Understanding Freon 22 Strain-Temperature Charts: A Complete Information
By admin / August 13, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Understanding Freon 22 Strain-Temperature Charts: A Complete Information
Associated Articles: Understanding Freon 22 Strain-Temperature Charts: A Complete Information
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we’ll discover the intriguing matter associated to Understanding Freon 22 Strain-Temperature Charts: A Complete Information. Let’s weave fascinating info and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Understanding Freon 22 Strain-Temperature Charts: A Complete Information
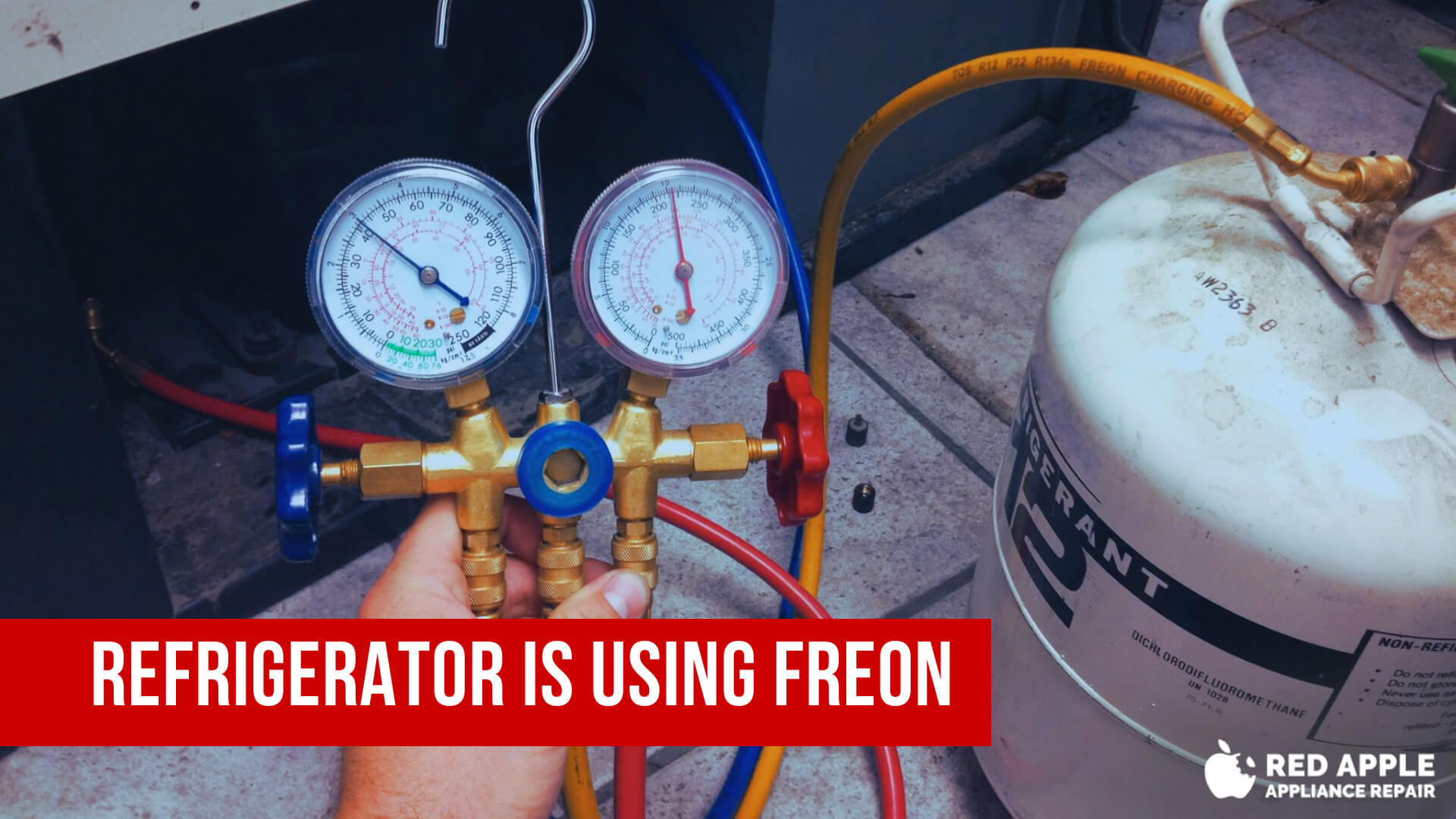
Freon 22, also referred to as chlorodifluoromethane (CHClF₂), was as soon as a broadly used refrigerant in air con and refrigeration techniques. Whereas its use is now considerably restricted attributable to its ozone-depleting potential, understanding its pressure-temperature (P-T) chart stays essential for technicians working with older techniques, for historic evaluation, and for understanding the rules of refrigeration cycles. This text gives a complete overview of Freon 22 P-T charts, their interpretation, functions, and limitations.
