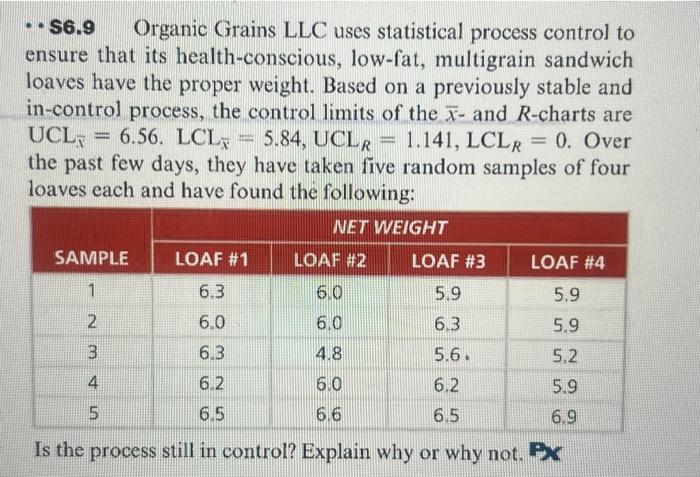
Understanding And Making use of R Charts In Statistical Course of Management
By admin / October 10, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Understanding and Making use of R Charts in Statistical Course of Management
Associated Articles: Understanding and Making use of R Charts in Statistical Course of Management
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by means of the intriguing matter associated to Understanding and Making use of R Charts in Statistical Course of Management. Let’s weave fascinating data and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Understanding and Making use of R Charts in Statistical Course of Management

Statistical Course of Management (SPC) is a vital methodology for monitoring and enhancing the consistency and high quality of processes. One of many important instruments inside SPC is the R chart, used to trace the variability or vary of a course of. In contrast to the X-bar chart, which screens the common of a course of, the R chart focuses solely on the dispersion of information factors across the central tendency. Understanding and successfully using R charts is important for figuring out sources of variation and implementing corrective actions to reinforce course of stability.
This text delves into the intricacies of R charts, masking their building, interpretation, and sensible purposes. We’ll discover the assumptions underlying their use, widespread pitfalls to keep away from, and the advantages of integrating R charts with different SPC instruments.
Understanding Course of Variation and the Function of the R Chart
Course of variation is inherent in any manufacturing or service course of. This variation can stem from quite a few sources, together with widespread causes (inherent to the method) and particular causes (assignable to particular occasions or elements). The objective of SPC is to establish and get rid of particular causes of variation, leaving solely the widespread trigger variation, which represents the inherent stability of the method.
The R chart, the place "R" denotes the vary, is designed to watch the dispersion of information inside subgroups. A subgroup is a small pattern of information collected at a selected cut-off date or from a specific location. The vary is solely the distinction between the biggest and smallest values inside a subgroup. By monitoring the vary over time, the R chart offers insights into the method variability. A steady course of will exhibit constant ranges, whereas an unstable course of will present erratic fluctuations within the vary.
Establishing an R Chart: A Step-by-Step Information
Constructing an R chart includes a number of key steps:
-
Information Assortment: Collect information from the method being monitored. It is essential to gather information in subgroups, making certain every subgroup is consultant of the method at a selected cut-off date. The subgroup dimension (n) is often between 4 and 5, although bigger subgroups can be utilized relying on the method and the obtainable information.
-
Calculate the Vary (R) for Every Subgroup: For every subgroup, decide the vary by subtracting the smallest worth from the biggest worth.
-
Calculate the Common Vary (R-bar): Sum the ranges from all subgroups and divide by the variety of subgroups (okay). This offers the common vary of the method. The system is:
R-bar = ΣRᵢ / okaythe place:
- Rᵢ is the vary of the i-th subgroup
- okay is the variety of subgroups
-
Decide Management Limits: Management limits outline the boundaries inside which the method is taken into account to be in management. The management limits for an R chart are calculated utilizing management chart constants (d₂, d₃, D₃, D₄), that are depending on the subgroup dimension (n). These constants are available in statistical tables or software program packages. The formulation are:
- Higher Management Restrict (UCL):
UCL = D₄ * R-bar - Decrease Management Restrict (LCL):
LCL = D₃ * R-bar
Word that D₃ is zero for subgroup sizes lower than 7. For these circumstances, the LCL is ready to zero, indicating {that a} vary of zero is not possible.
