Decoding The R-410A AC Strain Chart: A Complete Information
By admin / July 25, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Decoding the R-410A AC Strain Chart: A Complete Information
Associated Articles: Decoding the R-410A AC Strain Chart: A Complete Information
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing subject associated to Decoding the R-410A AC Strain Chart: A Complete Information. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the R-410A AC Strain Chart: A Complete Information

Refrigerant R-410A has change into the business customary for residential and lightweight industrial air-con techniques, changing the ozone-depleting R-22. Understanding its pressure-temperature relationship is essential for technicians performing diagnostics, repairs, and installations. This text delves into the intricacies of the R-410A stress chart, explaining its use, limitations, and methods to interpret its information successfully for optimum system efficiency and effectivity.
Understanding the Strain-Temperature Relationship in Refrigeration Cycles
Earlier than diving into the specifics of the R-410A chart, it is vital to know the basic precept behind it: the connection between stress and temperature in a refrigerant’s thermodynamic cycle. Refrigerants, like R-410A, bear a steady cycle of section modifications (liquid to vapor and vice versa) as they take up and launch warmth. These section modifications happen at particular pressures and temperatures, and this relationship is exactly what the pressure-temperature chart illustrates.
The chart shows two key stress traces:
- Excessive-Facet Strain: This represents the stress throughout the high-pressure aspect of the refrigeration cycle, encompassing the condenser and liquid line. Excessive-side stress is mostly greater than atmospheric stress.
- Low-Facet Strain: This represents the stress throughout the low-pressure aspect, encompassing the evaporator and suction line. Low-side stress is often decrease than atmospheric stress.
The pressures on either side are instantly influenced by the temperature of the refrigerant at every level within the cycle. Increased temperatures correspond to greater pressures, and decrease temperatures correspond to decrease pressures. This relationship isn’t linear however follows a posh thermodynamic curve, precisely depicted within the R-410A stress chart.
Studying and Deciphering the R-410A Strain Chart
The R-410A stress chart is often introduced as a graph with temperature on the horizontal axis (normally in levels Fahrenheit or Celsius) and stress on the vertical axis (normally in kilos per sq. inch (PSI) or kilopascals (kPa)). Two distinct curves are normally proven: one for saturated liquid stress and one for saturated vapor stress.
- Saturated Liquid Line: This line represents the stress at which the refrigerant exists solely as a liquid at a given temperature. Any stress under this line signifies the presence of vapor throughout the liquid.
- Saturated Vapor Line: This line represents the stress at which the refrigerant exists solely as a vapor at a given temperature. Any stress above this line signifies the presence of liquid throughout the vapor.
The world between these two traces represents a two-phase area the place each liquid and vapor coexist. The exact proportion of liquid and vapor relies on the particular stress and temperature inside this area.
Utilizing the Chart for Diagnostics
The R-410A stress chart is a useful device for diagnosing issues in air-con techniques. By measuring the high-side and low-side pressures and evaluating them to the chart’s values on the corresponding suction and discharge temperatures, technicians can establish potential points:
- Low Low-Facet Strain: This might point out a refrigerant leak, restricted airflow over the evaporator coil, a defective compressor, or a malfunctioning growth system.
- Excessive Low-Facet Strain: This may counsel a restricted refrigerant movement within the suction line, a defective growth system, or an overcharged system.
- Low Excessive-Facet Strain: This might level to a refrigerant leak, inadequate airflow over the condenser coil, a defective compressor, or a restricted liquid line.
- Excessive Excessive-Facet Strain: This might point out a restricted refrigerant movement within the liquid line, a defective condenser fan, a clogged filter drier, or an overcharged system.
Components Affecting Strain Readings
It is essential to grasp that a number of elements can affect the precise stress readings past the straightforward temperature-pressure relationship illustrated on the chart:
- Ambient Temperature: The ambient temperature considerably impacts condenser stress. Increased ambient temperatures result in greater condenser pressures.
- Airflow: Inadequate airflow over the evaporator and condenser coils can drastically have an effect on stress readings. Restricted airflow will increase stress on the affected aspect.
- Refrigerant Cost: An overcharged or undercharged system will deviate from the chart’s predicted pressures.
- Elevation: Altitude impacts the boiling level of the refrigerant, influencing stress readings. Increased altitudes lead to decrease pressures.
- System Elements: Blockages, leaks, or malfunctions in any element of the refrigeration cycle can distort the stress readings.
Limitations of the Strain Chart
Whereas the R-410A stress chart is a strong diagnostic device, it is important to acknowledge its limitations:
- It is a simplified illustration: The chart solely considers the saturated liquid and saturated vapor states. It would not account for superheated vapor or subcooled liquid, that are widespread situations in real-world techniques.
- It would not diagnose all issues: Whereas stress readings present priceless clues, they do not pinpoint the precise trigger of each malfunction. Additional diagnostics are sometimes vital.
