A Kaleidoscope Of Atoms: Exploring The Colourful Chart Of Nuclides
By admin / June 17, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
A Kaleidoscope of Atoms: Exploring the Colourful Chart of Nuclides
Associated Articles: A Kaleidoscope of Atoms: Exploring the Colourful Chart of Nuclides
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to A Kaleidoscope of Atoms: Exploring the Colourful Chart of Nuclides. Let’s weave fascinating info and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
A Kaleidoscope of Atoms: Exploring the Colourful Chart of Nuclides

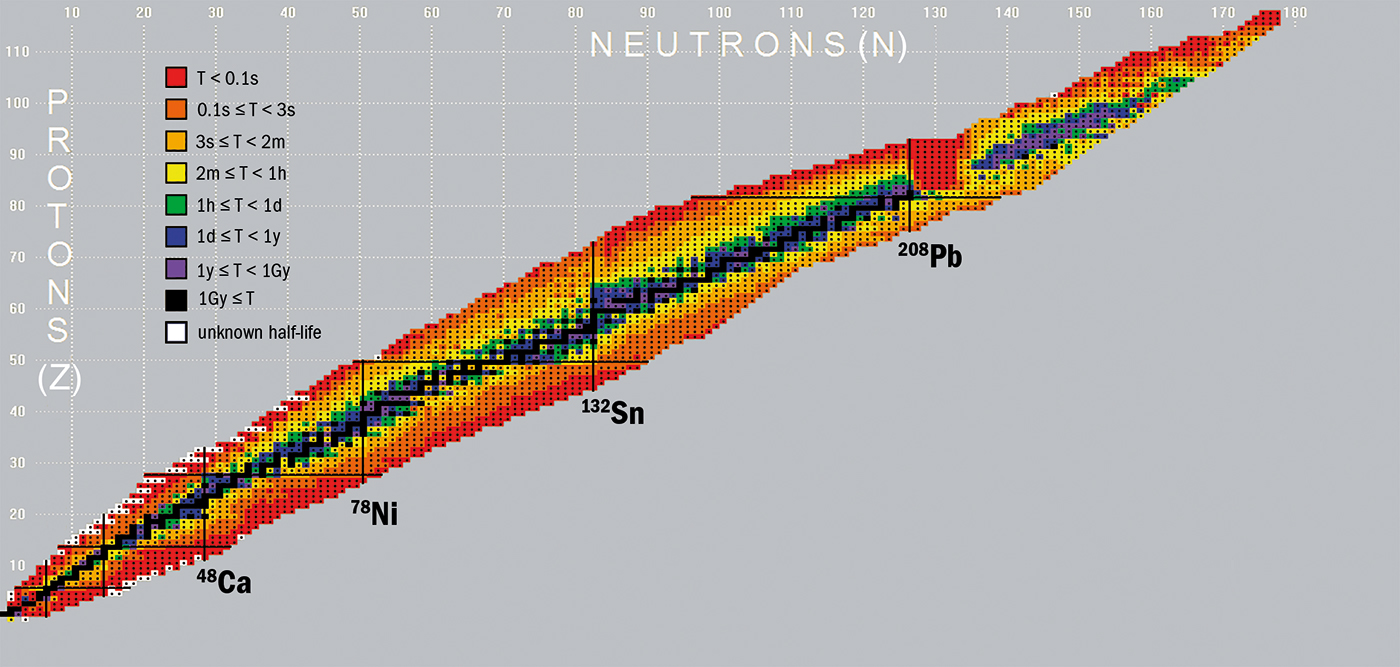
The Chart of Nuclides, typically referred to as the Segrè chart (after Emilio Segrè, a Nobel laureate in physics), is excess of a easy desk of parts. It is a vibrant tapestry woven from the elemental constructing blocks of matter – protons and neutrons – revealing the intricate construction and conduct of atomic nuclei. This seemingly advanced chart, bursting with coloration and knowledge, holds the important thing to understanding nuclear stability, radioactive decay, and the very nature of matter itself. Its colourful illustration, nevertheless, just isn’t merely aesthetic; it is a highly effective visible instrument that encodes huge quantities of knowledge, making the seemingly chaotic world of nuclear physics surprisingly accessible.
