Decoding The Refrigerant R-410A Charging Chart: A Complete Information
By admin / June 20, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Decoding the Refrigerant R-410A Charging Chart: A Complete Information
Associated Articles: Decoding the Refrigerant R-410A Charging Chart: A Complete Information
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we are going to discover the intriguing subject associated to Decoding the Refrigerant R-410A Charging Chart: A Complete Information. Let’s weave fascinating data and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the Refrigerant R-410A Charging Chart: A Complete Information

Refrigerant R-410A, a zeotropic mix of difluoromethane (R-32) and pentafluoroethane (R-125), has grow to be a ubiquitous refrigerant in air-con and refrigeration methods, significantly in residential and light-weight business purposes. Its larger effectivity in comparison with its predecessor, R-22, and higher environmental profile (although not with out its drawbacks) have led to its widespread adoption. Nonetheless, precisely charging an R-410A system is essential for optimum efficiency and longevity. This necessitates a deep understanding of the refrigerant charging chart and the elements influencing its utility.
This text delves into the intricacies of R-410A charging charts, explaining their objective, decoding their knowledge, and highlighting the essential concerns for correct and protected refrigerant charging. We may also focus on the restrictions of charts and the significance of supplementary instruments and methods.
Understanding the Function of an R-410A Charging Chart
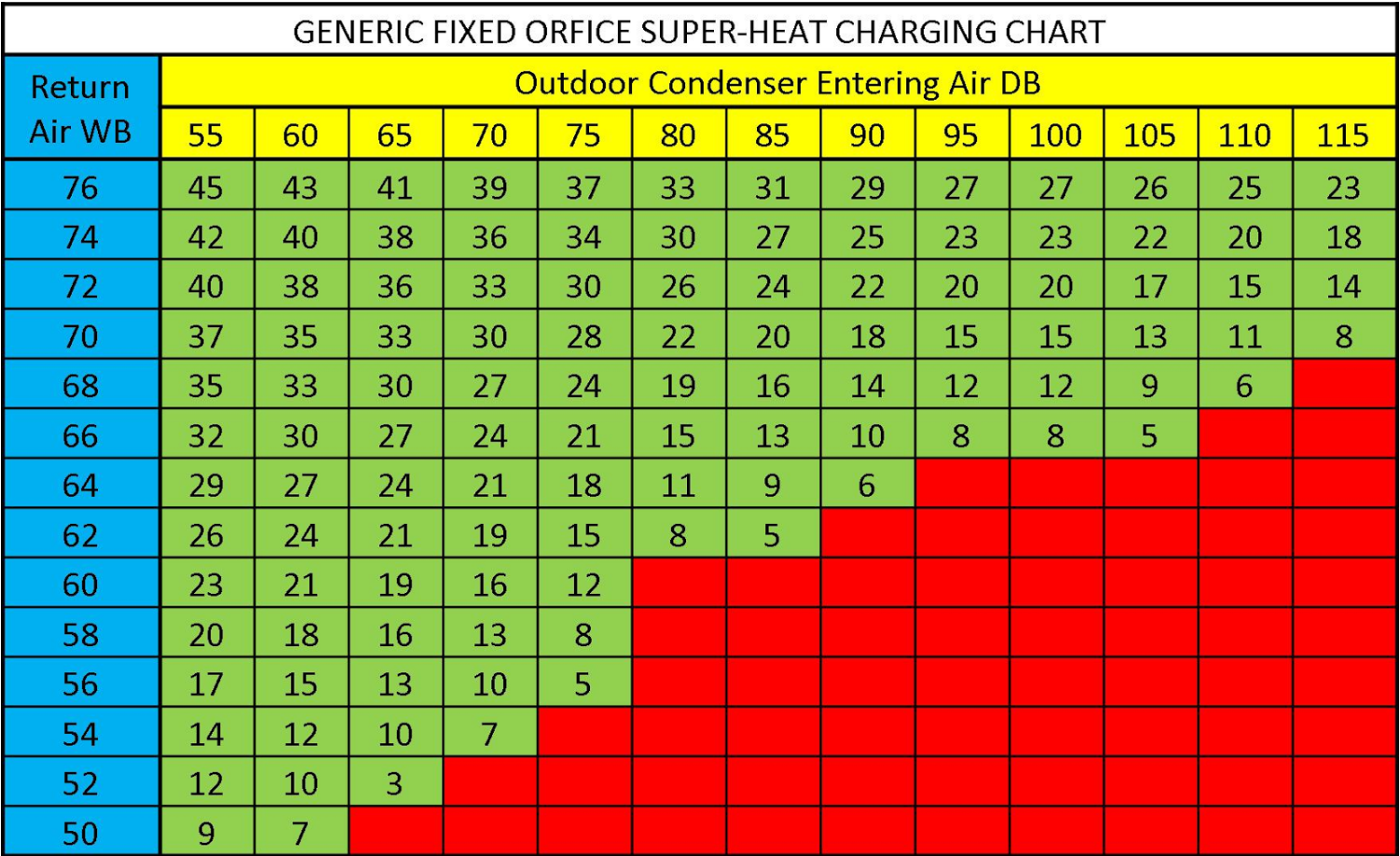
An R-410A charging chart serves as a vital information for figuring out the correct quantity of refrigerant wanted for a selected air-con or refrigeration system. In contrast to single-component refrigerants, zeotropic blends like R-410A have various compositions relying on strain and temperature. Which means merely weighing the refrigerant is not ample for correct charging. The chart accounts for these variations, offering the required refrigerant cost primarily based on a number of key parameters:
- System Capability (BTU/hr or kW): The cooling capability of the system dictates the required refrigerant mass. Bigger methods naturally require extra refrigerant.
