Decoding The Ledger: Understanding The 5 Fundamental Account Varieties In Your Chart Of Accounts
By admin / November 10, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Decoding the Ledger: Understanding the 5 Fundamental Account Varieties in Your Chart of Accounts
Associated Articles: Decoding the Ledger: Understanding the 5 Fundamental Account Varieties in Your Chart of Accounts
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by way of the intriguing matter associated to Decoding the Ledger: Understanding the 5 Fundamental Account Varieties in Your Chart of Accounts. Let’s weave fascinating data and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the Ledger: Understanding the 5 Fundamental Account Varieties in Your Chart of Accounts

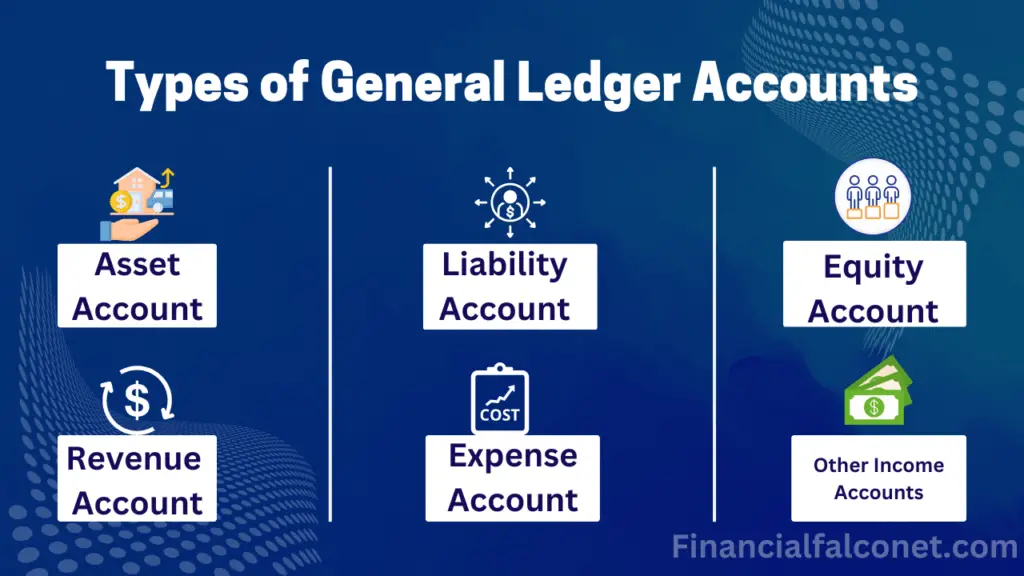
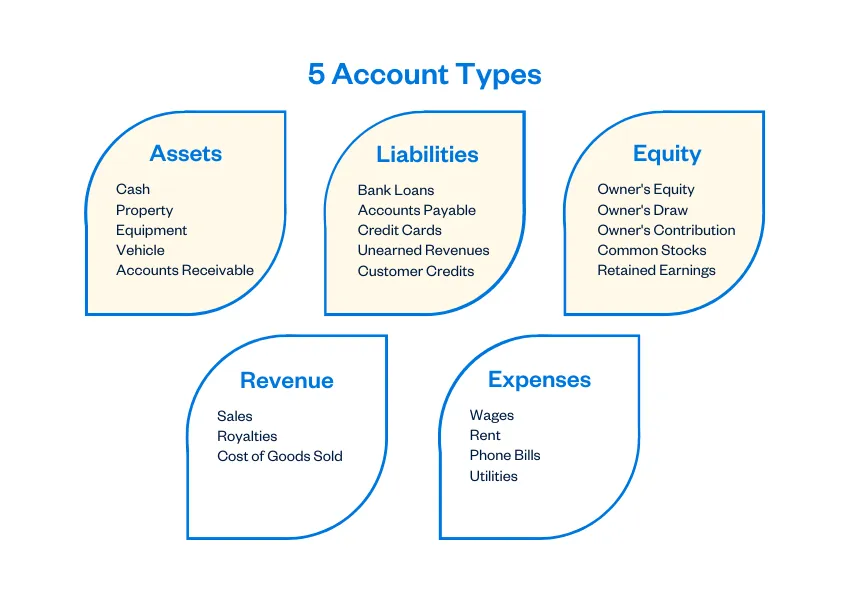
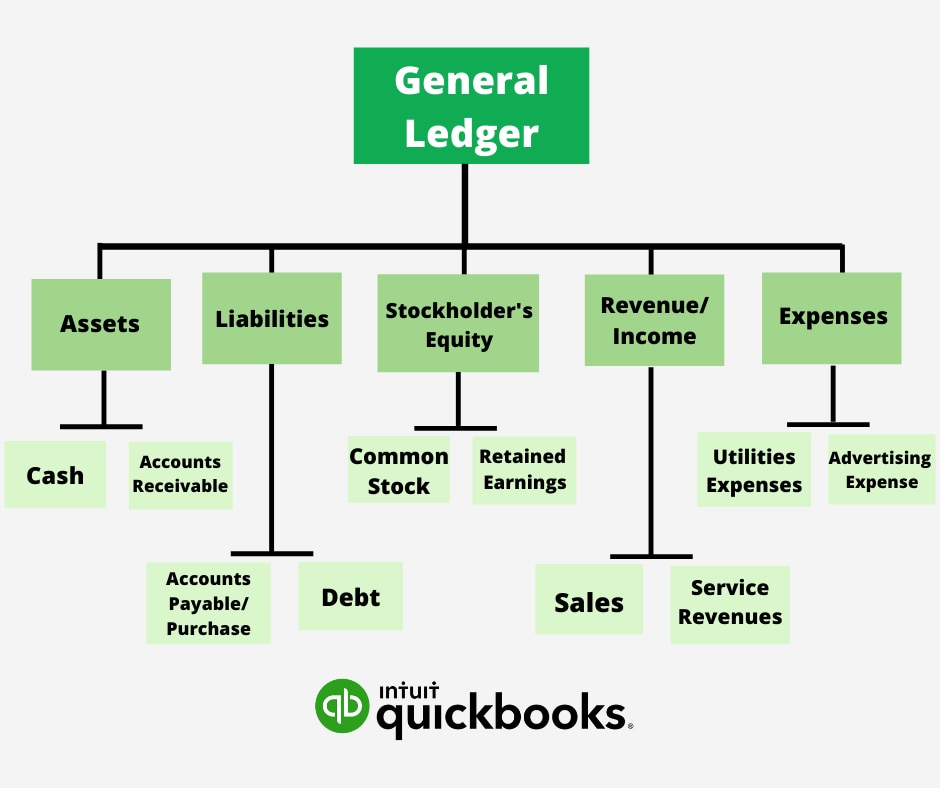
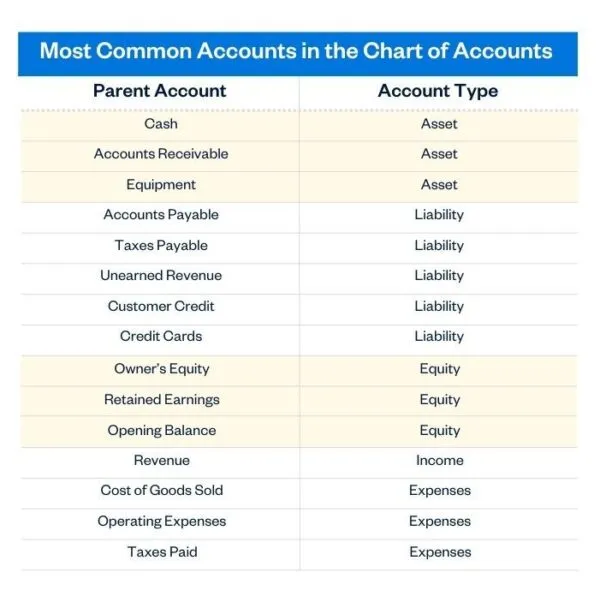
A chart of accounts (COA) is the spine of any sound monetary system. It is a structured listing of all of the accounts a enterprise makes use of to report its monetary transactions. Consider it as an in depth organizational map to your firm’s funds, permitting you to trace revenue, bills, belongings, liabilities, and fairness. Whereas the particular accounts inside a COA can differ relying on the trade and measurement of the enterprise, 5 important account varieties kind the muse: Belongings, Liabilities, Fairness, Income, and Bills. Understanding these classes is essential for correct monetary reporting, efficient monetary administration, and knowledgeable decision-making.
1. Belongings:
Belongings characterize what an organization owns and controls, with the expectation that these belongings will present future financial advantages. These advantages can manifest in varied types, similar to producing income, enhancing effectivity, or facilitating future operations. Belongings are usually listed on the steadiness sheet so as of liquidity – that means how shortly they are often transformed into money. The 5 important subcategories of belongings are:
-
Present Belongings: These are belongings anticipated to be transformed into money, bought, or used up inside one 12 months or the corporate’s working cycle, whichever is longer. Examples embrace:
- Money and Money Equivalents: This consists of foreign money, checking accounts, financial savings accounts, and short-term, extremely liquid investments like Treasury payments.
- Accounts Receivable: Cash owed to the corporate by prospects for items or providers bought on credit score.
- Stock: Items held on the market within the extraordinary course of enterprise. This will embrace uncooked supplies, work-in-progress, and completed items.
- Pay as you go Bills: Bills paid prematurely, similar to lease, insurance coverage, or subscriptions. These are thought-about belongings as a result of they characterize future advantages.
