Deep Dive Into P-Charts In Minitab: A Complete Information To Course of Management And Diagnostics
By admin / August 31, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Deep Dive into P-Charts in Minitab: A Complete Information to Course of Management and Diagnostics
Associated Articles: Deep Dive into P-Charts in Minitab: A Complete Information to Course of Management and Diagnostics
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to Deep Dive into P-Charts in Minitab: A Complete Information to Course of Management and Diagnostics. Let’s weave fascinating info and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Deep Dive into P-Charts in Minitab: A Complete Information to Course of Management and Diagnostics

Course of management charts are important instruments for monitoring the soundness and efficiency of processes. Amongst these, the p-chart holds a singular place, particularly designed for analyzing the proportion of nonconforming items in a pattern. Minitab, a strong statistical software program package deal, supplies a strong platform for creating, analyzing, and decoding p-charts, providing a wealth of diagnostic instruments to know course of habits. This text will delve deep into the creation, interpretation, and diagnostic capabilities of p-charts inside Minitab, equipping readers with the data to successfully make the most of this highly effective instrument for high quality enchancment.
Understanding P-Charts: Monitoring Proportion Nonconforming
In contrast to management charts for steady information (like X-bar and R charts), p-charts give attention to attribute information – information that’s categorized as conforming or nonconforming to a particular high quality attribute. The p-chart plots the proportion (p) of nonconforming items in a pattern over time. Every pattern represents a subgroup of items inspected, and the proportion of defects in every subgroup is plotted on the chart. The chart then contains management limits, usually set at three commonplace deviations above and under the central line (representing the common proportion of nonconforming items).
Making a P-Chart in Minitab:
The method of making a p-chart in Minitab is easy:
-
Knowledge Entry: Your information ought to be organized with at the least two columns: one figuring out the subgroup (e.g., pattern quantity, time interval) and one other indicating the variety of nonconforming items in every subgroup. A 3rd column, representing the pattern dimension (variety of items inspected in every subgroup) can also be mandatory.
-
Statistical Evaluation: Navigate to "Stat" -> "Management Charts" -> "Attributes Charts" -> "P".
-
Knowledge Choice: Specify the columns containing your subgroup identifier, the variety of nonconforming items, and the pattern dimension.
-
Choices: Minitab affords a number of choices to customise your chart. These embrace:
- Methodology for estimating the middle line: You possibly can select between utilizing the general proportion of nonconforming items from all subgroups or specifying a goal worth.
- Methodology for calculating management limits: Minitab makes use of the usual deviation of the proportion to calculate management limits. You possibly can select between totally different strategies for calculating this commonplace deviation, influencing the sensitivity of the chart.
- Subgroup dimension: In case your subgroup dimension is fixed, Minitab will routinely calculate management limits. Nonetheless, if the subgroup dimension varies, Minitab will regulate the management limits accordingly.
- Assessments for particular causes: Minitab affords varied exams for detecting particular causes of variation, equivalent to factors exterior the management limits, runs above or under the central line, and tendencies.
-
Chart Creation: After you have specified your information and choices, Minitab will generate your p-chart, displaying the proportion of nonconforming items for every subgroup, together with the central line and higher and decrease management limits.
Deciphering the P-Chart:
A steady course of, free from particular causes of variation, will exhibit factors randomly distributed throughout the management limits. Factors exterior the management limits, or patterns throughout the management limits (e.g., runs, tendencies), point out potential issues requiring investigation.
-
Factors exterior the management limits: These point out a major shift within the course of proportion of nonconforming items, suggesting a particular reason behind variation. The investigation ought to give attention to figuring out and eliminating the foundation reason behind this shift.
-
Runs: A collection of consecutive factors above or under the central line signifies a possible shift within the course of imply, even when the factors stay throughout the management limits.
