The Y-Chart: A Versatile Instrument For VLSI Design Evaluation And Optimization
By admin / May 30, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
The Y-Chart: A Versatile Instrument for VLSI Design Evaluation and Optimization
Associated Articles: The Y-Chart: A Versatile Instrument for VLSI Design Evaluation and Optimization
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to The Y-Chart: A Versatile Instrument for VLSI Design Evaluation and Optimization. Let’s weave fascinating info and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
The Y-Chart: A Versatile Instrument for VLSI Design Evaluation and Optimization

The complexity of recent Very-Giant-Scale Integration (VLSI) designs necessitates refined evaluation and optimization strategies. Amongst these, the Y-chart, a strong graphical illustration, performs an important position in understanding and managing the trade-offs inherent in chip design. This text delves into the intricacies of the Y-chart, exploring its functions, benefits, and limitations inside the VLSI design circulation.
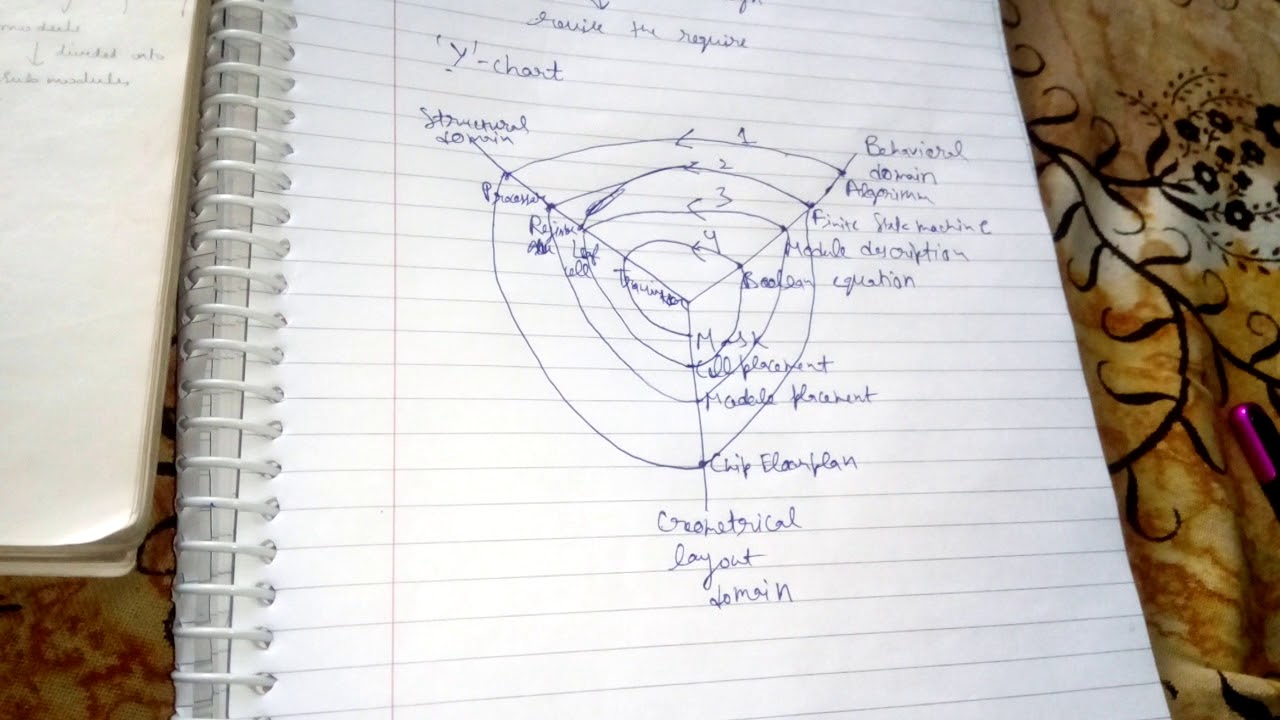
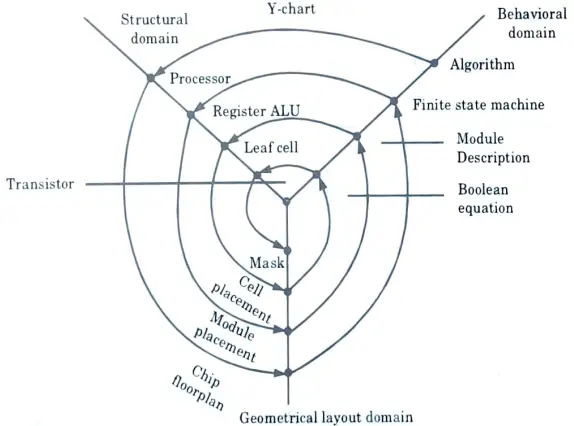
Understanding the Three Dimensions of the Y-Chart
The Y-chart, also referred to as the power-performance-area (PPA) chart, depicts the elemental trade-offs between three key efficiency metrics in VLSI design:
- Efficiency: Measured usually by clock frequency (f), throughput, or latency. Increased efficiency typically implies quicker processing capabilities.
