A P-chart Measures Choose A C-chart Measures
By admin / August 6, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
a p-chart measures choose a c-chart measures
Associated Articles: a p-chart measures choose a c-chart measures
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we are going to discover the intriguing subject associated to a p-chart measures choose a c-chart measures. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
P-Charts vs. C-Charts: Selecting the Proper Management Chart for Your Information

Statistical Course of Management (SPC) is a robust instrument for monitoring and bettering the standard of processes. Management charts are a key element of SPC, visually representing course of efficiency over time and highlighting potential areas for enchancment. Among the many numerous forms of management charts, the p-chart and the c-chart are ceaselessly used to observe the proportion of nonconforming models and the variety of defects per unit, respectively. Nonetheless, selecting between these two charts requires a cautious understanding of their underlying assumptions and the character of the information being analyzed. This text will delve into the specifics of p-charts and c-charts, clarifying their functions, highlighting their variations, and offering steering on deciding on the suitable chart for a given state of affairs.
Understanding P-Charts: Monitoring Proportion Nonconforming
A p-chart is used to observe the proportion of nonconforming models in a pattern. That is notably helpful when coping with attributes information – information that’s categorized as both conforming or nonconforming primarily based on a particular attribute. Examples embrace:
- Proportion of faulty objects in a manufacturing batch: Monitoring the proportion of defective digital elements in a cargo.
- Buyer satisfaction charge: Monitoring the proportion of shoppers who report satisfaction with a services or products.
- Error charge in information entry: Measuring the proportion of incorrectly entered information factors in a big dataset.
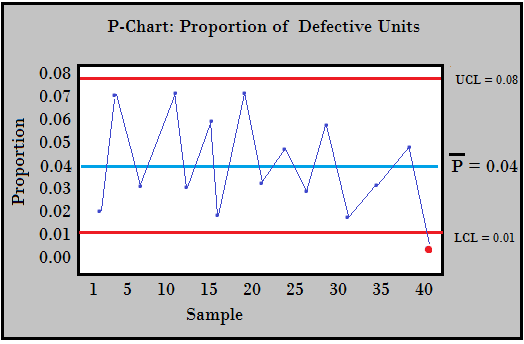
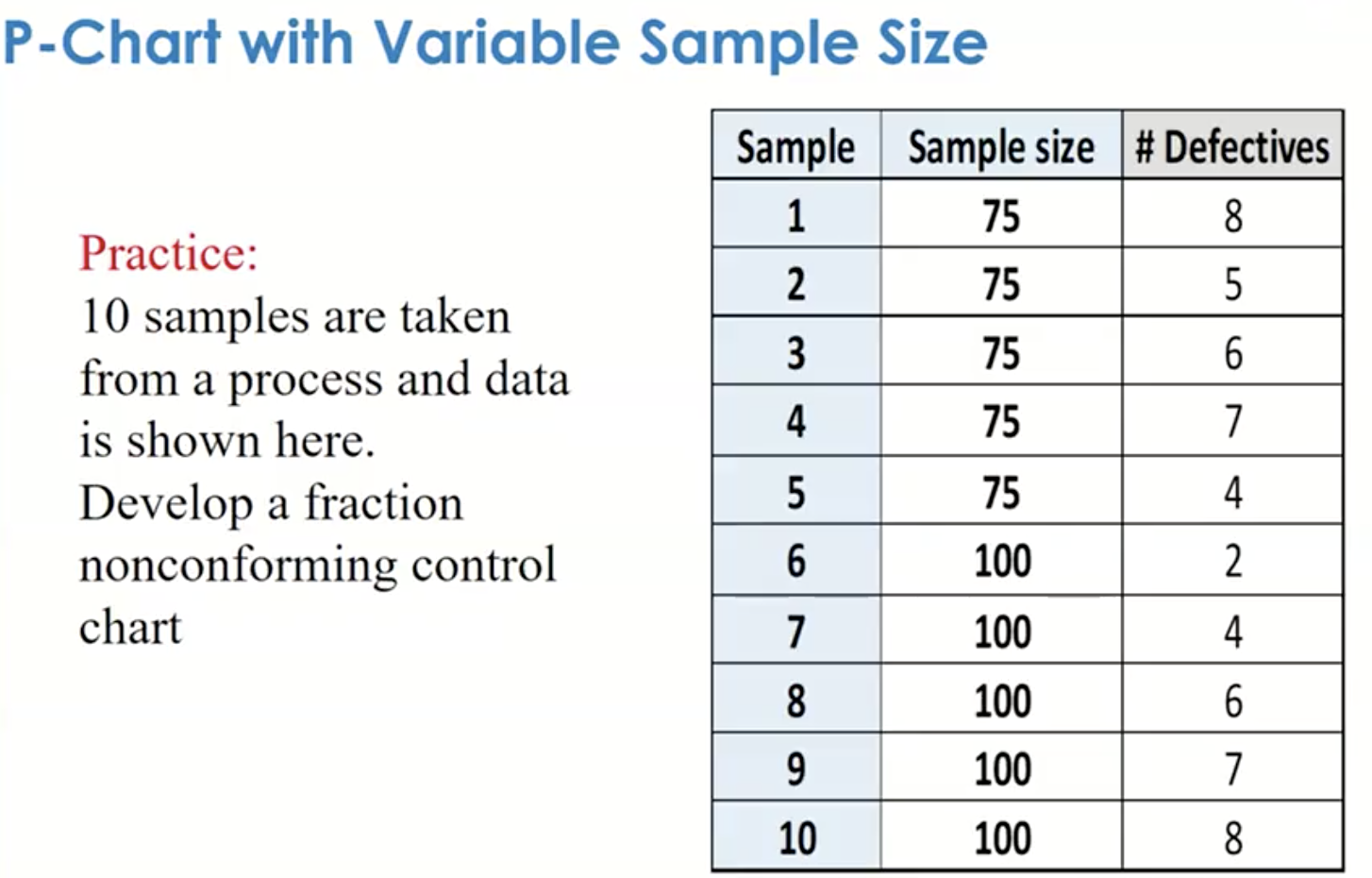
The important thing attribute of p-chart information is that every pattern represents a proportion (p) derived from a set pattern measurement (n). The pattern measurement (n) stays fixed all through the monitoring course of. The chart plots the pattern proportions (p) over time, together with the management limits calculated primarily based on the historic information. These management limits symbolize the anticipated vary of variation within the proportion of nonconforming models if the method is in a state of statistical management.
