U-Charts: Unveiling The Energy Of Management Charts For Steady Knowledge With Low Counts
By admin / August 19, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
U-Charts: Unveiling the Energy of Management Charts for Steady Knowledge with Low Counts
Associated Articles: U-Charts: Unveiling the Energy of Management Charts for Steady Knowledge with Low Counts
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we’ll discover the intriguing subject associated to U-Charts: Unveiling the Energy of Management Charts for Steady Knowledge with Low Counts. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
U-Charts: Unveiling the Energy of Management Charts for Steady Knowledge with Low Counts

Management charts are indispensable instruments in statistical course of management (SPC), offering a visible illustration of course of stability and serving to establish potential sources of variation. Whereas many are acquainted with X-bar and R charts for steady information, conditions come up the place the pattern measurement is constantly small, usually only one or two observations per subgroup. In these eventualities, conventional management charts grow to be unreliable, necessitating the usage of specialised methods. The u-chart emerges as a strong answer, particularly designed for analyzing steady information with low counts, offering precious insights into course of habits and aiding in high quality enchancment efforts.
This text delves into the intricacies of u-chart methodology, exploring its functions, underlying ideas, building, interpretation, and limitations. We are going to study the circumstances below which a u-chart is suitable and distinction it with different management chart strategies. Moreover, we’ll talk about the sensible implications of u-chart evaluation and provide steerage on its efficient implementation.
Understanding the Limitations of Conventional Management Charts with Low Counts
Conventional management charts, reminiscent of X-bar and R charts, assume a comparatively massive pattern measurement for every subgroup. These charts depend on the central restrict theorem, which states that the distribution of pattern means approaches normality because the pattern measurement will increase. When coping with small pattern sizes, this assumption is violated, resulting in inaccurate management limits and doubtlessly deceptive interpretations. The variability inherent in small samples can considerably inflate the management limits, making it troublesome to detect true shifts within the course of imply. Conversely, slim management limits would possibly result in an extreme variety of false alarms, hindering the effectiveness of the management chart.
Introducing the u-Chart: A Answer for Low Depend Knowledge
The u-chart is a management chart particularly designed for monitoring the variety of defects or nonconformities per unit. Whereas seemingly centered on discrete information, the u-chart might be tailored for steady information when the variety of observations per subgroup is constantly low. On this context, "defects" or "nonconformities" can symbolize situations the place a steady variable falls exterior a predefined specification restrict or exceeds a sure threshold. The important thing distinction is that as a substitute of monitoring the common worth of the continual variable, the u-chart tracks the charge of occurrences the place the variable falls exterior the suitable vary.
Setting up a u-Chart: A Step-by-Step Information
Setting up a u-chart entails a number of key steps:
-
Knowledge Assortment: Collect information on the variety of occurrences (defects) per unit (subgroup) over a specified interval. Every unit represents a pattern, and the variety of defects inside that unit is the info level for the chart.
-
Calculating the Common Defect Fee (ū): Sum the whole variety of defects throughout all models and divide by the whole variety of models. This supplies the common defect charge (ū), which serves because the central line of the u-chart.
-
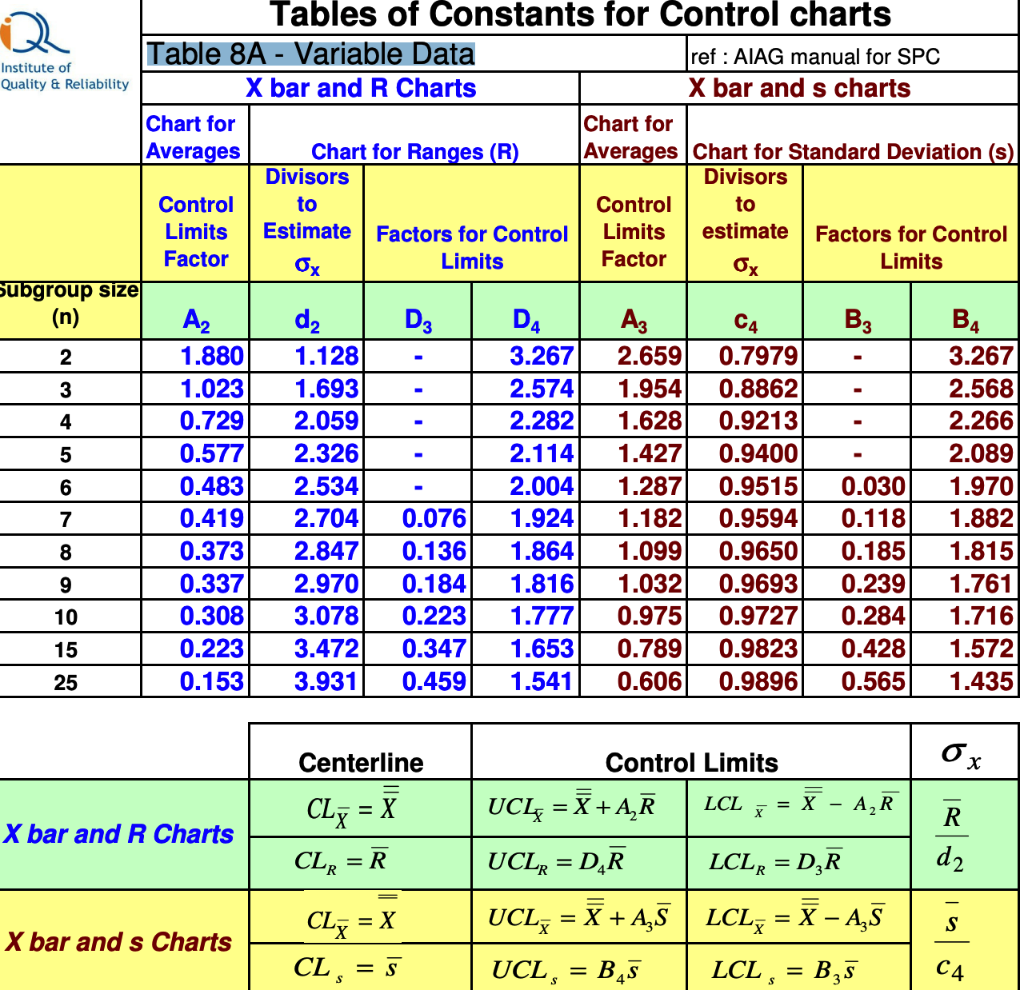
Calculating the Management Limits: The management limits are calculated utilizing the common defect charge (ū) and a selected management chart fixed (sometimes 3 for 99.7% confidence). The formulation for the higher management restrict (UCL) and decrease management restrict (LCL) are:
- UCL = ū + 3√(ū/n)
- LCL = ū – 3√(ū/n)