-
Traits: A constant upward or downward pattern within the plotted factors suggests a gradual shift within the course of, presumably indicating a deteriorating course of or a gradual change in enter supplies or course of parameters.
-
Stratification: If the information is stratified (e.g., by operator, machine, or shift), it is essential to create separate p-charts for every stratum to establish potential sources of variation.
Minitab’s Diagnostic Capabilities:
Minitab enhances the p-chart’s utility with its highly effective diagnostic options:
-
Assessments for Particular Causes: Minitab routinely performs varied exams for particular causes of variation, flagging potential issues within the course of. These exams embrace:
- Assessments 1-8: These exams establish factors exterior the management limits, runs above or under the central line, tendencies, and different patterns indicative of particular trigger variation.
- Nelson Guidelines: These guidelines supply a extra complete set of exams for figuring out particular causes, offering a extra delicate evaluation.
-
Functionality Evaluation: As soon as the method is deemed steady (factors inside management limits and no vital patterns), Minitab permits for functionality evaluation, assessing the method’s potential to satisfy specified high quality necessities. This evaluation supplies metrics equivalent to PPM (elements per million) defects and sigma ranges, offering a quantitative evaluation of course of efficiency.
-
Session Window Output: Minitab’s session window supplies detailed statistical info, together with the estimated proportion of nonconforming items, the usual deviation of the proportion, the management limits, and the outcomes of the particular trigger exams. This info is essential for a complete understanding of the method habits.
-
Graphical Output: The chart itself supplies a visible illustration of the method habits over time, permitting for simple identification of potential issues. The clear show of management limits and the flagged factors makes it straightforward to establish areas requiring consideration.
Addressing Out-of-Management Factors:
When out-of-control factors are recognized, a scientific investigation is essential. This includes:
-
Verification: Affirm the information accuracy. Have been there any errors in information assortment or entry?
-
Root Trigger Evaluation: Use instruments like brainstorming, 5 Whys, fishbone diagrams, and Pareto charts to establish the underlying reason behind the out-of-control factors.
-
Corrective Motion: Implement corrective actions to get rid of the foundation trigger.
-
Monitoring: Proceed monitoring the method utilizing the p-chart to make sure the corrective actions have been efficient and the method stays steady.
Limitations of P-Charts:
Whereas p-charts are highly effective instruments, they’ve limitations:
-
Assumption of Independence: P-charts assume that the nonconforming items inside a subgroup are unbiased. If this assumption is violated (e.g., resulting from clustering of defects), the outcomes could also be deceptive.
-
Subgroup Dimension: The accuracy of the management limits relies on the subgroup dimension. Small subgroup sizes can result in wider management limits and diminished sensitivity. Conversely, excessively giant subgroup sizes can masks delicate shifts within the course of.
-
Knowledge Necessities: P-charts require a adequate variety of subgroups to supply dependable outcomes. A small variety of subgroups can result in inaccurate management limits and unreliable conclusions.
Conclusion:
Minitab’s p-chart performance supplies a complete and user-friendly method to monitoring the proportion of nonconforming items in a course of. By combining visible illustration with subtle diagnostic capabilities, Minitab empowers customers to establish and tackle course of instability, resulting in improved high quality and diminished defects. Understanding the ideas of p-charts, leveraging Minitab’s options, and using a scientific method to investigating out-of-control factors are essential for efficient course of management and steady enchancment. The detailed info offered by Minitab, coupled with a radical understanding of course of habits, permits data-driven decision-making, leading to extra sturdy and environment friendly processes. Keep in mind to all the time take into account the constraints of the p-chart and make sure the assumptions are met for correct and dependable outcomes.

![]()



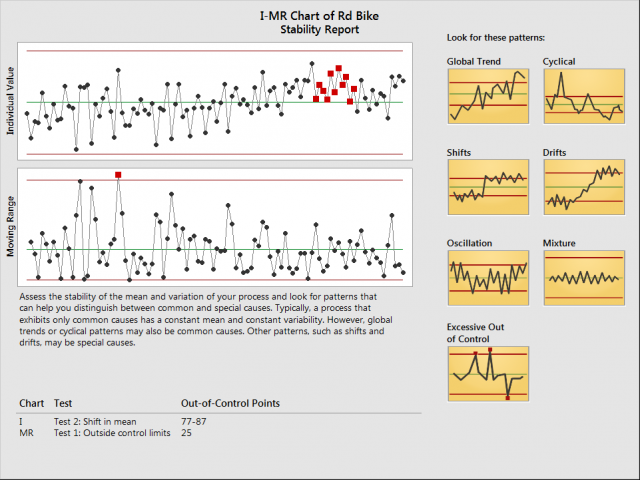

Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered useful insights into Deep Dive into P-Charts in Minitab: A Complete Information to Course of Management and Diagnostics. We hope you discover this text informative and useful. See you in our subsequent article!