Distinction Between Histogram And Bar Chart
By admin / October 11, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
distinction between histogram and bar chart
Associated Articles: distinction between histogram and bar chart
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to distinction between histogram and bar chart. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
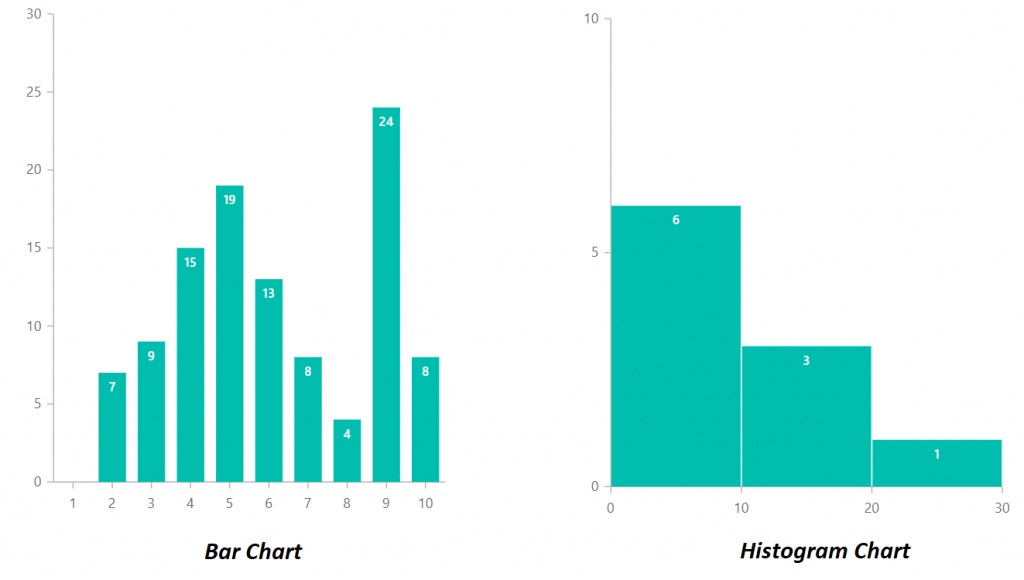
Histograms vs. Bar Charts: Unveiling the Nuances of Information Visualization
![What is the difference between a bar graph and a histogram? [SOLVED]](https://d138zd1ktt9iqe.cloudfront.net/media/seo_landing_files/screenshot-2021-03-01-at-9-17-06-am-1614570481.png)
Histograms and bar charts are each highly effective instruments for visualizing knowledge, ceaselessly used to current frequencies or counts of various classes or values. Nonetheless, regardless of their superficial