- Energy: Encompasses each static (leakage) and dynamic energy consumption. Decrease energy consumption is important for extending battery life in moveable gadgets and lowering power prices in information facilities.
- Space: Refers back to the silicon space occupied by the design. Smaller space interprets to decrease manufacturing prices and probably larger yields.
These three parameters aren’t impartial; optimizing one usually necessitates compromises within the others. As an illustration, rising the clock frequency (bettering efficiency) could result in larger dynamic energy consumption and probably a bigger space as a result of want for quicker transistors and wider buses. The Y-chart visually represents these intricate relationships, permitting designers to discover the design area successfully.
Visualizing the Design Area with the Y-Chart
The Y-chart is a three-dimensional illustration, usually projected onto a two-dimensional airplane for simpler visualization. Every level within the chart represents a selected design configuration, outlined by its efficiency, energy, and space traits. A set of design factors, obtained via numerous design explorations (e.g., altering transistor sizing, clock frequency, architectural decisions), types a design area cloud. This cloud offers beneficial insights into the achievable trade-offs and potential design optimization paths.
Completely different projections of the 3D Y-chart can spotlight particular relationships. For instance, a 2D projection exhibiting efficiency versus energy can illustrate the power effectivity of various design choices. Equally, a efficiency versus space projection highlights the impression of space optimization on velocity. The selection of projection relies on the precise design objectives and priorities.
Functions of the Y-Chart in VLSI Design
The Y-chart finds in depth functions all through the VLSI design circulation, together with:
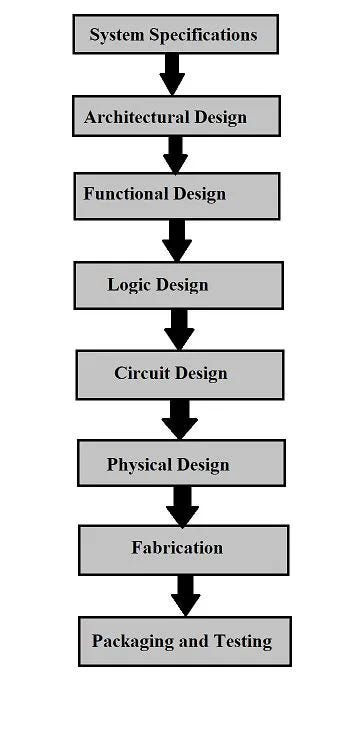
- Architectural Exploration: In the course of the preliminary levels of design, the Y-chart helps consider totally different architectural alternate options. Designers can discover numerous configurations (e.g., pipelining, parallelism) and assess their impression on PPA. This permits knowledgeable choices relating to the optimum structure for the goal software.
- Microarchitectural Optimization: As soon as the structure is chosen, the Y-chart assists in optimizing microarchitectural parameters. This includes exploring totally different implementations of purposeful items, reminiscence hierarchies, and interconnect networks, evaluating their impact on PPA.
