Decoding Shoulder Ache: A Complete Information To Diagnostic Chart Areas
By admin / July 6, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Decoding Shoulder Ache: A Complete Information to Diagnostic Chart Areas
Associated Articles: Decoding Shoulder Ache: A Complete Information to Diagnostic Chart Areas
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing subject associated to Decoding Shoulder Ache: A Complete Information to Diagnostic Chart Areas. Let’s weave fascinating info and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding Shoulder Ache: A Complete Information to Diagnostic Chart Areas

Shoulder ache is a pervasive downside, affecting people throughout age teams and exercise ranges. Its complexity stems from the shoulder’s intricate anatomy, a confluence of bones, muscle tissues, tendons, ligaments, and bursae working in live performance. Pinpointing the supply of shoulder ache requires a scientific method, usually using diagnostic charts to categorize the ache’s location, character, and related signs. This text explores key diagnostic chart areas related to shoulder ache, offering a complete overview for each healthcare professionals and people in search of to know their situation.
I. Anatomical Chart Areas and Related Ache Patterns:
Understanding the anatomy is essential for deciphering shoulder ache. The shoulder joint is just not a single entity however a fancy system of articulations: the glenohumeral joint (the ball-and-socket joint between the humerus and scapula), the acromioclavicular joint (the place the acromion means of the scapula meets the clavicle), and the sternoclavicular joint (the place the clavicle meets the sternum). Muscle mass, tendons, ligaments, and bursae surrounding these joints contribute considerably to shoulder operate and are frequent sources of ache.
A. Glenohumeral Joint Ache:
Ache originating from the glenohumeral joint usually presents as deep, aching ache within the anterior (entrance) and lateral (outer) points of the shoulder. The ache can radiate down the arm, particularly with particular actions. Diagnostic charts could categorize this ache primarily based on:
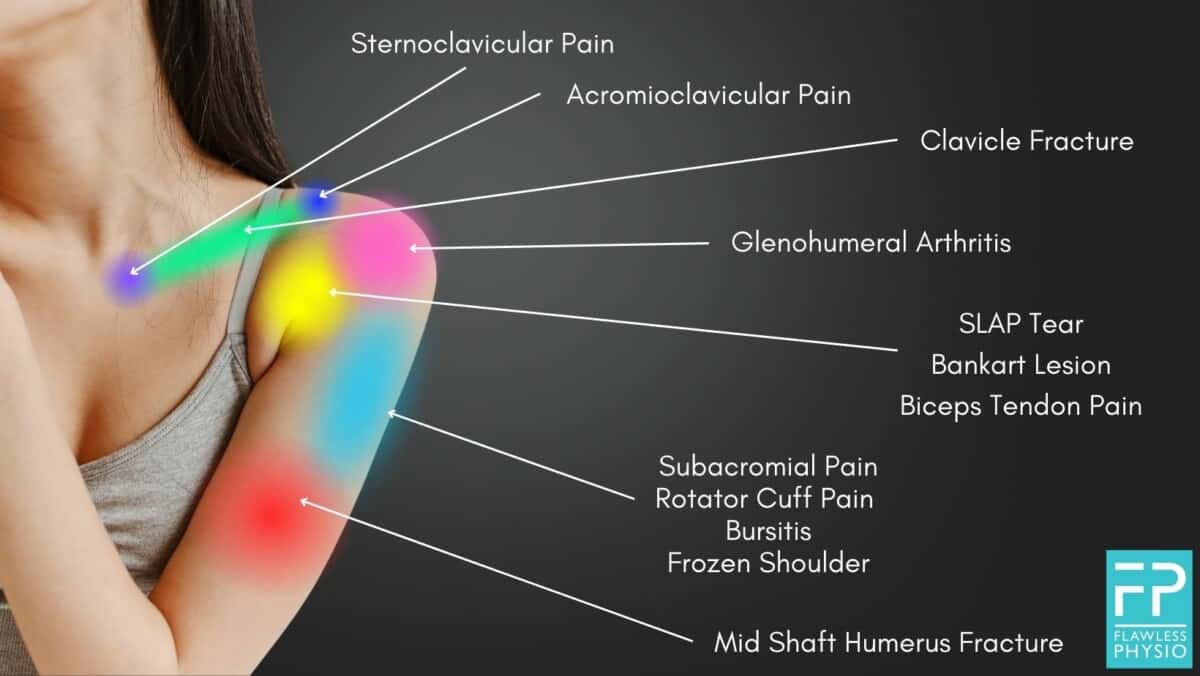
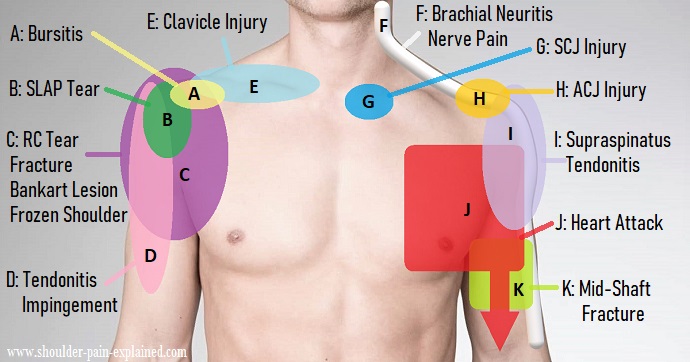
- Anterior Shoulder Ache: This usually signifies points with the anterior glenohumeral ligaments, rotator cuff tendons (subscapularis), or the biceps tendon. Circumstances like anterior instability, labral tears, and subacromial bursitis may cause the sort of ache.
