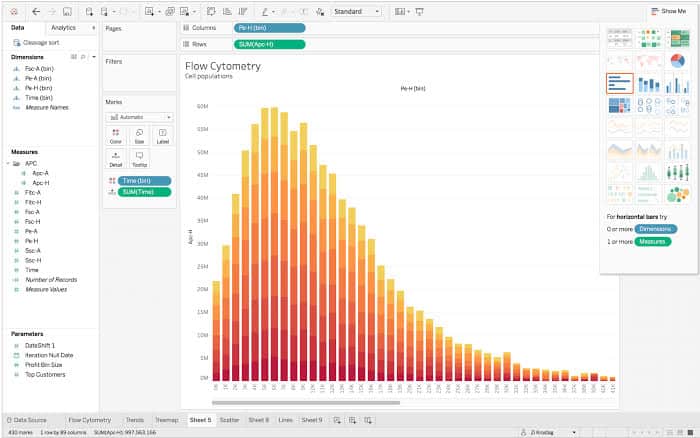
Whereas guide development affords helpful perception, software program supplies effectivity and precision. In style choices embody Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets, LibreOffice Calc, and devoted information visualization instruments like Tableau and Energy BI. The precise steps fluctuate barely relying on the software program, however the normal rules stay the identical:
-
Information enter: Enter your information right into a spreadsheet or database. Set up it in a tabular format with classes in a single column and values in one other.
-
Chart creation: Most software program packages have a built-in chart wizard. Choose "Bar Chart" and specify whether or not you desire a vertical or horizontal chart, grouped or stacked.
-
Customization: That is the place you may refine your chart’s look. Customise the next:
- Axis labels and titles: Guarantee clear and concise labeling.
- Bar colours and patterns: Select colours which are visually interesting and assist in differentiation. Keep away from utilizing too many colours, as this may litter the chart.
- Gridlines: Use gridlines sparingly; too many will be distracting.
- Information labels: Add information labels to every bar for readability, particularly if the chart is advanced.
- Chart measurement and determination: Select an acceptable measurement and determination in your supposed use.
-
Export and sharing: As soon as happy, export your chart in an appropriate format (e.g., PNG, JPG, PDF) for sharing in shows, experiences, or publications.
IV. Aesthetic Issues and Greatest Practices
The visible attraction of a bar chart considerably impacts its effectiveness. Take into account these greatest practices:
-
Preserve it easy: Keep away from cluttering the chart with pointless components. Concentrate on readability and ease of interpretation.
-
Use acceptable colours: Select colours which are visually interesting and assist in differentiation. Think about using a shade palette that aligns together with your model or theme.
-
Keep constant spacing: Guarantee constant spacing between bars and labels for a clear {and professional} look.
-
Use clear and concise labels: Keep away from overly lengthy or technical labels. Use abbreviations if mandatory.
-
Select an acceptable font: Use a legible font that’s constant together with your total design.
-
Keep away from 3D results: 3D results can distort the notion of knowledge and make the chart more durable to learn.
-
Reduce chartjunk: Keep away from pointless components resembling extreme gridlines, borders, or shading.
V. Past the Fundamentals: Superior Methods
As soon as you have mastered the basics, discover superior methods to reinforce your bar charts:
-
Error bars: Embody error bars to indicate the uncertainty or variability related together with your information.
-
Annotations: Add annotations to focus on particular information factors or tendencies.
-
Interactive components: If utilizing software program that enables for interactivity, add options resembling tooltips or drill-downs to offer extra detailed info.
-
Information transformations: Remodel your information (e.g., utilizing logarithms) if the vary is simply too giant or the distribution is skewed.
VI. Conclusion:
Creating efficient bar charts is a mix of technical ability and creative sensibility. By understanding the rules of knowledge preparation, chart development, and visible design, you may create compelling visualizations that successfully talk your information and insights. Whether or not you select the guide strategy for a deeper understanding or leverage software program for effectivity, the important thing lies in cautious planning, meticulous execution, and a concentrate on clear communication. Mastering the artwork of the bar chart empowers you to rework uncooked information into highly effective narratives, influencing choices and fostering understanding.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered helpful insights into Mastering the Artwork of the Bar Chart: A Complete Information to DIY Information Visualization. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!