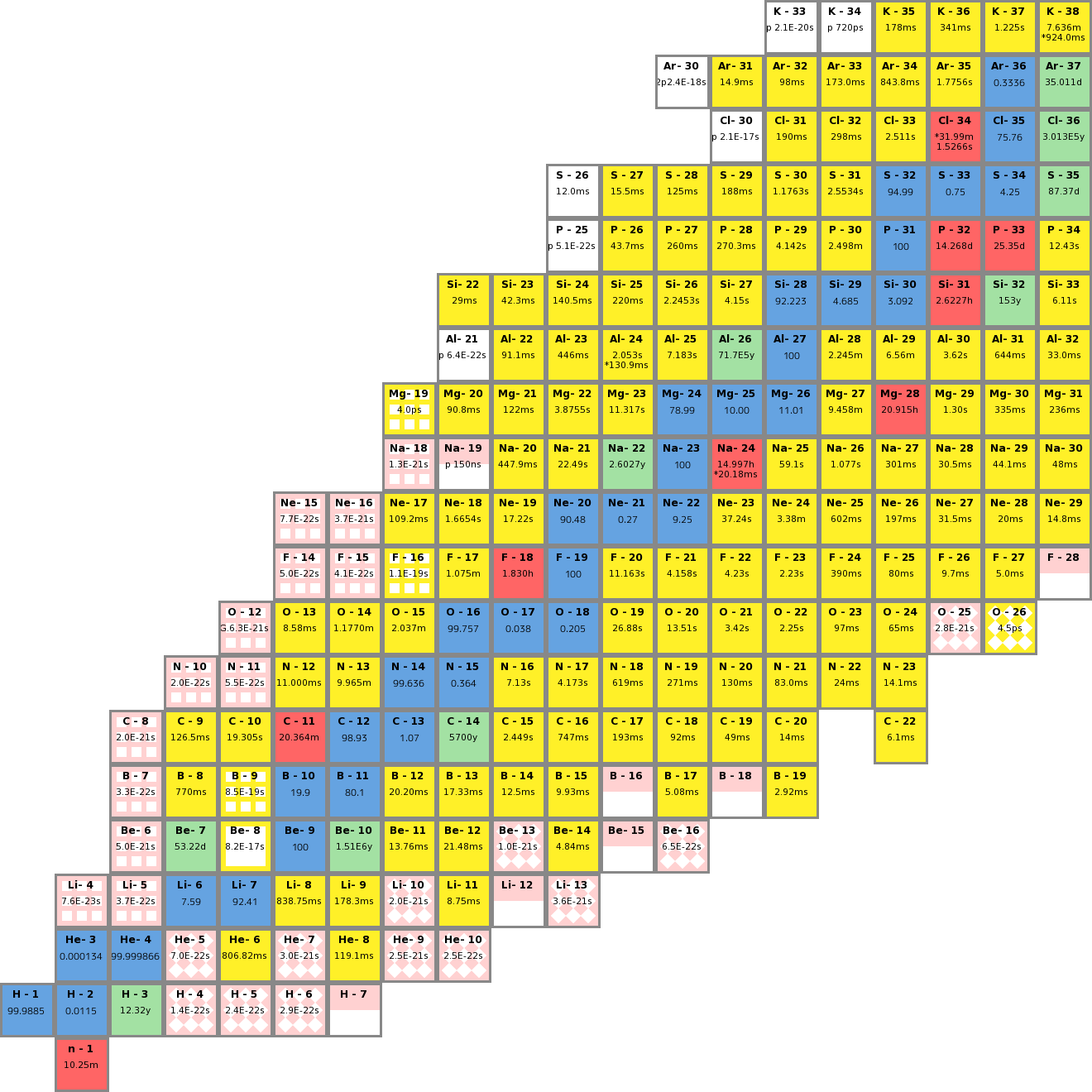
The chart itself is a two-dimensional illustration of all recognized isotopes, organized by the variety of protons (atomic quantity, Z) alongside the horizontal axis and the variety of neutrons (neutron quantity, N) alongside the vertical axis. Every sq. represents a particular nuclide – a selected species of atom characterised by its distinctive mixture of protons and neutrons. The sheer variety of nuclides – over 3,000 – necessitates a compact and informative visible system, which is achieved by means of a classy color-coding scheme.