Calculating Management Limits for a P-Chart:
The management limits for a p-chart are calculated utilizing the next formulation:
-
Heart Line (CL):
p̄ = Σpi / okaythe placep̄is the typical proportion of nonconforming models,piis the proportion of nonconforming models within the i-th pattern, andokayis the variety of samples. -
Higher Management Restrict (UCL):
p̄ + 3√(p̄(1-p̄)/n) -
Decrease Management Restrict (LCL):
p̄ - 3√(p̄(1-p̄)/n)
Notice: If the calculated LCL is damaging, it’s usually set to zero, as a proportion can’t be damaging.
Deciphering P-Charts:
Factors persistently falling throughout the management limits point out that the method is secure and working predictably. Factors falling outdoors the management limits counsel that the method is uncontrolled, indicating a possible shift within the proportion of nonconforming models. This might be because of numerous elements, together with modifications in supplies, gear malfunctions, or operator errors. Investigating the causes of those out-of-control factors is essential for course of enchancment.
Understanding C-Charts: Monitoring Variety of Defects per Unit
A c-chart is used to observe the variety of defects per unit (or per pattern). In contrast to p-charts, which deal with the proportion of nonconforming models, c-charts take care of the depend of defects. The pattern measurement (n) is implicitly thought-about to be fixed; nevertheless, it’s not explicitly used within the management restrict calculations. Examples of c-chart functions embrace:
- Variety of defects in a manufactured product: Counting the variety of scratches or blemishes on a painted floor.
- Variety of errors in a software program program: Monitoring the variety of bugs discovered throughout testing.
- Variety of accidents in a office: Monitoring the variety of security incidents over time.
The important thing assumption of a c-chart is that the variety of defects per unit follows a Poisson distribution. Which means that the defects happen randomly and independently, and the typical variety of defects stays comparatively fixed over time.
Calculating Management Limits for a C-Chart:
The management limits for a c-chart are calculated utilizing the next formulation:
-
Heart Line (CL):
c̄ = Σci / okaythe placec̄is the typical variety of defects per unit,ciis the variety of defects within the i-th unit, andokayis the variety of models. -
Higher Management Restrict (UCL):
c̄ + 3√c̄ -
Decrease Management Restrict (LCL):
c̄ - 3√c̄
Much like p-charts, if the calculated LCL is damaging, it’s set to zero.
Deciphering C-Charts:
Much like p-charts, factors persistently falling throughout the management limits point out a secure course of. Factors outdoors the management limits counsel that the method is uncontrolled and requires investigation. Nonetheless, the interpretation focuses on the variety of defects relatively than the proportion of nonconforming models.
Selecting Between P-Charts and C-Charts: A Comparative Evaluation
The selection between a p-chart and a c-chart will depend on the character of the information and the particular goal of the monitoring course of. This is a abstract of the important thing variations:
| Characteristic | P-Chart | C-Chart |
|---|---|---|
| Information Sort | Proportion nonconforming (p) | Variety of defects (c) |
| Pattern Measurement | Fixed (n) | Implicitly fixed, not utilized in calculations |
| Distribution | Binomial (approximated by regular) | Poisson |
| Focus | Proportion of nonconforming models | Variety of defects per unit |
| Utility | Monitoring share of defectives | Monitoring variety of defects per merchandise/unit |
When to Use a P-Chart:
- When you’re within the proportion of nonconforming models in a pattern of fixed measurement.
- When the pattern measurement is giant sufficient (usually n > 50) for the binomial distribution to be approximated by a standard distribution.
- When you’re monitoring attributes information, classifying models as both conforming or nonconforming.
When to Use a C-Chart:
- When you’re within the variety of defects per unit, whatever the pattern measurement.
- When the variety of defects per unit follows a Poisson distribution.
- When you’re monitoring the variety of defects in a unit or merchandise.
Sensible Issues:
- Information Assortment: Correct and constant information assortment is essential for the efficient use of each p-charts and c-charts. Clear definitions of conforming and nonconforming models or defects are essential.
- Pattern Measurement: The selection of pattern measurement for p-charts impacts the sensitivity of the chart. Bigger pattern sizes present better precision however require extra effort in information assortment. For c-charts, pattern measurement is much less crucial.
- Course of Stability: Each charts assume that the method is secure when the information is collected to ascertain the management limits. If the method is considerably unstable, the management limits is probably not dependable.
- Software program Instruments: Quite a few statistical software program packages and spreadsheets can be utilized to create and analyze p-charts and c-charts, simplifying the method.
Conclusion:
P-charts and c-charts are priceless instruments for monitoring course of high quality. By understanding their respective traits and assumptions, practitioners can choose the suitable chart for his or her particular information and aims. Cautious consideration of information kind, pattern measurement, and course of stability is important for the efficient implementation and interpretation of those highly effective management charts, in the end resulting in improved course of management and decreased variability. Do not forget that the right utility of those charts, mixed with diligent investigation of out-of-control alerts, is essential to reaching important high quality enhancements.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied priceless insights right into a p-chart measures choose a c-chart measures. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!