The Significance of Strain-Temperature Relationships in Refrigeration
Refrigeration techniques depend on the thermodynamic properties of refrigerants to attain cooling. The core precept includes the refrigerant’s section change between liquid and vapor states. By manipulating stress and temperature, the refrigerant absorbs warmth because it evaporates (low stress, low temperature) and releases warmth because it condenses (excessive stress, excessive temperature). The P-T chart gives a visible illustration of those section modifications, permitting technicians to shortly decide the refrigerant’s state based mostly on its stress and temperature readings.
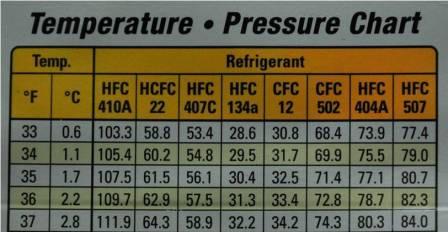
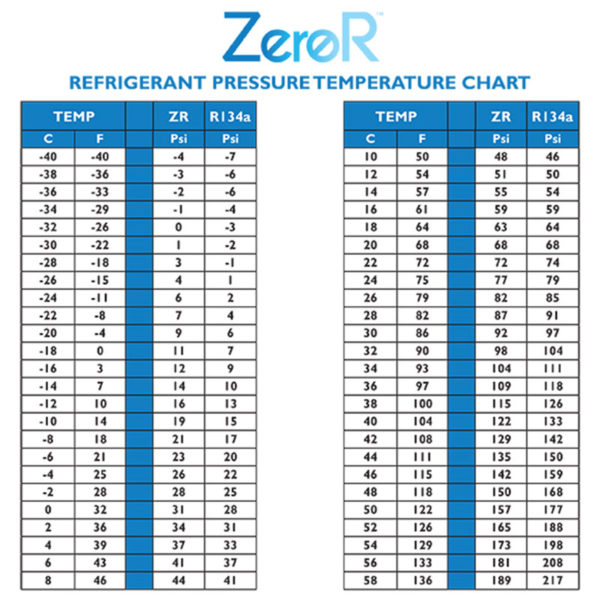
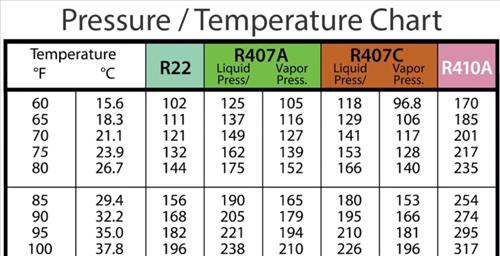
Understanding the Freon 22 P-T Chart
A Freon 22 P-T chart sometimes presents stress on the vertical axis (often in kilos per sq. inch, psi, or kilopascals, kPa) and temperature on the horizontal axis (often in levels Fahrenheit or Celsius). The chart shows a number of key traces and areas:
-
Saturation Curve: That is a very powerful function. It represents the boundary between the liquid and vapor phases of the refrigerant. Factors on this curve point out that the refrigerant exists as a saturated combination of liquid and vapor. The curve separates the subcooled liquid area (under the curve) from the superheated vapor area (above the curve).
-
Subcooled Liquid Area: On this area, the refrigerant is fully within the liquid section and its temperature is decrease than the saturation temperature at a given stress. This area is characterised by excessive density and low quantity.
