Change Transfusion In Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia: A Complete Information With Bilirubin Chart Interpretation
By admin / September 17, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Change Transfusion in Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia: A Complete Information with Bilirubin Chart Interpretation
Associated Articles: Change Transfusion in Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia: A Complete Information with Bilirubin Chart Interpretation
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we are going to discover the intriguing subject associated to Change Transfusion in Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia: A Complete Information with Bilirubin Chart Interpretation. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Change Transfusion in Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia: A Complete Information with Bilirubin Chart Interpretation

Neonatal hyperbilirubinemia, characterised by elevated bilirubin ranges in a new child’s blood, is a typical scientific problem. Whereas typically benign and managed conservatively, extreme hyperbilirubinemia can result in kernicterus, a doubtlessly devastating neurological situation. Change transfusion, a process involving the substitute of a good portion of the toddler’s blood quantity with donor blood, serves as a vital intervention in these extreme circumstances. This text supplies a complete overview of change transfusion, specializing in its indications, process, potential issues, and the essential function of bilirubin charting in guiding therapeutic selections.
Understanding Bilirubin and its Pathophysiology in Neonates
Bilirubin, a byproduct of heme breakdown, exists in two varieties: unconjugated (oblique) and conjugated (direct). Unconjugated bilirubin is insoluble in water and doubtlessly neurotoxic. The liver conjugates bilirubin, making it water-soluble and excretable. Neonates are notably prone to hyperbilirubinemia resulting from a number of components:
- Immature hepatic operate: The new child liver’s skill to conjugate and excrete bilirubin is restricted within the preliminary days of life.
- Elevated bilirubin manufacturing: Hemolysis (breakdown of purple blood cells) is extra frequent in newborns, resulting in greater bilirubin manufacturing.
- Elevated enterohepatic circulation: Delayed bowel actions can result in recirculation of bilirubin, additional elevating ranges.
- Lowered intestinal flora: The intestine microbiome performs a job in bilirubin metabolism, and its immaturity in newborns can contribute to greater bilirubin ranges.
Medical Presentation and Prognosis of Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia
Jaundice, a yellowish discoloration of the pores and skin and sclera (whites of the eyes), is the hallmark signal of hyperbilirubinemia. The severity and timing of jaundice are essential in figuring out the necessity for intervention. Prognosis includes:
- Bodily examination: Assessing the extent and development of jaundice.
- Transcutaneous bilirubinometry (TcB): A non-invasive methodology to measure bilirubin ranges by means of the pores and skin. Whereas handy, TcB readings may be influenced by components like pores and skin pigmentation and hydration.
- Serum bilirubin measurement: A blood take a look at offering a exact measurement of complete, direct, and oblique bilirubin ranges. That is the gold customary for assessing hyperbilirubinemia.
Indications for Change Transfusion
Change transfusion is a life-saving process reserved for extreme hyperbilirubinemia when much less invasive remedies like phototherapy have failed or are inadequate. The choice to carry out an change transfusion is predicated on a number of components, together with:
- Serum bilirubin ranges: The precise threshold varies relying on the toddler’s age, gestational age, and scientific situation. Nonetheless, typically, ranges exceeding these indicated on the nomogram (mentioned under) are thought-about essential.
- Charge of bilirubin rise: A quickly rising bilirubin degree necessitates pressing intervention.
- Medical indicators of bilirubin encephalopathy (kernicterus): These embrace lethargy, poor feeding, hypotonia, high-pitched cry, and opisthotonos (arching of the again). The presence of those indicators signifies fast want for change transfusion.
- Acidosis: Metabolic acidosis can worsen the consequences of hyperbilirubinemia.
- Different threat components: Prematurity, important hemolysis, and sure infections enhance the chance of kernicterus.
The Bilirubin Nomogram: A Guiding Software
The bilirubin nomogram is a vital device used to information decision-making relating to change transfusion. It depicts the connection between serum bilirubin ranges, age (in hours), and gestational age. The nomogram supplies a visible illustration of the chance of kernicterus at completely different bilirubin ranges and helps clinicians decide the suitable intervention. A number of completely different nomograms exist, and their interpretation ought to be guided by native tips and institutional protocols.
(Insert a pattern bilirubin nomogram right here. This might ideally be a high-quality picture of a generally used nomogram. Because of the limitations of this text-based format, a visible illustration can’t be included. Nonetheless, the reader ought to be directed to available assets on-line displaying these nomograms.)
