Decoding Japan’s GDP Chart: A Two-Decade Journey Of Stagnation And Resilience
By admin / September 25, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Decoding Japan’s GDP Chart: A Two-Decade Journey of Stagnation and Resilience
Associated Articles: Decoding Japan’s GDP Chart: A Two-Decade Journey of Stagnation and Resilience
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we are going to discover the intriguing matter associated to Decoding Japan’s GDP Chart: A Two-Decade Journey of Stagnation and Resilience. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding Japan’s GDP Chart: A Two-Decade Journey of Stagnation and Resilience

Japan’s economic system, as soon as a worldwide powerhouse, has introduced an enchanting, albeit advanced, narrative over the previous 20 years. Its GDP chart, a visible illustration of this journey, reveals a narrative of exceptional resilience punctuated by intervals of stagnation and punctuated by important exterior shocks. Understanding this chart requires delving into the underlying financial forces, structural challenges, and coverage responses which have formed Japan’s financial trajectory for the reason that flip of the millennium.
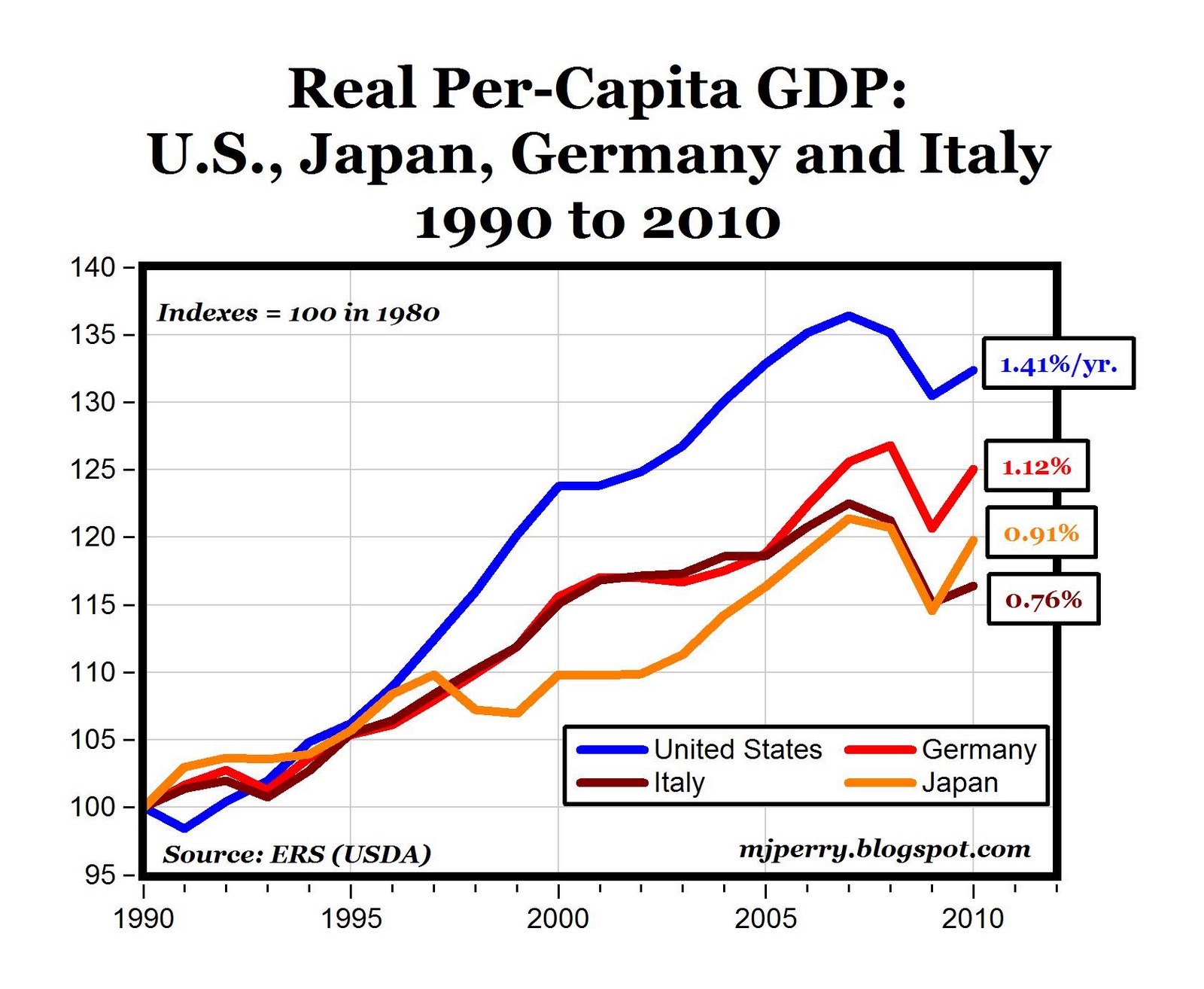
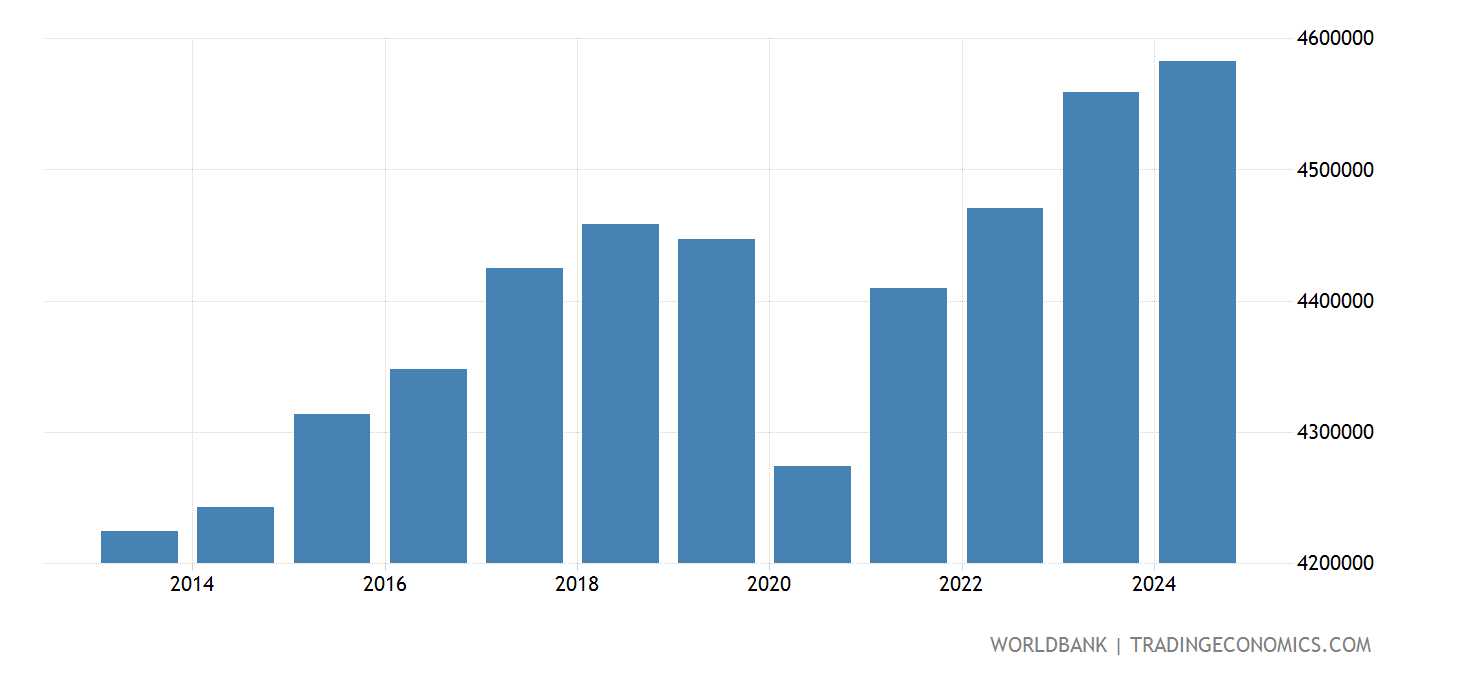
A Visible Overview: The Ups and Downs of Japan’s GDP
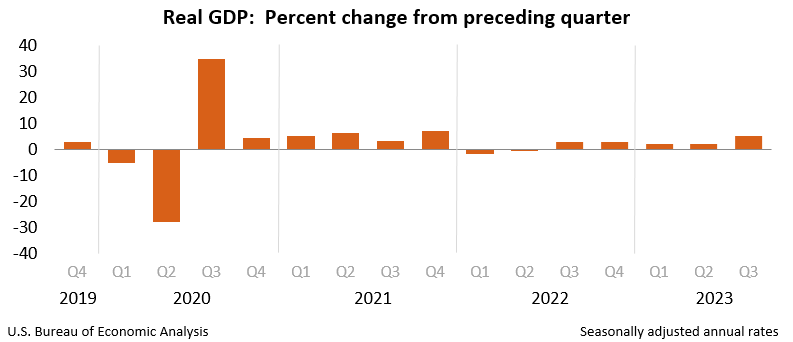
A typical chart depicting Japan’s nominal GDP from 2000 to the current would reveal a comparatively flat trajectory. Not like the explosive progress skilled by some rising economies, Japan’s GDP progress has been characterised by modest will increase, interspersed with intervals of contraction or near-stagnation. The preliminary years of the twenty first century noticed a interval of comparatively steady, albeit sluggish, progress, adopted by a pointy decline throughout the international monetary disaster of 2008-2009. Subsequent restoration was sluggish, and the economic system has since struggled to realize sustained, strong progress. The COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 precipitated one other important dip, highlighting the economic system’s vulnerability to international shocks. Whereas there was some restoration since, the general pattern stays one in all comparatively sluggish progress in comparison with historic requirements and different superior economies.
