Decoding The Acidity: A Complete Information To The PH Of Fruits And Their Implications
By admin / October 12, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Decoding the Acidity: A Complete Information to the pH of Fruits and Their Implications
Associated Articles: Decoding the Acidity: A Complete Information to the pH of Fruits and Their Implications
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by means of the intriguing matter associated to Decoding the Acidity: A Complete Information to the pH of Fruits and Their Implications. Let’s weave fascinating info and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the Acidity: A Complete Information to the pH of Fruits and Their Implications

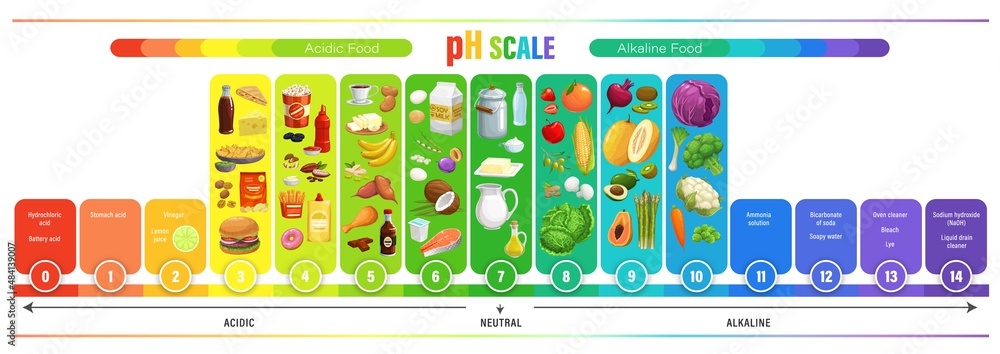
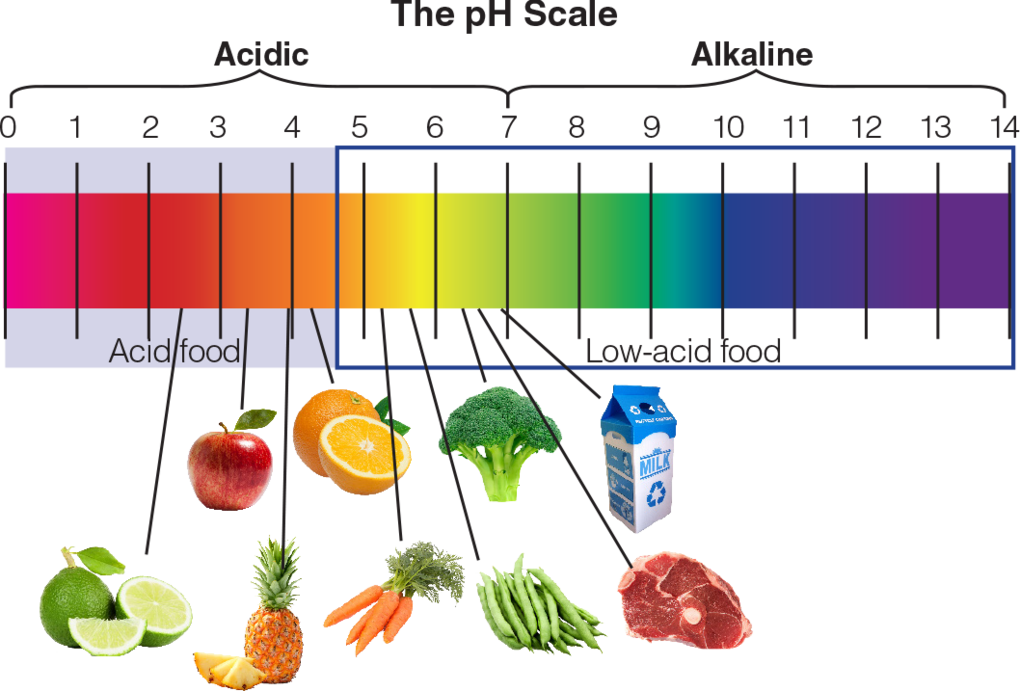
The pH scale, starting from 0 to 14, measures the acidity or alkalinity of a substance. A pH of seven is impartial, whereas values beneath 7 point out acidity and values above 7 point out alkalinity. Fruits, being naturally acidic, usually fall on the decrease finish of this scale. Understanding the pH of fruits is essential for numerous causes, starting from culinary purposes and preserving meals to understanding their affect on well being and even skincare. This text gives a complete chart of the pH of widespread fruits, explains the components influencing their pH ranges, and discusses the implications of those ranges in numerous contexts.