- Evaporating Temperature: That is the temperature at which the refrigerant absorbs warmth from the house being cooled. It is often measured on the evaporator outlet.
- Condensing Temperature: That is the temperature at which the refrigerant releases warmth to the ambient atmosphere. It is usually measured on the condenser outlet.
- Superheat and Subcooling: These are essential parameters that point out the effectivity and security of the system. Superheat measures the temperature of the refrigerant vapor after it has utterly vaporized, whereas subcooling measures the temperature of the liquid refrigerant after it has utterly condensed. Optimum superheat and subcooling values are important for environment friendly operation and stop compressor injury.
Deciphering the R-410A Charging Chart
R-410A charging charts are usually offered as tables or graphs. They current the refrigerant cost (often in ounces or kilograms) as a perform of the parameters talked about above. To make use of the chart successfully:
-
Determine the System’s Capability: Decide the cooling capability of the air-con or refrigeration system in BTU/hr or kW. This data is often discovered on the system’s nameplate.
-
Measure Evaporating and Condensing Temperatures: Use appropriately calibrated thermometers or temperature sensors to measure the evaporating and condensing temperatures below regular working situations. These measurements ought to be taken after the system has run for a ample interval to succeed in secure working temperatures.
-
Decide Superheat and Subcooling: Correct superheat and subcooling measurements are essential. These are usually measured utilizing a manifold gauge set geared up with temperature sensors. The specified superheat and subcooling values will fluctuate relying on the precise system and producer’s suggestions, however typically fall inside a selected vary (e.g., 10-12°F superheat and 5-10°F subcooling).
-
Find the Right Cost on the Chart: Utilizing the system capability, evaporating temperature, condensing temperature, superheat, and subcooling values, find the corresponding refrigerant cost on the chart. Interpolation could also be mandatory if the precise values aren’t straight listed.
-
Cost the System: Fastidiously add or take away refrigerant as wanted to attain the goal cost indicated on the chart. At all times observe the producer’s directions and security precautions.
Elements Influencing Refrigerant Cost
A number of elements can affect the required refrigerant cost, even for methods with the identical capability:
- Line Set Size: Longer refrigerant strains require a bigger cost to compensate for the elevated refrigerant quantity inside the strains.
- Line Set Diameter: Thinner strains require a barely larger cost as a result of elevated frictional strain drop.
- Elevation: Increased altitudes require a barely decrease refrigerant cost as a result of decrease ambient pressures.
- Ambient Temperature: Excessive ambient temperatures can affect the working pressures and, consequently, the required cost.
- System Element Variations: Slight variations in element manufacturing can impression the optimum cost.
Limitations of R-410A Charging Charts
Whereas charging charts are invaluable instruments, they’ve limitations:
- Approximations: Charts present approximate values. They do not account for all doable variations in system elements and working situations.
- Assumptions: Charts usually make assumptions about splendid system situations, which can not at all times be met in real-world eventualities.
- Lack of Dynamic Knowledge: Charts usually present static values, not contemplating dynamic adjustments in working situations.
- Inaccurate Measurements: Inaccurate measurements of temperature and strain can result in incorrect refrigerant costs.
Past the Chart: Supplementary Instruments and Strategies
To beat the restrictions of charging charts, technicians usually make the most of supplementary instruments and methods:
- Digital Refrigerant Scales: These scales present correct refrigerant weighing, making certain exact cost quantities.
- Manifold Gauge Units with Temperature Sensors: These instruments enable for exact measurement of superheat and subcooling, essential for optimum system efficiency.
- Subcooling and Superheat Calculators: These calculators can help in figuring out the optimum refrigerant cost primarily based on varied system parameters.
- System Efficiency Evaluation: Analyzing the system’s efficiency (e.g., cooling capability, strain drops, temperature variations) might help fine-tune the refrigerant cost.
- Producer’s Suggestions: At all times seek the advice of the producer’s particular directions and proposals for the actual system being charged.
Security Precautions
Working with refrigerants requires strict adherence to security procedures:
- Correct Air flow: Guarantee ample air flow to forestall the buildup of refrigerant vapor.
- Private Protecting Tools (PPE): Put on applicable PPE, together with security glasses, gloves, and respiratory safety.
- Leak Detection: Use applicable leak detection tools to determine and restore any leaks earlier than charging the system.
- Restoration and Recycling: At all times get better and recycle refrigerant from previous methods to attenuate environmental impression.
- Coaching and Certification: Correct coaching and certification are important for dealing with refrigerants safely and successfully.
Conclusion
R-410A charging charts are important instruments for technicians working with air-con and refrigeration methods. Nonetheless, they need to be used together with different instruments and methods, together with correct measurements, supplementary calculations, and a radical understanding of system dynamics. Prioritizing security and adhering to producer’s suggestions are paramount to make sure environment friendly, dependable, and environmentally accountable system operation. Do not forget that correct refrigerant charging isn’t just about attaining the proper weight; it is about optimizing system efficiency, maximizing effectivity, and prolonging the lifespan of the tools. Improper charging can result in decreased effectivity, compressor injury, and untimely system failure. Subsequently, a complete understanding of R-410A charging charts and their utility is essential for any HVAC/R technician.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered priceless insights into Decoding the Refrigerant R-410A Charging Chart: A Complete Information. We admire your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!