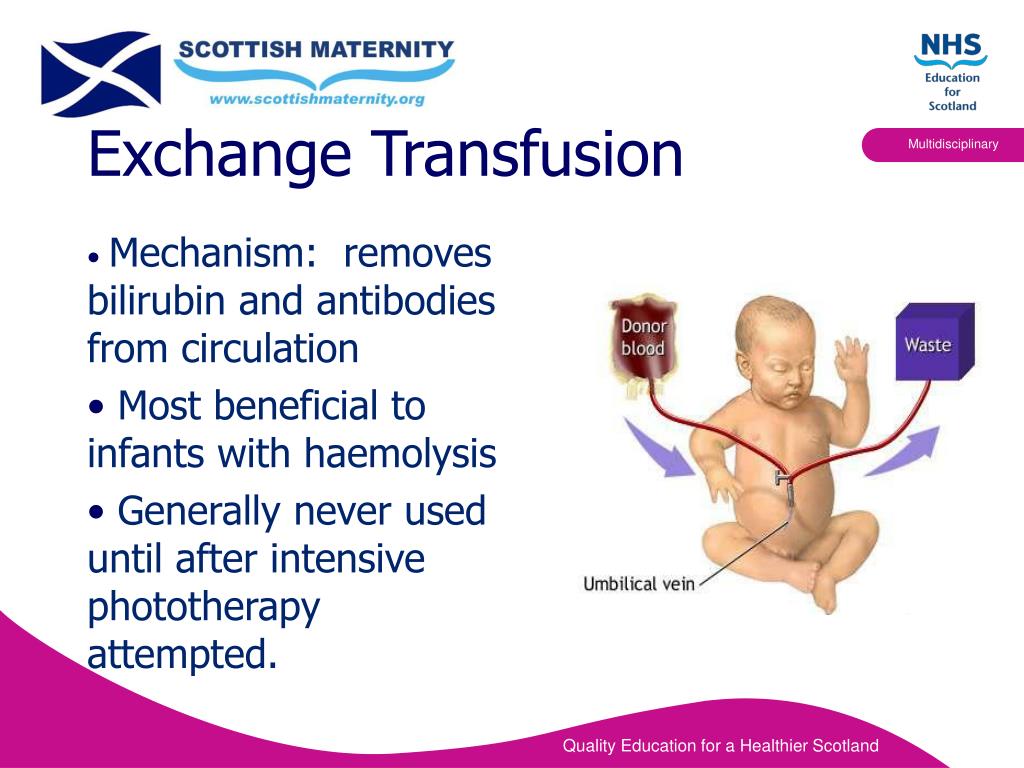
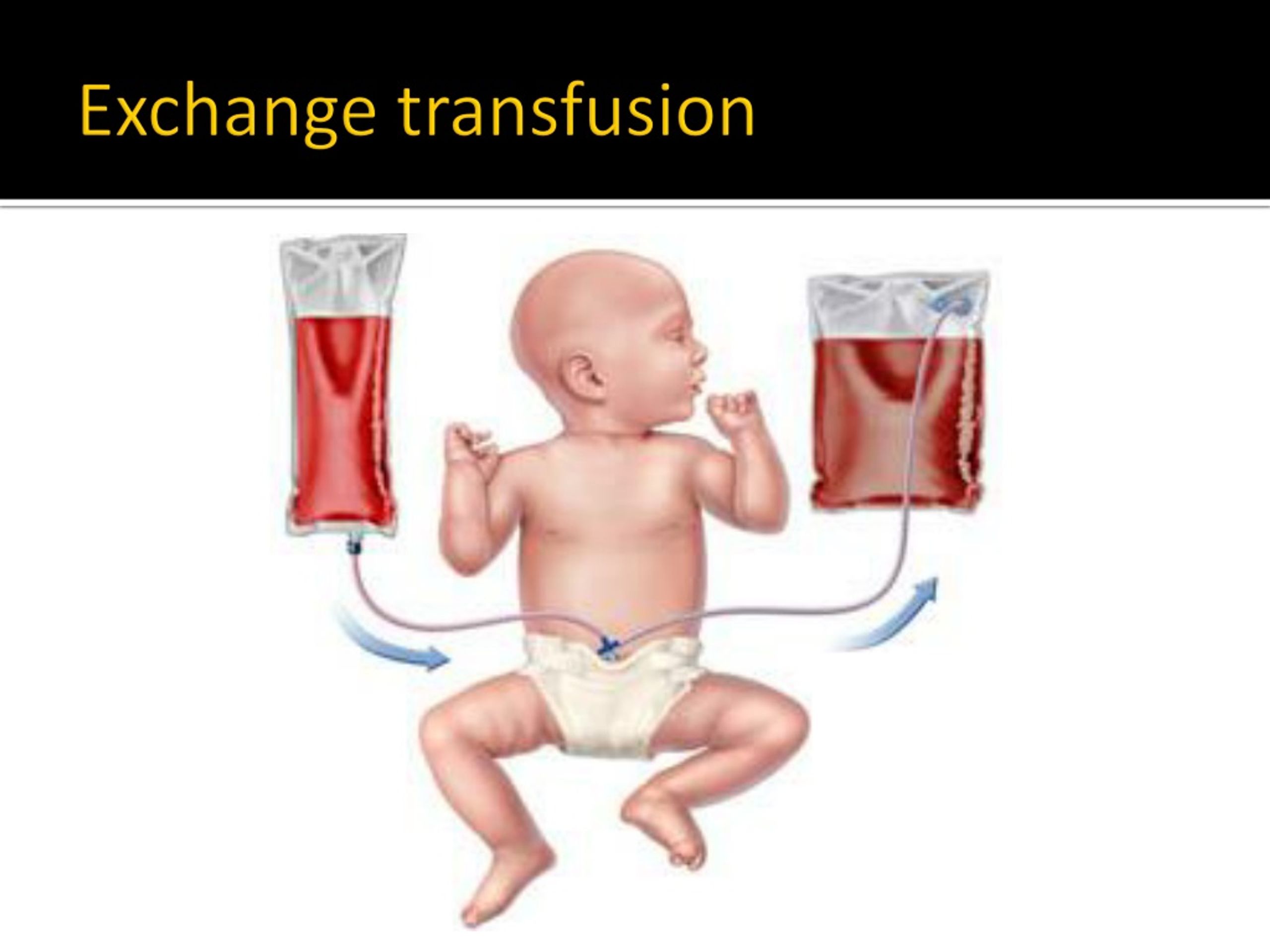
The Change Transfusion Process
Change transfusion includes the gradual elimination and substitute of the toddler’s blood with appropriate donor blood. The process is usually carried out utilizing an umbilical venous catheter or peripheral vein entry. The method is sluggish and punctiliously monitored to keep away from issues. Key steps embrace:
- Pre-procedure preparation: The toddler is assessed for very important indicators, blood sort and Rh issue are confirmed, and the donor blood is cross-matched.
- Catheter insertion: A catheter is inserted right into a vein.
- Blood change: Small volumes of the toddler’s blood are eliminated and changed with equal volumes of donor blood. That is repeated till a good portion of the toddler’s blood quantity has been exchanged (sometimes 50-100% of the blood quantity).
- Submit-procedure monitoring: Very important indicators, bilirubin ranges, and hematocrit are intently monitored.
Potential Issues of Change Transfusion
Whereas a life-saving process, change transfusion carries potential dangers:
- Hypocalcemia: Citrate within the donor blood can chelate calcium, resulting in hypocalcemia.
- Hypothermia: The transfused blood may be cooler than the toddler’s physique temperature.
- An infection: Threat of an infection from contaminated blood.
- Cardiac arrhythmias: Electrolyte imbalances may cause arrhythmias.
- Thrombosis: Catheter-related thrombosis.
- Bleeding: From the catheter insertion web site or different bleeding websites.
- Hemolysis: Incompatibility between donor and recipient blood.
- Air embolism: Unintended introduction of air into the bloodstream.
Submit-Change Transfusion Care
