Decoding The Cloth Of Success: Understanding Organizational Charts In The Textile Business
By admin / October 15, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Decoding the Cloth of Success: Understanding Organizational Charts within the Textile Business
Associated Articles: Decoding the Cloth of Success: Understanding Organizational Charts within the Textile Business
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we’ll discover the intriguing subject associated to Decoding the Cloth of Success: Understanding Organizational Charts within the Textile Business. Let’s weave fascinating info and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the Cloth of Success: Understanding Organizational Charts within the Textile Business

The textile business, a worldwide behemoth encompassing fiber manufacturing, yarn manufacturing, weaving and knitting, dyeing and ending, and attire manufacturing, requires intricate organizational constructions to handle its complicated processes and huge provide chains. Understanding the organizational chart of a textile firm, no matter its dimension or specialization, is essential to comprehending its operational effectivity, strategic course, and general success. This text delves into the varied organizational constructions generally employed throughout the textile business, exploring their strengths, weaknesses, and the roles and obligations related to key positions.
I. Widespread Organizational Buildings within the Textile Business:
The selection of organizational construction relies upon closely on components like firm dimension, product range, geographical attain, and strategic aims. A number of widespread constructions are prevalent:
A. Purposeful Construction:
This conventional construction organizes departments based mostly on specialised features like manufacturing, advertising, finance, human sources, and analysis & improvement. Every division operates independently, reporting to a senior supervisor or vice chairman.
- Benefits: Clear strains of authority, specialization results in experience, environment friendly useful resource allocation inside departments.
- Disadvantages: Siloed communication, sluggish decision-making, lack of cross-functional collaboration, problem adapting to alter. Within the textile business, this may result in bottlenecks between departments (e.g., manufacturing delays impacting advertising timelines).
B. Divisional Construction:
This construction teams actions based mostly on product strains, geographical areas, or buyer segments. Every division operates as a semi-autonomous unit with its personal practical departments.
- Benefits: Elevated responsiveness to market calls for, higher accountability for efficiency, fosters innovation inside divisions.
- Disadvantages: Duplication of sources throughout divisions, potential for conflicting objectives, challenges in coordinating actions throughout divisions. In a textile firm with various product strains (e.g., attire, house textiles, industrial materials), this construction permits for specialised administration of every.
C. Matrix Construction:
This construction combines parts of practical and divisional constructions, making a twin reporting system. Workers report back to each a practical supervisor (e.g., manufacturing supervisor) and a undertaking or product supervisor.
- Benefits: Improved communication and collaboration, environment friendly useful resource utilization, flexibility in responding to altering calls for.
- Disadvantages: Complicated reporting construction, potential for conflicting directions, requires robust communication and coordination expertise. This construction is useful in tasks requiring cross-functional collaboration, like growing a brand new textile expertise.
D. Community Construction:
This construction depends on outsourcing and strategic partnerships to carry out numerous features. The core firm focuses on core competencies whereas contracting out different duties to exterior suppliers.
- Benefits: Flexibility, diminished overhead prices, entry to specialised experience.
- Disadvantages: Lack of management over sure processes, dependence on exterior companions, potential for communication and coordination challenges. That is turning into more and more widespread within the textile business, significantly for smaller corporations specializing in design and branding.
E. Hybrid Buildings:
Many textile corporations make the most of hybrid constructions, combining parts of various organizational fashions to leverage their strengths whereas mitigating their weaknesses. For example, a big multinational textile firm may make use of a divisional construction geographically, with every regional division using a practical construction internally.
II. Key Roles and Obligations inside a Textile Firm’s Organizational Chart:
The particular roles and obligations differ based mostly on the corporate’s construction and dimension, however some widespread positions embody:
A. Prime Administration:
- Chief Government Officer (CEO): General strategic course, efficiency, and progress.
- Chief Working Officer (COO): Oversees each day operations, manufacturing, and provide chain administration.
- Chief Monetary Officer (CFO): Monetary planning, budgeting, and reporting.
- Chief Advertising Officer (CMO): Branding, product improvement, gross sales, and advertising methods.
B. Center Administration:
- Plant Supervisor/Manufacturing Supervisor: Oversees manufacturing processes, high quality management, and effectivity.
- Provide Chain Supervisor: Manages sourcing of uncooked supplies, logistics, and stock administration.
- Analysis & Improvement Supervisor: Develops new textile applied sciences, supplies, and processes.
- Human Sources Supervisor: Manages worker relations, recruitment, coaching, and compensation.
- Gross sales Supervisor: Manages gross sales groups, buyer relationships, and distribution channels.
- Advertising Supervisor: Develops advertising campaigns, promoting, and promotional methods.
C. Operational Stage:
- Manufacturing Supervisors/Foremen: Straight supervise manufacturing staff, guaranteeing high quality and effectivity.
- High quality Management Inspectors: Examine completed items to make sure they meet high quality requirements.
- Designers: Create textile designs and patterns.
- Technicians: Function and preserve equipment and tools.
- Gross sales Representatives: Work together instantly with clients, taking orders and managing accounts.
III. The Impression of Know-how and Globalization:
The textile business is present process a major transformation pushed by technological developments and globalization. These components are impacting organizational constructions in a number of methods:
- Automation and Robotics: Elevated automation is decreasing the necessity for giant numbers of guide laborers, resulting in flatter organizational constructions and a larger emphasis on expert technicians and engineers.
- Provide Chain Administration Software program: Refined software program is bettering provide chain visibility and effectivity, permitting corporations to optimize their operations and cut back prices.
- E-commerce and Digital Advertising: The expansion of e-commerce is remodeling advertising and gross sales methods, requiring corporations to adapt their organizational constructions to accommodate on-line channels.
- Globalization and Outsourcing: Corporations are more and more outsourcing manufacturing and different features to international locations with decrease labor prices, resulting in extra complicated and geographically dispersed organizational constructions.
IV. Future Traits:
The way forward for organizational charts within the textile business will probably be formed by:
- Agile methodologies: Adopting agile rules to boost flexibility and responsiveness to market adjustments.
- Information analytics and AI: Using information analytics and synthetic intelligence to optimize decision-making and enhance effectivity.
- Sustainability and moral sourcing: Integrating sustainability and moral issues into organizational constructions and decision-making processes.
- Elevated collaboration and data sharing: Breaking down silos and fostering larger collaboration between departments and throughout the availability chain.
Conclusion:
The organizational chart of a textile firm is a dynamic reflection of its strategic objectives, operational capabilities, and the exterior surroundings. Understanding these constructions, the roles inside them, and the affect of technological and world forces is essential for anybody concerned on this complicated and ever-evolving business. The profitable textile firm of the longer term will likely be one that may adapt its organizational construction to leverage expertise, embrace sustainability, and foster a tradition of collaboration and innovation. By fastidiously contemplating these components, textile corporations can weave collectively a profitable and resilient organizational material for years to come back.