the place ‘n’ represents the variety of observations (potential defects) per unit. Word that if the LCL is calculated as unfavourable, it’s set to zero, as a unfavourable defect charge is unimaginable.
-
Plotting the Chart: Plot the variety of defects per unit on the y-axis in opposition to the subgroup quantity on the x-axis. Draw the central line at ū and the UCL and LCL as horizontal strains.
-
Decoding the Chart: Factors falling exterior the management limits recommend potential out-of-control circumstances, indicating a major shift within the course of. Patterns inside the management limits, reminiscent of traits or cycles, might also warrant investigation.
Purposes of u-Charts in Steady Knowledge Evaluation
The u-chart’s adaptability makes it helpful in various conditions involving steady information with low counts:
-
Monitoring floor defects: Inspecting a small variety of elements for floor flaws (e.g., scratches, pits) per batch. The variety of defects per element is plotted on the u-chart.
-
Analyzing gear failures: Monitoring the variety of gear malfunctions per week or month, the place every week/month is a subgroup. The variety of failures represents the defects.
-
Monitoring contamination ranges: Assessing the variety of contamination particles per pattern in a cleanroom setting. Every pattern represents a subgroup, and the variety of particles is the defect rely.
-
Evaluating chemical impurities: Measuring the variety of situations the place the focus of an impurity exceeds a specified threshold in a small batch of chemical merchandise.
-
High quality management in manufacturing: Monitoring the variety of models failing a selected high quality take a look at per manufacturing run, the place every run is a subgroup.
Comparability with Different Management Charts
The u-chart differs from different management charts in a number of key elements:
-
c-chart: The c-chart displays the variety of defects per unit, nevertheless it assumes a relentless pattern measurement (variety of alternatives for defects) for every subgroup. The u-chart is extra versatile, accommodating variable pattern sizes.
-
p-chart: The p-chart tracks the proportion of faulty models in a pattern. It’s appropriate for bigger pattern sizes and isn’t straight relevant to steady information with low counts.
-
X-bar and R charts: These charts should not appropriate for small pattern sizes as a result of violation of the central restrict theorem assumption.
Limitations of u-Charts
Whereas highly effective, u-charts have some limitations:
-
Assumption of randomness: The u-chart assumes that the defects happen randomly and independently inside every unit. If there is a systematic sample in defect incidence, the chart’s interpretation could also be deceptive.
-
Sensitivity to small adjustments: With small pattern sizes, the u-chart will not be delicate sufficient to detect small shifts within the course of.
-
Knowledge necessities: Correct u-chart building requires cautious information assortment and constant recording of the variety of defects per unit.
Conclusion: Empowering High quality Enchancment with u-Charts
The u-chart affords a precious instrument for monitoring steady information with low counts, addressing a crucial hole in conventional management chart methodology. By specializing in the speed of occurrences of defects reasonably than the common worth of the continual variable, the u-chart supplies a sturdy and insightful solution to assess course of stability and establish potential areas for enchancment. Understanding its ideas, building, interpretation, and limitations is essential for efficient implementation and attaining significant leads to high quality management and course of optimization. Correct software of the u-chart can result in important enhancements in course of effectivity, lowered waste, and enhanced product high quality. Nonetheless, it is vital to keep in mind that the u-chart is only one instrument within the broader SPC toolbox, and its software ought to be rigorously thought-about primarily based on the particular traits of the info and the targets of the evaluation. Combining the u-chart with different statistical strategies and incorporating material experience can additional improve its effectiveness in driving steady enchancment.




Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied precious insights into U-Charts: Unveiling the Energy of Management Charts for Steady Knowledge with Low Counts. We admire your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!