- Quick-Time period Investments: Investments which are simply convertible to money inside a 12 months.
-
Non-Present Belongings (Lengthy-Time period Belongings): These are belongings anticipated to supply advantages for multiple 12 months. They’re usually much less liquid than present belongings and characterize a longer-term funding. Examples embrace:
- Property, Plant, and Gear (PP&E): This consists of land, buildings, equipment, tools, and automobiles used within the enterprise’s operations. These belongings are usually depreciated over their helpful lives.
- Intangible Belongings: These are non-physical belongings with worth, similar to patents, copyrights, emblems, and goodwill. These are sometimes amortized over their helpful lives.
- Lengthy-Time period Investments: Investments that aren’t anticipated to be transformed to money inside a 12 months.
- Deferred Tax Belongings: These come up when an organization has paid extra taxes than it presently owes, making a future tax profit.
2. Liabilities:
Liabilities characterize an organization’s obligations to others – what it owes. These are claims in opposition to the corporate’s belongings and characterize future sacrifices of financial advantages. Like belongings, liabilities are additionally categorized primarily based on their maturity date.
-
Present Liabilities: These are obligations due inside one 12 months or the working cycle. Examples embrace:
- Accounts Payable: Cash owed to suppliers for items or providers bought on credit score.
- Salaries Payable: Wages owed to workers.
- Curiosity Payable: Curiosity owed on loans or different debt.
- Quick-Time period Loans Payable: Loans due inside one 12 months.
- Unearned Income: Funds acquired from prospects for items or providers that haven’t but been delivered or carried out.
-
Non-Present Liabilities (Lengthy-Time period Liabilities): These are obligations due past one 12 months. Examples embrace:
- Lengthy-Time period Loans Payable: Loans due in multiple 12 months.
- Bonds Payable: Debt securities issued by the corporate.
- Deferred Tax Liabilities: These come up when an organization has paid much less tax than it presently owes, making a future tax obligation.
- Pension Liabilities: Obligations to pay retirement advantages to workers.
3. Fairness:
Fairness represents the residual curiosity within the belongings of the corporate after deducting its liabilities. It is the homeowners’ stake within the enterprise. For companies, that is sometimes called shareholder’s fairness, whereas for sole proprietorships and partnerships, it is merely proprietor’s fairness. Key parts of fairness embrace:
- Frequent Inventory: Represents the possession shares issued to buyers.
- Retained Earnings: Gathered income that haven’t been distributed to shareholders as dividends.
- Treasury Inventory: Firm’s personal inventory that has been repurchased.
- Extra Paid-in Capital: Quantities acquired from shareholders in extra of the par worth of the inventory.
4. Income:
Income represents the inflows of belongings or settlements of liabilities ensuing from the extraordinary actions of a enterprise. It is the cash earned from the sale of products or providers. Examples embrace:
- Gross sales Income: Income generated from the sale of products.
- Service Income: Income generated from offering providers.
- Curiosity Income: Income earned from interest-bearing investments.
- Rental Income: Income earned from renting out property.
- Royalty Income: Income earned from licensing mental property.
5. Bills:
Bills characterize the outflows of belongings or incurrences of liabilities ensuing from the extraordinary actions of a enterprise. They’re the prices incurred in producing income. Bills are deducted from income to reach at internet revenue or internet loss. Examples embrace:
- Price of Items Offered (COGS): The direct prices related to producing items bought.
- Salaries Expense: Wages paid to workers.
- Lease Expense: Price of renting premises.
- Utilities Expense: Price of electrical energy, water, and fuel.
- Promoting Expense: Price of promoting and advertising.
- Depreciation Expense: The systematic allocation of the price of a tangible asset over its helpful life.
- Amortization Expense: The systematic allocation of the price of an intangible asset over its helpful life.
- Curiosity Expense: Price of borrowing cash.
The Interrelationship of Accounts:
These 5 important account varieties are interconnected. The accounting equation, Belongings = Liabilities + Fairness, is a basic precept that governs the connection between them. Each transaction impacts no less than two accounts to take care of this steadiness. For example, buying tools on credit score will increase each belongings (tools) and liabilities (accounts payable). Equally, incomes income will increase belongings (money) and fairness (retained earnings). Understanding this interconnectedness is important for sustaining correct monetary data and producing dependable monetary stories. The accuracy and element of your chart of accounts straight affect the standard of your monetary statements, permitting for higher monetary planning, evaluation, and in the end, enterprise success. Common assessment and updating of your COA are essential to make sure it stays related and efficient as what you are promoting grows and evolves.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/chart-accounts.asp_final-438b76f8e6e444dd8f4cd8736b0baa6a.png)

Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered beneficial insights into Decoding the Ledger: Understanding the 5 Fundamental Account Varieties in Your Chart of Accounts. We respect your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!