similarities, they serve distinct functions and make use of basically completely different approaches to knowledge illustration. Understanding these variations is essential for efficient knowledge communication and correct interpretation of visible representations. This text delves deep into the distinctions between histograms and bar charts, clarifying their purposes and highlighting the potential pitfalls of misusing one for the opposite.
Bar Charts: Categorical Information Champions
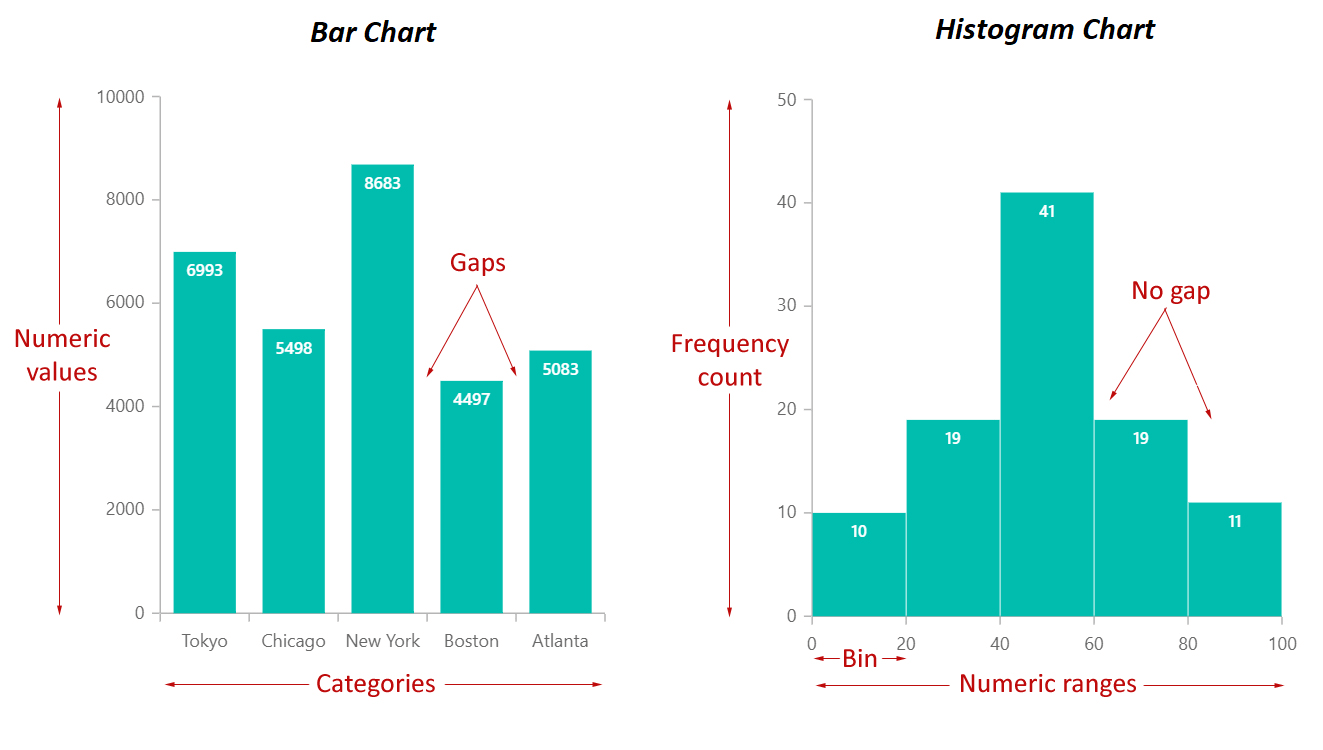
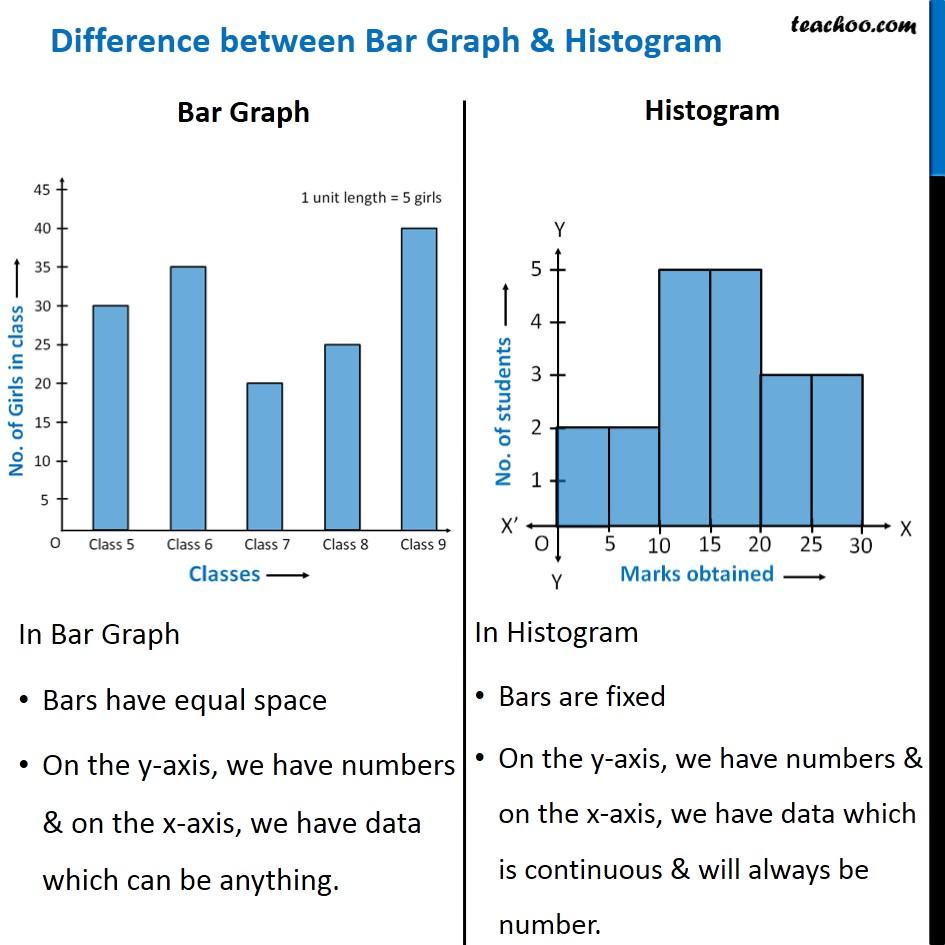
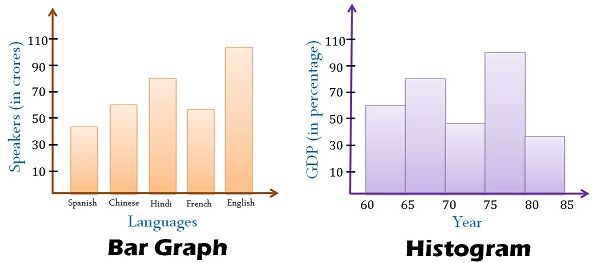
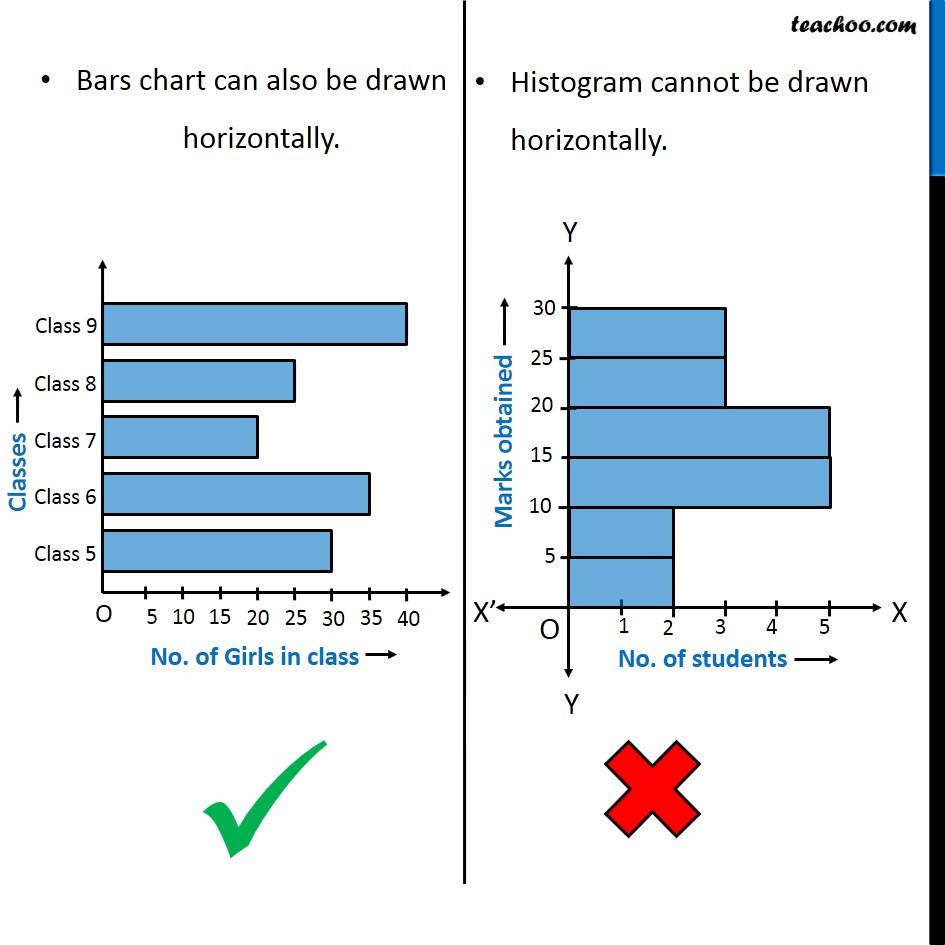
Bar charts are primarily designed to show the frequencies or proportions of categorical knowledge. Categorical knowledge represents qualitative traits that may be divided into distinct teams or classes. These classes will be nominal (unordered, like colours or forms of fruits) or ordinal (ordered, like schooling ranges or buyer satisfaction scores). The important thing characteristic of a bar chart is that the classes alongside the horizontal axis are discrete and unbiased; there is a clear separation between every class, and the order usually does not inherently matter (until it is an ordinal scale).
Every bar in a bar chart represents a particular class, and its top (or size, relying on the orientation) corresponds to the frequency or proportion of observations falling inside that class. The bars are usually separated by gaps, visually emphasizing the distinct nature of the classes. This separation is essential as a result of it prevents misinterpretation of the info as steady.
Examples of acceptable makes use of for bar charts:
- Gross sales efficiency by area: Evaluating gross sales figures throughout completely different geographical areas.