-
Saturated Liquid Line: This line runs alongside the underside of the saturation curve, representing the state the place the refrigerant is fully within the liquid section at its saturation temperature.
-
Saturated Vapor Line: This line runs alongside the highest of the saturation curve, representing the state the place the refrigerant is fully within the vapor section at its saturation temperature.
-
Superheated Vapor Area: On this area, the refrigerant is fully within the vapor section, and its temperature is increased than the saturation temperature at a given stress. This area is characterised by decrease density and better quantity.
-
Vital Level: This level represents the very best temperature and stress at which the liquid and vapor phases can coexist. Past this level, the refrigerant exists as a supercritical fluid.
Deciphering the Chart:
To make use of the chart, you have to measure the refrigerant’s stress and temperature at a particular level within the refrigeration system. By finding the corresponding level on the chart, you possibly can decide the refrigerant’s state (subcooled liquid, saturated combination, or superheated vapor). This info is essential for diagnosing issues, akin to leaks, improper cost, or compressor malfunction.
For instance, if the stress studying is 100 psi and the temperature studying is 60°F, and the purpose falls inside the subcooled liquid area, it signifies that the refrigerant is in a liquid state and is colder than its saturation temperature at that stress. Conversely, some extent within the superheated vapor area signifies that the refrigerant is a vapor and warmer than its saturation temperature at that stress. Some extent on the saturation curve signifies a mix of liquid and vapor.
Purposes of Freon 22 P-T Charts:
-
Refrigerant Cost Dedication: Technicians use P-T charts to find out the right amount of refrigerant in a system. By measuring the stress and temperature at varied factors, they’ll calculate the refrigerant cost and determine potential undercharges or overcharges.
-
Troubleshooting and Diagnostics: Deviations from anticipated stress and temperature readings can point out issues inside the system, akin to leaks, compressor failures, condenser fouling, or evaporator points. The P-T chart helps pinpoint the situation and nature of those issues.
-
System Efficiency Analysis: The chart helps assess the effectivity and efficiency of the refrigeration system. By evaluating measured pressures and temperatures to the chart’s values, technicians can determine areas for enchancment or potential upkeep wants.
-
Security Concerns: Understanding the stress and temperature relationships is essential for security. Extreme pressures can result in system failures and potential hazards. The chart helps technicians function the system inside protected working parameters.
Limitations of Freon 22 P-T Charts:
-
Accuracy: P-T charts present approximate values. Precise pressures and temperatures could range barely attributable to elements akin to refrigerant purity, system design, and ambient circumstances.
-
Assumptions: The charts are based mostly on sure assumptions, akin to best gasoline habits and negligible stress drops within the system. These assumptions could not all the time maintain true in real-world situations.
-
Out of date Refrigerant: Because of environmental issues, Freon 22 is being phased out. Whereas the P-T chart stays helpful for understanding older techniques, it is essential to know the environmental influence and transition to environmentally pleasant refrigerants.
-
Restricted Info: The chart primarily gives details about the refrigerant’s state. It would not present details about different essential parameters, akin to refrigerant move fee, warmth switch charges, and compressor effectivity.
Conclusion:
Freon 22 P-T charts are invaluable instruments for technicians working with older refrigeration techniques. Understanding easy methods to interpret these charts is crucial for correct refrigerant charging, troubleshooting, and making certain protected operation. Nonetheless, it is essential to recollect the constraints of those charts and the significance of transitioning to environmentally pleasant refrigerants. Whereas Freon 22’s use is declining, understanding its thermodynamic properties by means of its P-T chart stays a basic side of refrigeration engineering and upkeep. The rules illustrated by the Freon 22 P-T chart are relevant to different refrigerants, highlighting the significance of understanding P-T relationships within the broader context of refrigeration know-how. Future technicians ought to deal with studying in regards to the P-T traits of recent, environmentally accountable refrigerants to make sure the sustainable way forward for cooling applied sciences.




Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered invaluable insights into Understanding Freon 22 Strain-Temperature Charts: A Complete Information. We admire your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!