Submit-procedure care focuses on monitoring for issues and assessing the effectiveness of the transfusion. This consists of:
- Steady monitoring of important indicators: Coronary heart charge, blood stress, respiratory charge, and temperature.
- Common bilirubin degree monitoring: To evaluate the effectiveness of the transfusion.
- Electrolyte monitoring: To detect and handle electrolyte imbalances.
- Supportive care: Offering ample diet and hydration.
Conclusion
Change transfusion is a essential intervention within the administration of extreme neonatal hyperbilirubinemia. The choice to carry out an change transfusion is complicated and requires cautious consideration of the toddler’s scientific situation, bilirubin ranges, and threat components. Correct interpretation of the bilirubin nomogram, coupled with shut monitoring of the toddler’s response to the process, is important for optimum outcomes. Whereas the process carries potential dangers, its life-saving potential makes it an indispensable device within the neonatologist’s armamentarium. Steady developments in neonatal care and improved understanding of hyperbilirubinemia proceed to refine the indications and strategies for change transfusion, enhancing the security and efficacy of this significant intervention. Additional analysis is at all times ongoing to refine the nomograms and optimize the change transfusion course of for improved affected person outcomes and decreased dangers.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered invaluable insights into Change Transfusion in Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia: A Complete Information with Bilirubin Chart Interpretation. We hope you discover this text informative and useful. See you in our subsequent article!