Decoding The 52-Week Treasury Invoice Yield Chart: A Complete Information
By admin / June 21, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Decoding the 52-Week Treasury Invoice Yield Chart: A Complete Information
Associated Articles: Decoding the 52-Week Treasury Invoice Yield Chart: A Complete Information
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to Decoding the 52-Week Treasury Invoice Yield Chart: A Complete Information. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the 52-Week Treasury Invoice Yield Chart: A Complete Information
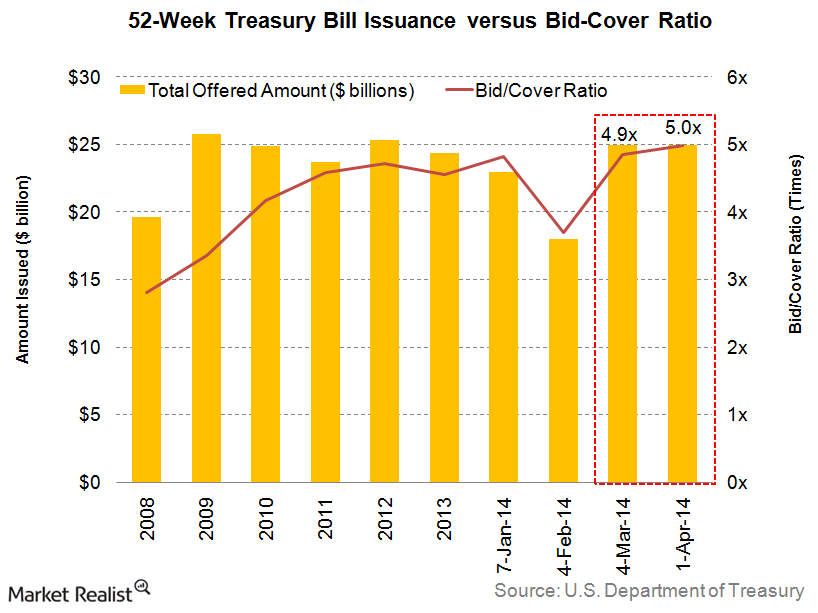
The 52-week Treasury invoice (T-bill) yield chart is a vital software for buyers, economists, and policymakers alike. It supplies a visible illustration of the return an investor can anticipate from buying a 52-week T-bill, a short-term debt instrument issued by the U.S. Treasury Division. Understanding this chart’s nuances can supply beneficial insights into prevailing rate of interest traits, financial well being, and potential funding methods. This text will delve into the intricacies of the 52-week T-bill yield chart, exploring its elements, interpretations, and implications.