Probably the most putting side of the chart is its use of coloration to point numerous properties of the nuclides. Whereas the precise coloration scheme can differ barely relying on the supply, a number of key options are constantly represented:
-
Stability: Probably the most basic distinction is between steady and unstable (radioactive) nuclides. Secure nuclides, these that don’t bear radioactive decay, are sometimes represented in black or darkish gray. This area of stability, often known as the "valley of stability," is a comparatively slim band working diagonally throughout the chart. The abundance of steady isotopes decreases because the atomic quantity will increase, a mirrored image of the rising complexity of nuclear forces.
-
Half-life: The half-life, the time it takes for half of a given pattern of a radioactive nuclide to decay, is an important attribute. That is typically represented by a gradient of coloration, with quick half-lives (starting from fractions of a second to minutes) proven in brilliant colours like pink, orange, or yellow, and longer half-lives (years, millennia, and even geological timescales) proven in progressively cooler colours like inexperienced, blue, or purple. This visible illustration permits for a fast evaluation of the relative stability of various nuclides.
-
Decay Modes: The style through which a radioactive nuclide decays is one other vital property. Totally different decay modes, akin to alpha decay (emission of an alpha particle, a helium nucleus), beta decay (emission of an electron or positron), gamma decay (emission of a gamma ray), and spontaneous fission (splitting of the nucleus into two smaller nuclei), are sometimes represented by totally different colours or symbols superimposed on the nuclide’s sq.. This offers insights into the nuclear processes driving the transformation of unstable nuclei into extra steady configurations.
-
Abundance: The pure abundance of a nuclide, its relative proportion within the Earth’s crust or the universe, is one other parameter incessantly integrated into the chart’s coloration scheme. Extra ample isotopes may be represented by darker shades, whereas much less ample ones are lighter. This offers context to the relative prevalence of various isotopes in nature.
-
Manufacturing Strategies: The chart may also point out how a selected nuclide is produced. Some nuclides are naturally occurring, whereas others are artificially produced in nuclear reactors or particle accelerators. This info is usually conveyed by means of totally different symbols or coloration variations.
The visible energy of the chart extends past easy coloration coding. The association of nuclides reveals vital developments and patterns:
-
The Valley of Stability: The focus of steady nuclides alongside a diagonal line illustrates the interaction between the sturdy nuclear power (which holds the nucleus collectively) and the electromagnetic power (which repels protons). The optimum neutron-to-proton ratio for stability varies with atomic quantity, explaining the curved form of the valley.