The Components Shaping the Chart: A Multifaceted Evaluation
A number of interconnected elements contribute to the form of Japan’s GDP chart:
1. The Misplaced Decade(s): The Lingering Impression of the Asset Bubble Burst: The Nineties witnessed the bursting of Japan’s asset bubble, resulting in a chronic interval of financial stagnation also known as the "Misplaced Decade" (and even "Misplaced Two A long time"). This era was marked by deflation, excessive ranges of company and family debt, and a reluctance of banks to lend, hindering funding and financial exercise. The legacy of this disaster continues to forged an extended shadow over the economic system, impacting funding, productiveness, and general progress potential.
2. Demographic Headwinds: An Getting old Inhabitants and Shrinking Workforce: Japan faces a quickly growing old inhabitants and a declining start fee, resulting in a shrinking workforce. This demographic shift poses important challenges to financial progress, because it reduces the pool of accessible labor and will increase the burden on the social safety system. The shrinking workforce necessitates elevated productiveness to take care of financial output, a problem that Japan has but to completely overcome.
3. Structural Rigidities: Limitations to Innovation and Competitors: Japan’s economic system has been criticized for its inflexible labor markets, bureaucratic hurdles, and resistance to structural reforms. These rigidities hinder innovation, entrepreneurship, and the environment friendly allocation of sources. The dominance of huge, established firms (keiretsu) can stifle competitors and stop the emergence of latest, dynamic companies. Overcoming these structural impediments is essential for fostering sustainable financial progress.
4. Exterior Shocks: World Financial Crises and Pure Disasters: Japan’s economic system just isn’t resistant to exterior shocks. The worldwide monetary disaster of 2008-2009 dealt a big blow, highlighting the nation’s dependence on international commerce and funding. Extra not too long ago, the COVID-19 pandemic additional uncovered its vulnerabilities. As well as, Japan is liable to pure disasters, resembling earthquakes and tsunamis, which might disrupt financial exercise and trigger important injury.
5. Authorities Insurance policies: A Balancing Act Between Stimulus and Reform: The Japanese authorities has applied numerous financial stimulus packages and coverage measures geared toward boosting progress. These embody financial easing by the Financial institution of Japan (BOJ), fiscal stimulus measures, and makes an attempt at structural reforms. Nonetheless, the effectiveness of those insurance policies has been debated, with some arguing that they haven’t been ample to deal with the underlying structural points. The problem lies in balancing short-term stimulus with long-term structural reforms that may foster sustainable progress.
6. Technological Innovation: A Double-Edged Sword: Whereas Japan boasts a powerful technological base, its capability to translate technological developments into sustained financial progress has been uneven. Whereas it excels in particular sectors, the general influence on productiveness and GDP progress has been much less pronounced than in another superior economies. Moreover, the shift in the direction of a digital economic system presents each alternatives and challenges for Japan.
Decoding the Chart: Past the Numbers
The GDP chart alone supplies solely a partial image of Japan’s financial actuality. It is essential to think about different indicators, resembling inflation, unemployment, productiveness, and revenue inequality, to achieve a extra complete understanding. Whereas the GDP chart might present comparatively sluggish progress, different indicators would possibly reveal constructive developments in particular sectors or areas. As an illustration, Japan’s technological prowess continues to be a supply of energy, albeit one which must be leveraged extra successfully for broader financial advantages.
Wanting Forward: Challenges and Alternatives
Japan’s financial future hinges on its capability to deal with the challenges outlined above. This requires a multi-pronged method that encompasses:
- Structural reforms: Overhauling inflexible labor markets, selling competitors, and streamlining rules are important to reinforce productiveness and innovation.
- Demographic coverage: Addressing the growing old inhabitants and shrinking workforce requires a mix of measures, together with immigration insurance policies, incentivizing larger start charges, and selling longer working lives.
- Technological development: Investing in analysis and improvement, fostering innovation, and selling the adoption of latest applied sciences are essential for sustaining competitiveness within the international economic system.
- Fiscal consolidation: Addressing the nation’s excessive ranges of public debt requires cautious fiscal administration and a dedication to long-term fiscal sustainability.
- World engagement: Sustaining robust financial ties with different international locations and collaborating actively in international financial governance are important for securing Japan’s financial future.
In conclusion, Japan’s GDP chart displays a fancy and evolving financial panorama. Whereas the previous 20 years have been characterised by sluggish progress and challenges, Japan possesses important strengths and potential. Efficiently navigating the challenges and capitalizing on the alternatives would require daring coverage selections, structural reforms, and a dedication to adapting to the altering international financial panorama. The longer term trajectory of Japan’s GDP will rely largely on its capability to beat its structural impediments and unleash its appreciable revolutionary capability. The chart, subsequently, serves not simply as a file of the previous, however as a roadmap for the longer term, highlighting the important want for transformative change.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered useful insights into Decoding Japan’s GDP Chart: A Two-Decade Journey of Stagnation and Resilience. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!