- Higher Management Restrict (UCL):
-
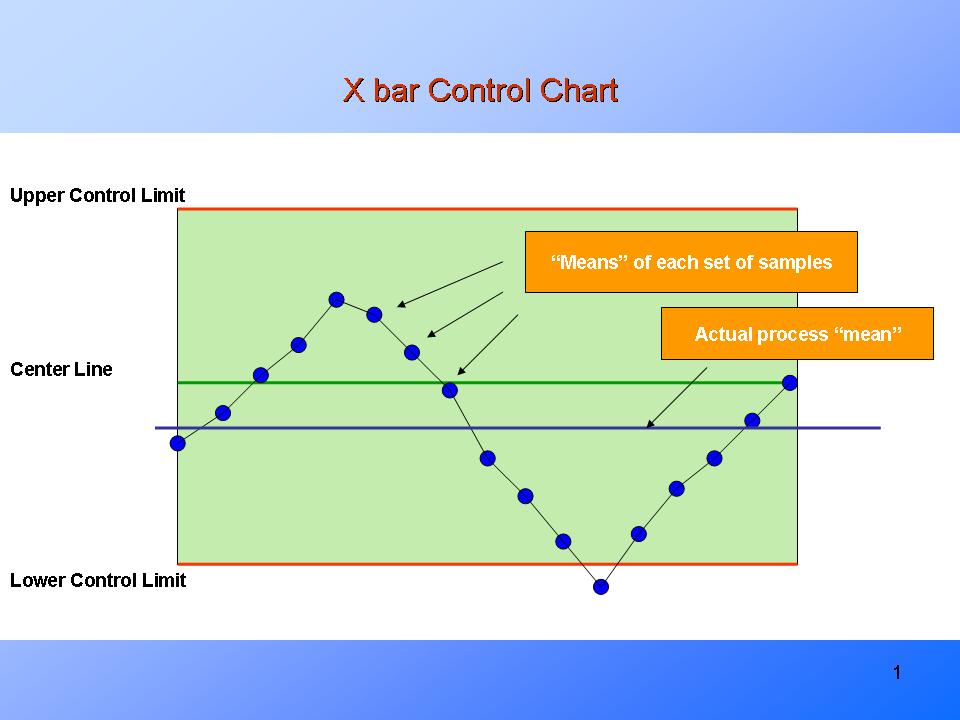
Plot the Information: Plot the vary (R) for every subgroup on the chart. The chart will embrace the middle line (R-bar), UCL, and LCL.
Deciphering an R Chart:
Deciphering an R chart includes figuring out patterns and deviations that point out course of instability. Key indicators of out-of-control circumstances embrace:
-
Factors outdoors the management limits: Any level falling above the UCL or under the LCL suggests the presence of particular trigger variation. This warrants investigation to establish and get rid of the foundation trigger.
-
Developments: A constant upward or downward development signifies a gradual shift in course of variability, doubtlessly indicating a deteriorating course of.
-
Cycles: Recurring patterns of excessive and low ranges counsel cyclical variations throughout the course of.
-
Stratification: Clustering of factors above or under the middle line signifies an absence of randomness, suggesting the presence of assignable causes.
-
Runs: A sequence of consecutive factors above or under the middle line, even when throughout the management limits, can sign a course of shift.
Assumptions of the R Chart:
The efficient use of R charts depends on a number of key assumptions:
-
Independence of Subgroups: Information inside every subgroup needs to be impartial of information in different subgroups.
-
Normality: Whereas not strictly required, the underlying information is assumed to be roughly usually distributed. Nonetheless, the R chart is comparatively strong to deviations from normality, significantly with bigger subgroup sizes.
-
Fixed Course of Variance: The method variability ought to stay comparatively fixed over time. If the method variance modifications considerably, the R chart might not precisely replicate the method habits.
-
Random Sampling: Subgroups needs to be randomly chosen to make sure representativeness.
Integrating R Charts with Different SPC Instruments:
R charts are best when used along side different SPC instruments, significantly the X-bar chart. The X-bar chart screens the method common, whereas the R chart screens the method variability. By analyzing each charts concurrently, a complete understanding of the method efficiency may be obtained. This mixed strategy permits for the identification of each shifts within the course of common and modifications in course of variability.
Benefits and Disadvantages of Utilizing R Charts:
Benefits:
- Simplicity: R charts are comparatively simple to assemble and interpret.
- Sensitivity to Variation: They’re efficient in detecting modifications in course of variability.
- Value-effective: They require minimal sources to implement.
- Broad Applicability: They are often utilized to a variety of processes.
Disadvantages:
- Sensitivity to Outliers: Excessive values inside a subgroup can considerably affect the vary and doubtlessly masks different variations.
- Subgroup Dimension Limitations: The effectiveness of R charts depends on the suitable selection of subgroup dimension.
- Assumption of Fixed Variance: Violation of this assumption can result in inaccurate interpretations.
Conclusion:
The R chart is a robust instrument for monitoring course of variability throughout the context of Statistical Course of Management. By understanding its rules, building, interpretation, and limitations, practitioners can successfully leverage this method to establish and tackle sources of variation, resulting in improved course of consistency and high quality. Keep in mind that the profitable implementation of R charts requires cautious planning, information assortment, and an intensive understanding of the method being monitored. Combining R charts with different SPC instruments, corresponding to X-bar charts, offers a extra complete strategy to course of management and steady enchancment. Common monitoring and immediate investigation of out-of-control indicators are essential for sustaining course of stability and reaching desired high quality ranges. Lastly, using statistical software program can drastically simplify the development and evaluation of R charts, permitting for extra environment friendly and correct monitoring of course of efficiency.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied useful insights into Understanding and Making use of R Charts in Statistical Course of Management. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!