- Lateral Shoulder Ache: This generally factors in the direction of rotator cuff tendinopathy (supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor), subacromial impingement, or acromioclavicular joint issues. Ache is commonly exacerbated by overhead actions.
- Posterior Shoulder Ache: Much less frequent than anterior or lateral ache, posterior glenohumeral joint ache may end up from posterior instability, rotator cuff tears (infraspinatus, teres minor), or referred ache from cervical backbone points.
B. Rotator Cuff Ache:
The rotator cuff muscle tissues (supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis) stabilize the shoulder and allow its wide selection of movement. Ache originating from these muscle tissues usually presents as:
- Supraspinatus Tendinopathy/Tear: Ache is felt laterally, usually worsening with abduction (lifting the arm away from the physique). Weak spot in abduction is a standard discovering.
- Infraspinatus/Teres Minor Tendinopathy/Tear: Ache is felt posteriorly and laterally, with weak spot in exterior rotation (turning the arm outwards).
- Subscapularis Tendinopathy/Tear: Ache is felt anteriorly, with weak spot in inside rotation (turning the arm inwards).
Diagnostic charts usually incorporate checks just like the empty can check (supraspinatus), exterior rotation lag signal (infraspinatus), and lift-off check (subscapularis) to evaluate rotator cuff operate and determine potential tears.
C. Acromioclavicular (AC) Joint Ache:
Ache within the AC joint is often localized to the highest of the shoulder, close to the bony prominence of the acromion. It is usually aggravated by direct stress or actions that stress the joint. Circumstances like AC joint arthritis, separation, or osteoarthritis may cause this ache.
D. Sternoclavicular (SC) Joint Ache:
Ache from the SC joint is situated on the base of the neck, close to the place the clavicle meets the sternum. It could actually radiate in the direction of the shoulder and is commonly related to restricted vary of movement. This ache may end up from arthritis, dislocations, or fractures.
E. Subacromial Bursa Ache:
The subacromial bursa cushions the rotator cuff tendons and the overlying acromion. Irritation of this bursa (subacromial bursitis) causes ache within the lateral and anterior shoulder, usually worsened by overhead actions. It steadily coexists with rotator cuff tendinopathy.
