Decoding The Spectrum: A Complete Information To Autism Spectrum Chart Checks And Their Limitations
By admin / June 21, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Decoding the Spectrum: A Complete Information to Autism Spectrum Chart Checks and Their Limitations
Associated Articles: Decoding the Spectrum: A Complete Information to Autism Spectrum Chart Checks and Their Limitations
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to Decoding the Spectrum: A Complete Information to Autism Spectrum Chart Checks and Their Limitations. Let’s weave fascinating info and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the Spectrum: A Complete Information to Autism Spectrum Chart Checks and Their Limitations
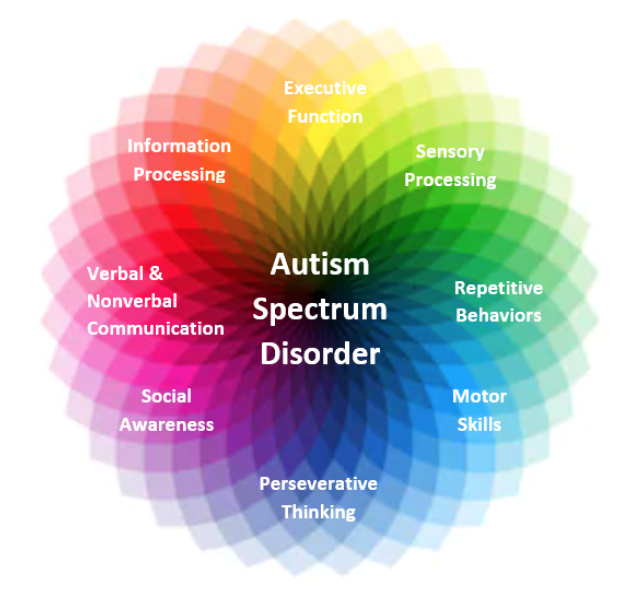
Autism spectrum dysfunction (ASD) is a fancy neurodevelopmental situation characterised by persistent challenges in social communication and interplay, and restricted, repetitive patterns of conduct, pursuits, or actions. Diagnosing ASD is a multifaceted course of, usually involving a mix of observational assessments, standardized assessments, and scientific interviews. Whereas no single check definitively diagnoses ASD, varied "chart assessments" – a colloquial time period encompassing varied screening instruments and diagnostic assessments – play an important position within the analysis course of. This text explores the panorama of those assessments, their strengths and weaknesses, and the essential significance of a holistic diagnostic strategy.
The Panorama of Autism Spectrum Chart Checks:
The time period "chart check" isn’t a proper scientific time period however moderately a basic descriptor for varied evaluation instruments used within the analysis of ASD. These instruments differ significantly of their format, objective, and the age vary they aim. They’ll broadly be categorized into:
-
Screening Instruments: These are transient questionnaires or checklists designed to establish people who might require additional analysis for ASD. They don’t seem to be diagnostic in themselves however function a primary step within the course of, flagging people who warrant a extra complete evaluation. Examples embody the Modified Guidelines for Autism in Toddlers (M-CHAT), the Social Communication Questionnaire (SCQ), and the Autism Spectrum Screening Questionnaire (ASSQ). These usually make the most of a scoring system, resulting in a "chart" of outcomes that helps clinicians decide the subsequent steps.
-
Diagnostic Assessments: These are extra complete and in-depth evaluations designed to offer a proper analysis of ASD. They usually contain a number of elements, together with standardized assessments assessing cognitive talents, adaptive functioning, language expertise, and social interplay. Examples embody the Autism Diagnostic Commentary Schedule (ADOS) and the Autism Diagnostic Interview-Revised (ADI-R). These assessments usually end in an in depth profile of the person’s strengths and weaknesses, which could possibly be represented in a summarized chart format for simpler interpretation.
-
Particular Ability Assessments: These goal explicit areas of concern associated to ASD, akin to language improvement (e.g., the Scientific Analysis of Language Fundamentals – CELF), motor expertise, or adaptive conduct (e.g., Vineland Adaptive Habits Scales). The outcomes of those assessments are sometimes offered in chart or graph type to visualise progress or deficits in particular talent areas.
Strengths and Limitations of Completely different Chart Checks:
Every sort of evaluation carries its personal set of benefits and drawbacks:
Screening Instruments:
- Strengths: Simple to manage, comparatively cheap, and can be utilized to display screen giant populations effectively. They may help establish people who warrant additional, extra in-depth analysis.
- Limitations: Excessive charges of false positives and false negatives are widespread. A optimistic screening outcome doesn’t equate to a analysis, and a damaging outcome doesn’t rule out ASD. They don’t seem to be appropriate for making definitive diagnoses. Cultural biases can even affect the outcomes.
Diagnostic Assessments:
- Strengths: Extra complete and rigorous than screening instruments, offering a extra detailed image of the person’s presentation. They’re designed to fulfill the diagnostic standards for ASD outlined within the DSM-5 or ICD-11. They usually contain observational assessments, offering invaluable insights into conduct and social interplay.