A Complete Chart of Fruit pH Ranges:
It is vital to preface this chart by stating that the pH of fruits can differ relying on a number of components, together with the number of fruit, its ripeness, rising situations, and even the tactic of measurement. The values introduced beneath are approximate averages and must be thought of as tips slightly than absolute figures.
| Fruit | pH Vary | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Apples | 3.0 – 4.0 | Varies vastly relying on selection and ripeness. |
| Apricots | 3.5 – 4.5 | Barely much less acidic than apples. |
| Bananas | 4.5 – 5.5 | Comparatively much less acidic in comparison with different fruits; ripens to larger pH. |
| Blackberries | 3.0 – 3.5 | Extremely acidic. |
| Blueberries | 3.0 – 4.0 | Extremely acidic. |
| Cantaloupe | 5.0 – 6.0 | Comparatively much less acidic; extra alkaline than most fruits. |
| Cherries | 3.5 – 4.5 | Acidity varies relying on selection. |
| Cranberries | 2.3 – 2.8 | Extraordinarily acidic; among the many most acidic fruits. |
| Grapes | 3.0 – 4.5 | Varies extensively relying on selection and ripeness. |
| Grapefruit | 2.8 – 3.3 | Extremely acidic. |
| Guava | 3.0 – 4.0 | Reasonably acidic. |
| Kiwi | 3.1 – 3.5 | Reasonably acidic. |
| Lemons | 2.0 – 2.6 | Extraordinarily acidic; among the many most acidic fruits. |
| Limes | 1.8 – 2.0 | Extraordinarily acidic; one of the vital acidic fruits. |
| Mangoes | 4.0 – 5.0 | Reasonably acidic. |
| Nectarines | 3.5 – 4.5 | Related acidity to peaches. |
| Oranges | 3.3 – 4.2 | Reasonably acidic. |
| Peaches | 3.5 – 4.5 | Reasonably acidic. |
| Pears | 3.5 – 4.5 | Reasonably acidic. |
| Pineapple | 3.2 – 4.0 | Reasonably acidic; accommodates bromelain, a proteolytic enzyme. |
| Plums | 2.8 – 4.0 | Acidity varies relying on selection. |
| Pomegranates | 2.8 – 4.0 | Acidity varies relying on ripeness and selection. |
| Raspberries | 3.0 – 3.5 | Extremely acidic. |
| Strawberries | 3.0 – 4.0 | Reasonably acidic. |
| Watermelon | 5.0 – 6.0 | Comparatively much less acidic; extra alkaline than most fruits. |
Elements Influencing Fruit pH:
A number of components contribute to the variability within the pH ranges of fruits:
- Selection: Totally different sorts of the identical fruit can exhibit important variations in acidity. For instance, Granny Smith apples are significantly extra acidic than Golden Scrumptious apples.
- Ripening: As fruits ripen, their pH usually will increase, turning into much less acidic. That is because of the breakdown of natural acids in the course of the ripening course of.
- Rising Circumstances: Environmental components equivalent to soil composition, daylight publicity, and rainfall can affect the acidity of fruits.
- Cultivation Practices: Fertilization and irrigation methods can affect the pH of the fruit.
- Put up-Harvest Dealing with: Storage situations and processing strategies may have an effect on the pH of fruits.
Implications of Fruit pH:
The pH of fruits has a number of vital implications:
- Culinary Purposes: Understanding the pH of fruits is essential for baking, preserving, and creating balanced flavors in dishes. Extremely acidic fruits are sometimes utilized in jams and jellies, whereas much less acidic fruits are higher suited to sure desserts.
- Meals Preservation: Acidity performs a significant position in preserving fruits. Excessive acidity inhibits the expansion of microorganisms, extending the shelf lifetime of jams, jellies, and different preserved meals.
- Well being Implications: The acidity of fruits can have an effect on their affect on the physique. Whereas some individuals profit from the antioxidants and different vitamins in acidic fruits, others might expertise digestive discomfort on account of excessive acidity. People with acid reflux disease or different digestive points might have to restrict their consumption of extremely acidic fruits.
- Skincare: Some fruits with excessive acidity are utilized in skincare merchandise on account of their exfoliating and brightening properties. Nonetheless, it is essential to make use of these merchandise cautiously, as excessive acidity can irritate delicate pores and skin.
- Tooth Enamel: Extremely acidic fruits can erode tooth enamel over time. Rinsing the mouth with water after consuming acidic fruits may also help mitigate this impact.
Using pH Information in On a regular basis Life:
The data of fruit pH will be utilized in numerous elements of each day life:
- Cooking: When making jams or jellies, utilizing a pH meter or check strips can guarantee the right acidity degree for optimum preservation.
- Baking: The acidity of fruits can have an effect on the feel and taste of baked items. Understanding this may also help in adjusting recipes for optimum outcomes.
- Dietary Selections: People with digestive sensitivities can use the pH chart to make knowledgeable decisions about fruit consumption, choosing much less acidic choices if needed.
- Gardening: Monitoring the pH of the soil may also help optimize rising situations for fruit timber and crops.
Conclusion:
The pH of fruits is a multifaceted attribute with important implications throughout numerous domains. Whereas the offered chart presents a common overview, it is essential to keep in mind that the precise pH can differ significantly. Understanding the components that affect fruit pH and its implications in culinary practices, well being, and skincare permits for knowledgeable decision-making and higher appreciation of those naturally various and nutritious meals. Additional analysis and detailed evaluation, probably utilizing pH meters and particular testing strategies, can present much more exact knowledge for particular fruit varieties and rising situations, additional enhancing our understanding of this significant facet of fruit composition. This data empowers us to make the most of fruits successfully and safely in our each day lives, from the kitchen to the backyard and even our skincare routines.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered invaluable insights into Decoding the Acidity: A Complete Information to the pH of Fruits and Their Implications. We hope you discover this text informative and useful. See you in our subsequent article!