- Buyer satisfaction scores: Exhibiting the distribution of responses (e.g., very happy, happy, impartial, dissatisfied, very dissatisfied).
- Product preferences: Illustrating the recognition of various product variants.
- Election outcomes: Displaying the variety of votes acquired by every candidate.
- Frequency of various blood varieties in a inhabitants: Representing the counts of every blood kind.
Histograms: Unveiling the Distribution of Numerical Information
Histograms, in contrast to bar charts, are designed to visualise the distribution of numerical knowledge. Numerical knowledge represents quantitative measurements that may be ordered and have a significant numerical scale. As a substitute of displaying particular person classes, histograms group numerical knowledge into intervals or bins, exhibiting the frequency of knowledge factors falling inside every bin. The important thing distinction right here is that the horizontal axis represents a steady numerical vary, not discrete classes.
The width of every bin in a histogram represents the vary of values it encompasses, and the peak of the bar represents the frequency (or density) of knowledge factors inside that vary. Crucially, the bars in a histogram are adjoining to one another, signifying the continual nature of the underlying knowledge. The absence of gaps emphasizes the movement of knowledge throughout the numerical vary. The selection of bin width considerably impacts the looks of the histogram, and cautious consideration is important to keep away from deceptive interpretations. Too few bins may obscure vital particulars, whereas too many bins may create a jagged and uninformative illustration.
Examples of acceptable makes use of for histograms:
- Distribution of examination scores: Exhibiting the frequency of scores inside completely different rating ranges.
- Earnings distribution in a metropolis: Visualizing the frequency of incomes inside specified earnings brackets.
- Heights of scholars in a category: Representing the distribution of pupil heights throughout completely different top ranges.
- Distribution of ages in a inhabitants: Exhibiting the frequency of individuals inside completely different age teams.
- Evaluation of response instances in an experiment: Visualizing the distribution of response instances throughout completely different time intervals.
Key Variations Summarized:
| Characteristic | Bar Chart | Histogram |
|---|---|---|
| Information Kind | Categorical (nominal or ordinal) | Numerical (steady or discrete) |
| X-axis | Discrete classes | Steady numerical ranges (bins) |
| Bar Spacing | Gaps between bars | No gaps between bars |
| Bar Top | Frequency or proportion of every class | Frequency or density inside every bin |
| Function | Examine classes, present proportions | Present knowledge distribution, determine patterns |
Misinterpretations and Widespread Errors:
One widespread mistake is utilizing a bar chart for numerical knowledge that must be represented utilizing a histogram. As an illustration, presenting earnings ranges as separate bars with out contemplating the continual nature of earnings results in a deceptive visualization. Equally, utilizing a histogram for categorical knowledge obscures the distinct nature of the classes and might result in incorrect interpretations.
One other potential pitfall is the inappropriate selection of bin width in a histogram. Too slender bins may create a loud and uneven illustration, whereas too broad bins may masks vital particulars concerning the knowledge distribution. The optimum bin width usually will depend on the dataset’s traits and the specified degree of element.
Lastly, it is essential to label axes clearly and supply a descriptive title to make sure that the visualization is definitely understood and interpreted accurately. With out correct labeling, even essentially the most correct chart can fail to convey its supposed message successfully.
Past the Fundamentals: Variations and Extensions
Each bar charts and histograms will be prolonged and modified to boost their informative worth. For instance:
- Stacked bar charts: These show a number of classes inside every bar, permitting for comparisons throughout completely different subgroups.
- Grouped bar charts: These place bars side-by-side for simpler comparability of a number of classes.
- Normalized histograms: These show relative frequencies or densities, making comparisons between histograms with completely different pattern sizes simpler.
- Density histograms: These use density as an alternative of frequency on the y-axis, offering a smoother illustration of the info distribution.
Conclusion:
Histograms and bar charts are important instruments for knowledge visualization, however their distinct purposes have to be rigorously thought-about. Understanding the elemental variations between these chart varieties is essential for creating efficient visualizations that precisely symbolize the info and facilitate clear communication. By selecting the suitable chart kind and being attentive to particulars like bin width and labeling, knowledge analysts can leverage these instruments to realize worthwhile insights and successfully talk their findings. Misusing these charts can result in misinterpretations and hinder the correct understanding of the underlying knowledge, emphasizing the significance of cautious consideration and choice when selecting between a histogram and a bar chart.



Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied worthwhile insights into distinction between histogram and bar chart. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!