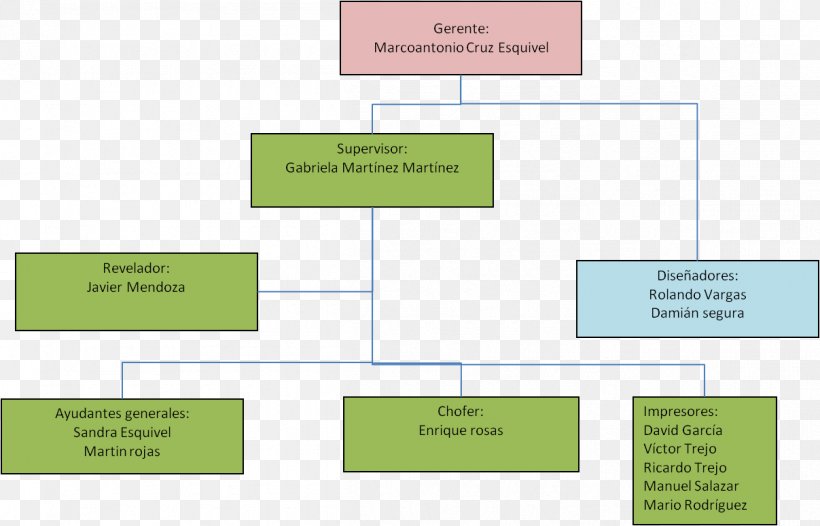

Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered worthwhile insights into Decoding the Cloth of Success: Understanding Organizational Charts within the Textile Business. We hope you discover this text informative and helpful. See you in our subsequent article!