-
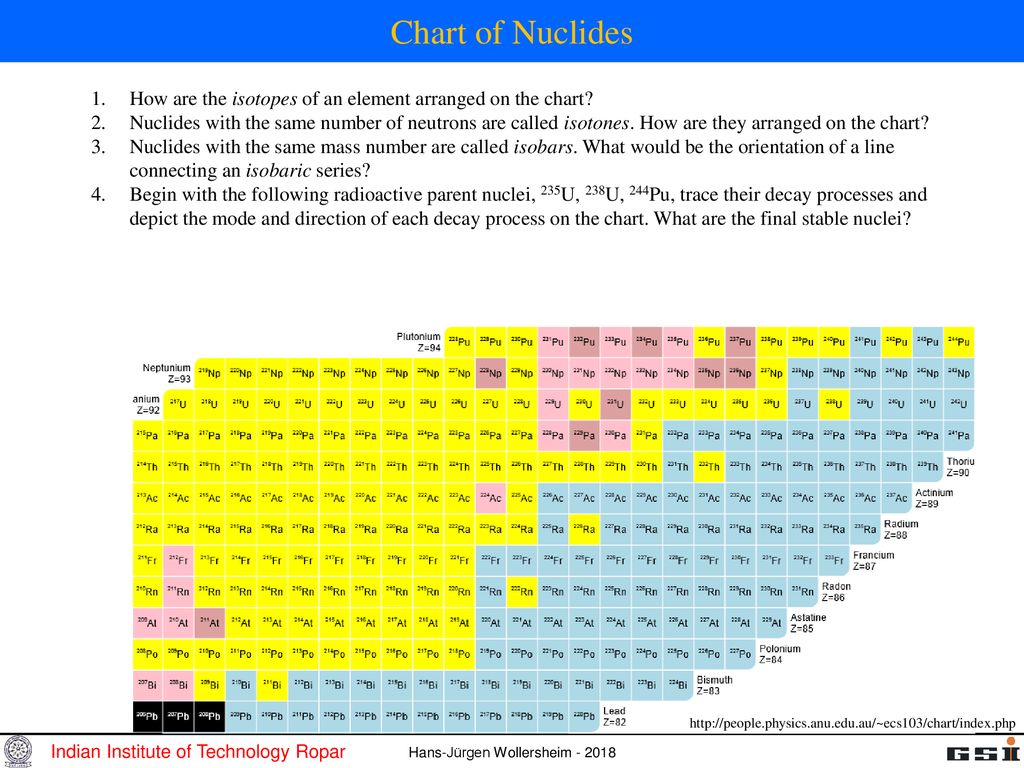
Isotopes and Isobars: The vertical columns symbolize isotopes (nuclides with the identical variety of protons however totally different numbers of neutrons), whereas horizontal rows symbolize isobars (nuclides with the identical mass quantity however totally different numbers of protons and neutrons). Evaluating isotopes and isobars highlights the results of various neutron numbers on nuclear stability.
-
Magic Numbers: Sure numbers of protons or neutrons (2, 8, 20, 28, 50, 82, 126) confer distinctive stability, a phenomenon referred to as "magic numbers." Nuclides with magic numbers of protons or neutrons are sometimes notably ample and steady, a mirrored image of the shell construction of the nucleus.
-
Radioactive Decay Chains: The chart vividly illustrates radioactive decay chains, sequences of decays that lead from an unstable guardian nuclide to a steady daughter nuclide. Following these chains permits for an in depth understanding of the transformations that happen throughout radioactive decay.
The Chart of Nuclides just isn’t merely a static illustration; it is a dynamic instrument that continues to evolve as new isotopes are found and our understanding of nuclear physics deepens. The continued analysis in nuclear science always provides new knowledge, refining our information of nuclear properties and increasing the chart’s scope. It serves as a useful useful resource for researchers in numerous fields, together with nuclear physics, chemistry, medication, and engineering.
In conclusion, the colourful Chart of Nuclides is a strong visible illustration of the advanced world of atomic nuclei. Its ingenious color-coding scheme, coupled with its strategic association of nuclides, offers a wealth of details about nuclear stability, radioactive decay, and the relative abundance of isotopes. It is a testomony to the facility of visualization in making advanced scientific ideas accessible and provoking additional exploration into the fascinating realm of nuclear physics. Its vibrant colours will not be simply aesthetically pleasing; they’re the important thing to unlocking the secrets and techniques held throughout the coronary heart of matter itself. The chart stays an important instrument for researchers and educators alike, providing a charming glimpse into the elemental constructing blocks of our universe and the intricate processes that govern their conduct. Its steady evolution displays the continuing progress in nuclear science and its enduring significance in understanding the world round us.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied useful insights into A Kaleidoscope of Atoms: Exploring the Colourful Chart of Nuclides. We hope you discover this text informative and helpful. See you in our subsequent article!