- Logic Synthesis and Optimization: Logic synthesis instruments can generate a number of implementations of a given logic operate with various PPA traits. The Y-chart helps analyze these implementations and choose the optimum one primarily based on the design constraints.
- Bodily Design Optimization: Throughout bodily design, the Y-chart aids in evaluating totally different placement and routing options. Completely different placement methods can considerably affect space and interconnect size, affecting each efficiency and energy.
- Know-how Choice: The Y-chart can be utilized to check totally different course of applied sciences (e.g., totally different FinFET nodes). This helps decide the optimum know-how primarily based on the specified PPA trade-offs.
- Energy Administration Methods: The Y-chart could be employed to judge the effectiveness of varied energy administration strategies, reminiscent of clock gating, voltage scaling, and energy gating. This enables designers to optimize energy consumption with out considerably impacting efficiency or space.
Benefits of Utilizing the Y-Chart
The Y-chart affords a number of benefits in VLSI design:
- Visible Illustration of Commerce-offs: The graphical nature of the Y-chart makes it simple to visualise and perceive the advanced interactions between efficiency, energy, and space.
- Design Area Exploration: It permits designers to discover a variety of design choices and establish potential Pareto optimum factors (design factors the place no enchancment in a single metric is feasible with out sacrificing one other).
- Knowledgeable Determination Making: The Y-chart offers a complete overview of the design area, enabling designers to make knowledgeable choices primarily based on the precise design constraints and priorities.
- Communication and Collaboration: The visible nature of the Y-chart facilitates efficient communication and collaboration amongst design crew members.
- Optimization Steerage: The chart helps establish areas of the design area that warrant additional exploration and optimization efforts.
Limitations of the Y-Chart
Regardless of its benefits, the Y-chart has sure limitations:
- Excessive Dimensionality: The three-dimensional nature of the Y-chart could be difficult to visualise and interpret, particularly when coping with a lot of design factors. Projections onto 2D planes can lose some info.
- Information Dependency: The accuracy and usefulness of the Y-chart rely closely on the accuracy and completeness of the info used to generate it. Inaccurate information can result in deceptive conclusions.
- Complexity of Evaluation: Analyzing a fancy Y-chart with quite a few design factors could be time-consuming and require specialised instruments.
- Lack of Consideration for Different Metrics: The Y-chart primarily focuses on PPA. Different essential design metrics, reminiscent of reliability, testability, and manufacturability, aren’t explicitly represented. Nonetheless, these elements can not directly affect the PPA trade-offs.
Superior Strategies and Instruments
A number of superior strategies and instruments improve the effectiveness of the Y-chart in VLSI design:
- Pareto Entrance Evaluation: Figuring out the Pareto optimum factors on the Y-chart is essential for choosing the right design choices. Algorithms and instruments are used to effectively establish these factors.
- Design Area Exploration Algorithms: Subtle algorithms, reminiscent of genetic algorithms and simulated annealing, can be utilized to discover the design area effectively and establish promising design factors.
- Machine Studying Strategies: Machine studying strategies are more and more getting used to foretell PPA traits and information the design exploration course of. This will considerably scale back the effort and time required for design optimization.
Conclusion
The Y-chart is an indispensable instrument in trendy VLSI design, offering a strong visible illustration of the inherent trade-offs between efficiency, energy, and space. By enabling efficient design area exploration and optimization, the Y-chart considerably contributes to the event of high-performance, energy-efficient, and cost-effective built-in circuits. Whereas limitations exist, the continued growth of superior strategies and instruments continues to boost the capabilities and applicability of this beneficial design methodology. The way forward for VLSI design hinges on successfully managing these trade-offs, and the Y-chart stays a cornerstone in attaining this purpose.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied beneficial insights into The Y-Chart: A Versatile Instrument for VLSI Design Evaluation and Optimization. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!