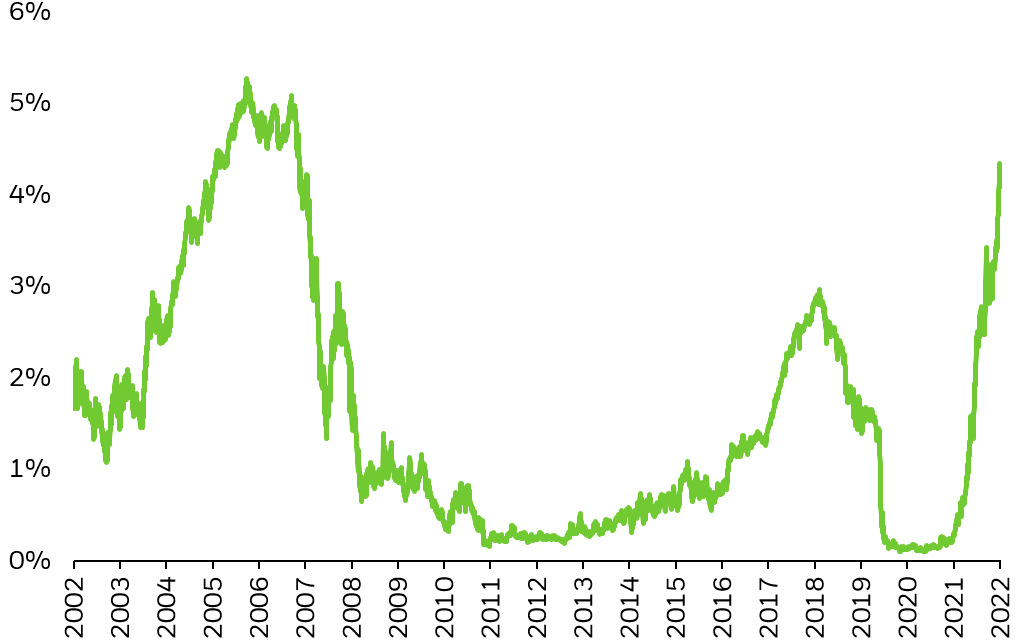
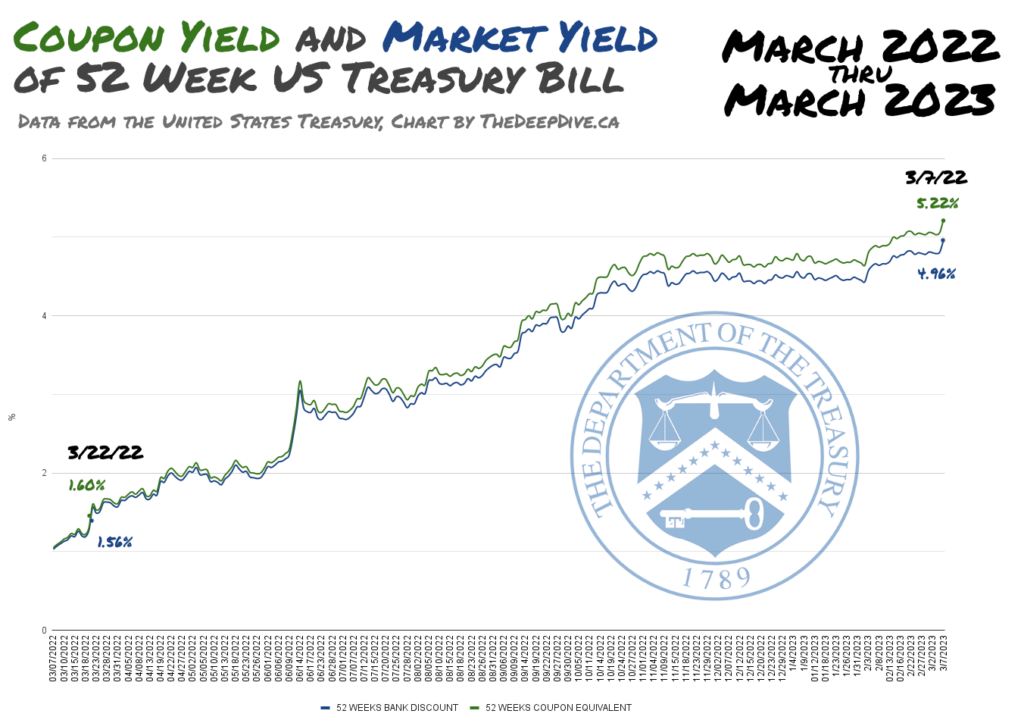
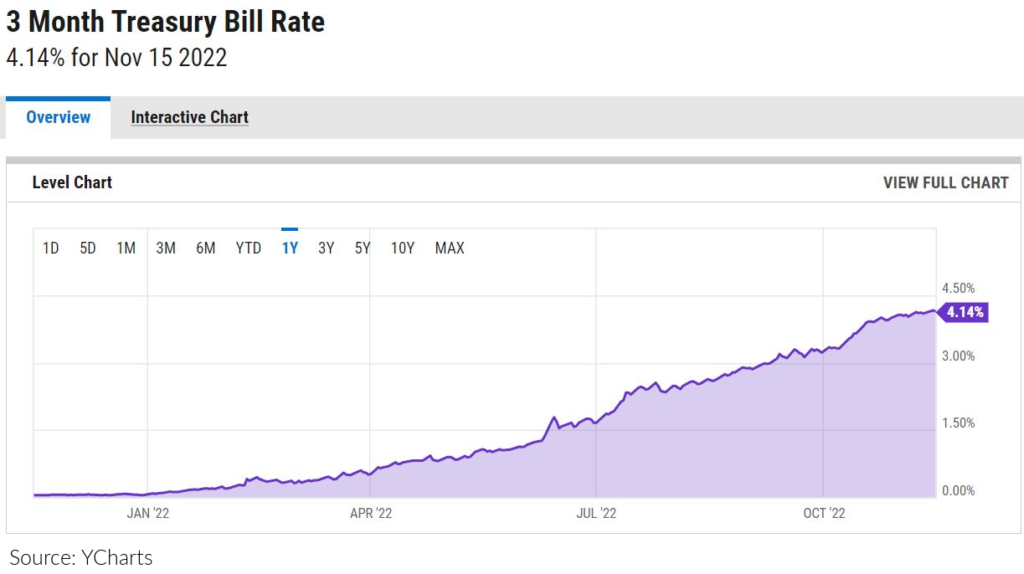
Understanding Treasury Payments and Their Yields
Earlier than diving into the chart itself, it is important to know the basics of T-bills. These are thought of one of many most secure investments globally, owing to their backing by the total religion and credit score of the U.S. authorities. They’re offered at a reduction to their face worth and mature after a specified interval (on this case, 52 weeks). The investor receives the face worth at maturity, representing the revenue. The yield represents the return on funding, expressed as an annualized proportion. This yield shouldn’t be fastened; it fluctuates primarily based on numerous market elements.
The 52-week T-bill yield is especially important as a result of it displays the market’s expectation of short-term rates of interest. It is a benchmark for different short-term debt devices and influences borrowing prices for companies and customers. A better yield signifies greater rates of interest, whereas a decrease yield suggests decrease rates of interest.
