Charting A Course: Understanding And Using Charts And Graphs For Efficient Knowledge Visualization
By admin / July 24, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Charting a Course: Understanding and Using Charts and Graphs for Efficient Knowledge Visualization
Associated Articles: Charting a Course: Understanding and Using Charts and Graphs for Efficient Knowledge Visualization
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate via the intriguing subject associated to Charting a Course: Understanding and Using Charts and Graphs for Efficient Knowledge Visualization. Let’s weave fascinating data and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Charting a Course: Understanding and Using Charts and Graphs for Efficient Knowledge Visualization

Knowledge visualization is the cornerstone of efficient communication in quite a few fields, from scientific analysis and enterprise analytics to journalism and on a regular basis life. Charts and graphs, the basic instruments of information visualization, remodel uncooked numerical information into simply digestible visible representations, revealing patterns, traits, and insights which may in any other case stay hidden. This text delves into the world of charts and graphs, exploring their numerous varieties, purposes, and greatest practices for creating compelling and informative visualizations.
The Energy of Visible Communication:
The human mind is inherently visible; we course of photos considerably sooner than textual content. Charts and graphs leverage this inherent benefit, permitting us to shortly grasp advanced data that will require vital effort and time to know via textual descriptions alone. A well-designed chart can immediately talk key findings, spotlight necessary traits, and facilitate knowledgeable decision-making. Conversely, a poorly designed chart will be deceptive, complicated, and even utterly ineffective, obscuring the very information it intends to light up.
Categorizing Charts and Graphs:
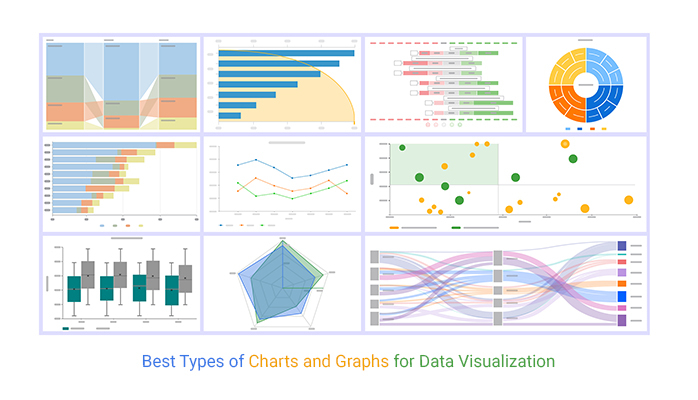
Charts and graphs are broadly categorized primarily based on the kind of information they signify and the relationships they illustrate. The most typical varieties embrace:
1. Bar Charts: These are perfect for evaluating discrete classes. Vertical or horizontal bars signify the magnitude of a variable for every class. Bar charts are wonderful for exhibiting variations between teams, highlighting the best and lowest values, and evaluating modifications over time when restricted to some time factors. Variations embrace clustered bar charts (evaluating a number of variables inside every class) and stacked bar charts (exhibiting the contribution of various elements to a complete).
2. Line Charts: Line charts are excellent for displaying steady information over time or throughout a steady vary. They’re significantly helpful for exhibiting traits and patterns, figuring out peaks and valleys, and illustrating correlations between variables. A number of strains will be plotted on the identical chart to match completely different datasets. A typical software is monitoring gross sales figures, inventory costs, or temperature modifications over time.
3. Pie Charts: Pie charts are round charts divided into segments, every representing a proportion of a complete. They’re efficient for exhibiting the relative sizes of various classes inside a single dataset. Nevertheless, they turn into much less efficient when coping with many classes or refined variations in proportions. Overuse of pie charts can result in visible muddle and issue in evaluating segments precisely.
4. Scatter Plots: Scatter plots show the connection between two steady variables. Every level on the plot represents a single information level, with its place decided by the values of the 2 variables. Scatter plots are helpful for figuring out correlations, clusters, and outliers. They’ll reveal optimistic correlations (variables improve collectively), detrimental correlations (one variable will increase as the opposite decreases), or no correlation.
5. Histograms: Histograms are used to signify the frequency distribution of a single steady variable. Knowledge is grouped into intervals (bins), and the peak of every bar represents the frequency or rely of information factors falling inside that interval. Histograms are beneficial for understanding the distribution of information, figuring out skewness, and detecting potential outliers.
6. Space Charts: Space charts are much like line charts, however the space beneath the road is full of colour. This emphasizes the magnitude of the information over time and is especially efficient for exhibiting cumulative totals or modifications in proportions.
7. Heatmaps: Heatmaps use colour gradients to signify the magnitude of information throughout two or extra variables. They’re helpful for visualizing giant datasets, figuring out patterns and correlations, and highlighting areas of excessive or low values. Frequent purposes embrace geographical information illustration or gene expression evaluation.
8. Field Plots (Field and Whisker Plots): Field plots summarize the distribution of a dataset utilizing quartiles. They present the median, quartiles, and potential outliers, offering a concise overview of information unfold and central tendency. They’re significantly helpful for evaluating distributions throughout completely different teams.
Finest Practices for Chart and Graph Creation:
Creating efficient charts and graphs entails greater than merely plotting information factors. A number of greatest practices guarantee readability, accuracy, and impression:
- Select the Proper Chart Kind: Choosing the suitable chart sort is essential. The selection relies on the kind of information, the message you wish to convey, and your viewers.
- **Clear and Concise





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied beneficial insights into Charting a Course: Understanding and Using Charts and Graphs for Efficient Knowledge Visualization. We respect your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!