- Accuracy relies on correct measurements: Inaccurate temperature or stress readings will result in misinterpretations of the chart. Correct calibration of gauges is essential.
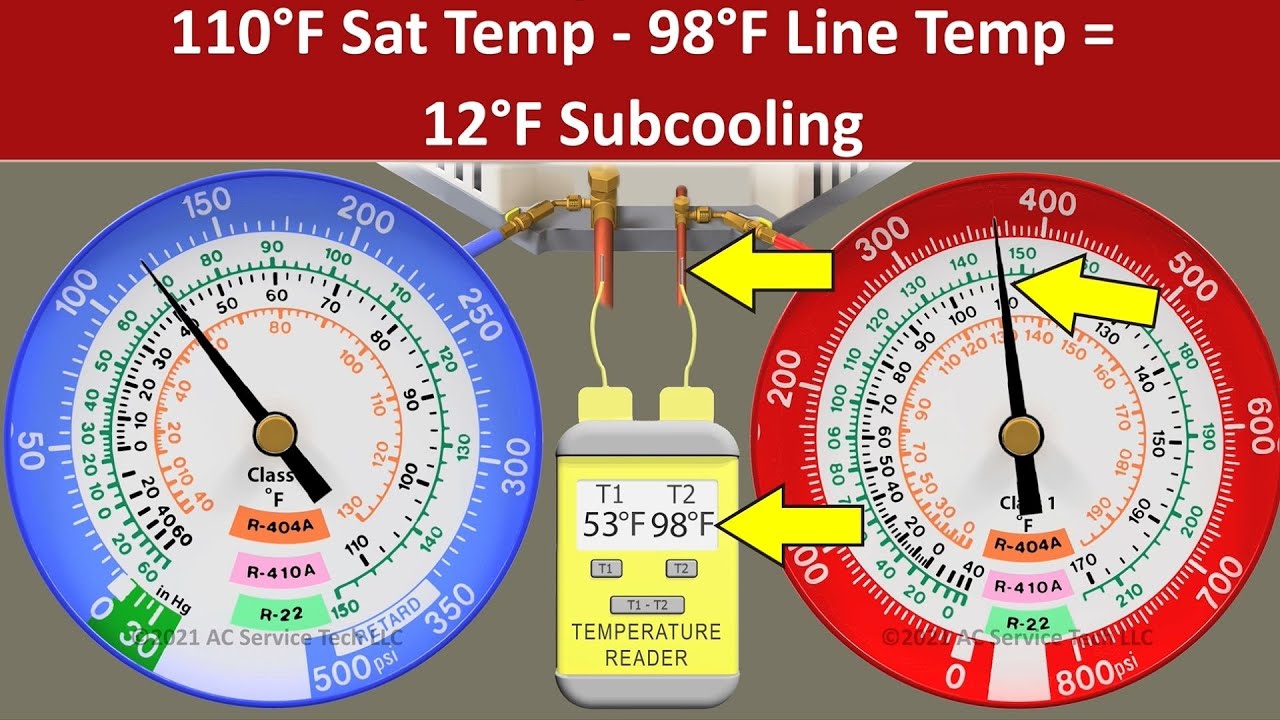
Past the Chart: Superheat and Subcooling
To achieve a extra complete understanding of the system’s efficiency, technicians want to contemplate superheat and subcooling:
- Superheat: That is the temperature distinction between the refrigerant’s precise temperature on the evaporator outlet and its saturation temperature on the corresponding stress. Correct superheat ensures full vaporization of the refrigerant earlier than it enters the compressor.
- Subcooling: That is the temperature distinction between the refrigerant’s precise temperature on the condenser outlet and its saturation temperature on the corresponding stress. Correct subcooling ensures the refrigerant is solely liquid earlier than coming into the growth system.
Measuring superheat and subcooling, at the side of stress readings from the chart, offers a extra correct evaluation of the system’s well being and effectivity.
Conclusion
The R-410A stress chart is a elementary device for HVAC technicians. By understanding the ideas behind the pressure-temperature relationship, precisely studying the chart, and contemplating elements influencing stress readings, technicians can successfully diagnose and resolve points in air-con techniques utilizing R-410A refrigerant. Nevertheless, it is essential to do not forget that the chart is just one piece of the diagnostic puzzle, and different measurements and assessments are sometimes required for a whole and correct prognosis. Steady studying and sensible expertise are important for mastering using the R-410A stress chart and making certain optimum efficiency of air-con techniques. All the time adhere to security precautions and seek the advice of related producer specs when working with refrigerants and HVAC gear.
![Free Printable 410A PT Chart Templates [PDF] High Altitude, 59% OFF](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/51dFJv3zBbL._AC_UF894,1000_QL80_.jpg)






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered priceless insights into Decoding the R-410A AC Strain Chart: A Complete Information. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!