Elements of the 52-Week T-Invoice Yield Chart
A typical 52-week T-bill yield chart shows the yield over time, often plotted towards a date axis. Key elements embrace:
- Yield (Y-axis): This axis represents the annualized yield proportion. The size sometimes ranges from 0% to a stage reflecting the historic highs and lows.
- Time (X-axis): This axis shows the time interval, often in days, weeks, months, or years, relying on the chart’s scope. It usually covers a number of years for instance long-term traits.
- Information Factors: These signify the precise 52-week T-bill yield on particular dates. They’re linked by a line to indicate the pattern.
- Development Strains: Charts usually embrace pattern strains to spotlight the general path of the yield (upward, downward, or sideways). These will be easy transferring averages or extra refined regression strains.
- Key Occasions: Some charts may embrace annotations highlighting important financial occasions (e.g., recessions, financial coverage adjustments, main geopolitical occasions) that will have influenced the yield.
Decoding the 52-Week T-Invoice Yield Chart
Decoding the chart requires understanding the connection between the yield and numerous financial elements.
-
Rising Yields: An upward pattern within the yield means that buyers demand greater returns for lending their cash to the federal government. This may be pushed by a number of elements:
- Inflationary pressures: Larger inflation erodes the buying energy of cash, main buyers to demand greater yields to compensate for the loss.
- Financial progress expectations: Robust financial progress usually results in greater rates of interest as companies and customers borrow extra.
- Federal Reserve coverage: The Federal Reserve (the central financial institution of the U.S.) can affect rates of interest by way of financial coverage instruments like adjusting the federal funds price. A tightening financial coverage (elevating rates of interest) often pushes T-bill yields greater.
- Elevated threat aversion: Throughout instances of financial uncertainty or geopolitical instability, buyers may search the protection of T-bills, growing demand and pushing yields greater.
-
Falling Yields: A downward pattern within the yield signifies that buyers are prepared to simply accept decrease returns. This may be because of:
- Low inflation: Low inflation reduces the necessity for greater yields to compensate for buying energy loss.
- Sluggish financial progress or recession: Throughout recessions, companies and customers borrow much less, resulting in decrease demand for funds and decrease yields.
- Free financial coverage: The Federal Reserve can decrease rates of interest to stimulate financial exercise, pushing T-bill yields down.
- Decreased threat aversion: Intervals of financial stability can result in decrease demand for the protection of T-bills, lowering yields.
Implications and Makes use of of the Chart
The 52-week T-bill yield chart has a number of sensible implications:
- Funding Choices: Traders use the chart to gauge the attractiveness of T-bills relative to different investments. Larger yields make T-bills extra interesting, whereas decrease yields may encourage buyers to discover higher-yielding options, albeit with probably greater threat.
- Financial Coverage Evaluation: Economists and policymakers use the chart to evaluate the effectiveness of financial coverage. The chart can present how adjustments within the federal funds price translate into adjustments in T-bill yields.
- Financial Forecasting: The yield can function a number one indicator of financial exercise. Rising yields can sign future financial progress, whereas falling yields can recommend a slowdown or recession.
- Danger Evaluation: The chart can assist assess the extent of threat aversion available in the market. Excessive yields in periods of financial stability may recommend elevated threat aversion because of geopolitical elements or different unexpected occasions.
- Hedging Methods: Traders can use T-bills to hedge towards rate of interest threat. By holding T-bills, buyers can defend themselves from losses if rates of interest rise unexpectedly.
Limitations of the Chart
Whereas the 52-week T-bill yield chart is a beneficial software, it is important to acknowledge its limitations:
- Simplified Illustration: The chart presents a simplified view of a posh market. It does not seize the nuances of particular person transactions or the total spectrum of things influencing yields.
- Backward-Trying: The chart reveals historic information, which can not precisely predict future yields. Market circumstances can change quickly, rendering previous efficiency an unreliable indicator of future outcomes.
- Restricted Scope: The chart focuses solely on the 52-week T-bill yield, ignoring different related market indicators. A holistic understanding requires contemplating different elements, reminiscent of longer-term bond yields, inflation charges, and financial progress forecasts.
Conclusion
The 52-week Treasury invoice yield chart supplies a beneficial, albeit incomplete, image of the short-term rate of interest atmosphere. By understanding its elements, deciphering its traits, and acknowledging its limitations, buyers, economists, and policymakers can acquire beneficial insights into prevailing market circumstances and make knowledgeable selections. Nonetheless, it is essential to make use of this chart along with different financial indicators and knowledgeable evaluation to develop a complete understanding of the market panorama and make sound monetary selections. The chart is a software, not a crystal ball, and ought to be used judiciously as half of a bigger analytical framework.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied beneficial insights into Decoding the 52-Week Treasury Invoice Yield Chart: A Complete Information. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!