II. Characterizing Shoulder Ache: Past Location
Diagnostic charts additionally think about the character of the ache:
- Sharp, stabbing ache: Suggests acute harm, resembling a fracture, dislocation, or acute bursitis.
- Boring, aching ache: Typically signifies continual situations like arthritis, tendinopathy, or muscle pressure.
- Burning ache: Could recommend nerve involvement, resembling cervical radiculopathy or thoracic outlet syndrome.
- Referred ache: Ache originating from one other space, such because the neck or coronary heart, could be felt within the shoulder. Cardiac ache, as an illustration, can current as left shoulder ache.
III. Related Signs and Diagnostic Concerns:
A whole diagnostic image necessitates contemplating signs past the ache itself:
- Weak spot: Signifies potential rotator cuff tear, muscle pressure, or nerve harm.
- Numbness/tingling: Suggests nerve compression, doubtlessly resulting from thoracic outlet syndrome or cervical radiculopathy.
- Swelling: Signifies irritation, presumably from bursitis, tendinitis, or harm.
- Restricted vary of movement: Suggests joint stiffness, muscle tightness, or harm.
- Clicking/popping: Could point out labral tears, instability, or different intra-articular points.
- Evening ache: Generally is a vital indicator of extreme situations like rotator cuff tears or arthritis.
IV. Imaging and Diagnostic Checks:
Diagnostic charts usually information the collection of applicable imaging and checks:
- X-rays: Establish fractures, dislocations, arthritis, and bone spurs.
- Ultrasound: Visualizes tender tissues like tendons, muscle tissues, and bursae, serving to diagnose rotator cuff tears, tendinopathy, and bursitis.
- MRI: Supplies detailed photos of all shoulder buildings, together with bones, ligaments, tendons, muscle tissues, and cartilage. It is significantly helpful for diagnosing labral tears and rotator cuff tears.
- CT scan: Affords detailed bone photos and is typically used to evaluate complicated fractures or bony abnormalities.
- Electromyography (EMG) and Nerve Conduction Research (NCS): Assess nerve operate and assist diagnose nerve compression syndromes like thoracic outlet syndrome.
V. Differential Analysis:
Shoulder ache can stem from a large number of situations. A complete diagnostic chart helps differentiate between these potentialities:
- Rotator cuff pathology: Tendinopathy, tears, impingement syndrome.
- Glenohumeral instability: Anterior, posterior, or multidirectional instability.
- Labral tears: Tears within the glenoid labrum, a hoop of cartilage surrounding the glenoid fossa.
- Acromioclavicular joint pathology: Arthritis, separation, osteoarthritis.
- Sternoclavicular joint pathology: Arthritis, dislocation.
- Subacromial bursitis: Irritation of the subacromial bursa.
- Frozen shoulder (adhesive capsulitis): Vital stiffness and restricted vary of movement.
- Thoracic outlet syndrome: Compression of nerves and blood vessels within the thoracic outlet.
- Cervical radiculopathy: Nerve root compression within the neck, inflicting referred ache to the shoulder.
- Referred ache from cardiac or different visceral sources: Ache originating from organs and referred to the shoulder.
VI. Conclusion:
Shoulder ache analysis requires a meticulous method that integrates affected person historical past, bodily examination findings, and applicable imaging and diagnostic checks. Diagnostic charts function useful instruments, organizing details about ache location, character, related signs, and potential underlying situations. By systematically evaluating these components, healthcare professionals can successfully determine the supply of shoulder ache and develop a customized therapy plan. This complete understanding empowers each clinicians and sufferers in navigating the complexities of shoulder ache and attaining optimum outcomes. Keep in mind, this text supplies common info and shouldn’t be thought-about an alternative to skilled medical recommendation. All the time seek the advice of with a healthcare skilled for correct analysis and therapy of shoulder ache.

.jpg)



Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied useful insights into Decoding Shoulder Ache: A Complete Information to Diagnostic Chart Areas. We recognize your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!