- Limitations: Time-consuming and costly to manage. They require specialised coaching to manage and interpret precisely. The outcomes may be influenced by components just like the kid’s temper, cooperation, and the examiner’s experience. They might not totally seize the complexity of ASD, probably overlooking refined nuances.
Particular Ability Assessments:
- Strengths: Present detailed details about particular areas of power and weak spot, which may inform intervention planning. They permit for monitoring progress over time.
- Limitations: They give attention to particular person expertise moderately than the general diagnostic image. They might not be delicate to the distinctive traits of ASD.
The Significance of a Holistic Method:
It’s essential to emphasise that no single "chart check" can present a definitive analysis of ASD. A complete analysis ought to contain a multidisciplinary staff, together with psychologists, psychiatrists, developmental pediatricians, and different specialists as wanted. The diagnostic course of ought to incorporate:
- Developmental Historical past: An in depth assessment of the person’s developmental milestones, together with early childhood improvement, language acquisition, and social interplay.
- Behavioral Observations: Direct commentary of the person’s conduct in varied settings, together with dwelling, faculty, and scientific settings.
- Mum or dad/Caregiver Interviews: Gathering info from dad and mom and caregivers in regards to the particular person’s conduct, challenges, and strengths.
- Standardized Assessments: Utilizing a mix of screening instruments and diagnostic assessments to assemble goal knowledge.
- Medical Analysis: Ruling out different medical situations which will mimic ASD signs.
The knowledge gathered from these varied sources is built-in to create a complete image of the person’s strengths, weaknesses, and total functioning. A analysis of ASD relies on a scientific judgment, not merely a rating on a single check.
Deciphering the Outcomes:
Deciphering the outcomes of any autism spectrum chart check requires experience. A excessive rating on a screening software doesn’t mechanically imply a analysis; moderately, it signifies a necessity for additional analysis. Equally, a low rating doesn’t rule out ASD, as some people with ASD might not exhibit all of the attribute signs. The outcomes of diagnostic assessments ought to be interpreted within the context of the person’s total scientific presentation and developmental historical past.
Moral Concerns:
Using autism spectrum chart assessments raises a number of moral concerns:
- Accuracy and Validity: The accuracy and validity of various assessments differ, and it’s essential to make use of assessments which might be dependable and acceptable for the person’s age and developmental stage.
- Cultural Bias: Some assessments could also be culturally biased, resulting in inaccurate outcomes for people from various cultural backgrounds.
- Knowledgeable Consent: Knowledgeable consent ought to be obtained from dad and mom or guardians earlier than administering any assessments.
- Confidentiality: The outcomes of assessments ought to be saved confidential and shared solely with licensed people.
Conclusion:
Autism spectrum chart assessments are invaluable instruments within the evaluation of ASD, however they shouldn’t be utilized in isolation. A complete and holistic strategy, involving a number of evaluation strategies and a multidisciplinary staff, is important for correct analysis and efficient intervention planning. Understanding the strengths and limitations of every check, together with the moral concerns concerned, is essential for making certain accountable and efficient use of those instruments within the analysis and help of people with ASD. The main focus ought to all the time stay on the person’s distinctive wants and strengths, making certain a customized and supportive strategy to their care. Finally, the purpose isn’t just to label a person however to grasp their distinctive profile and supply the mandatory help to assist them thrive.





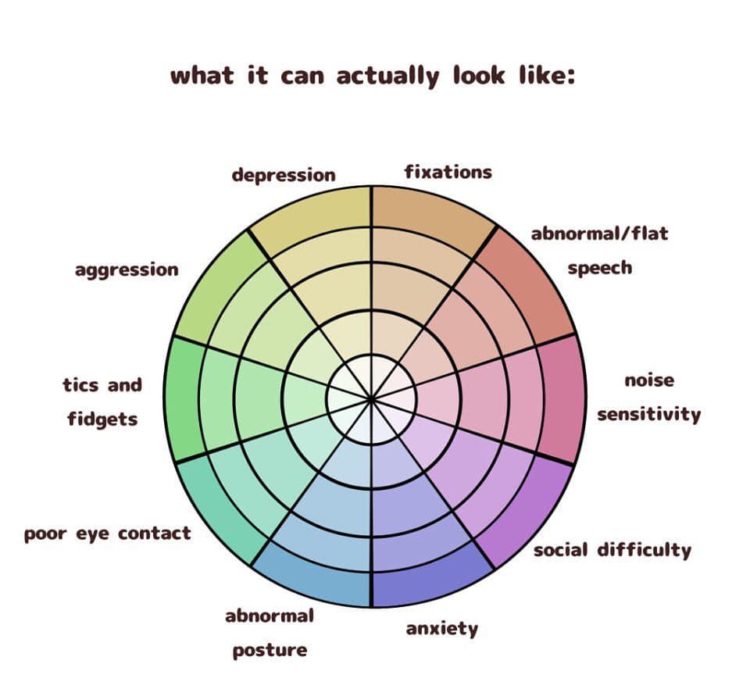
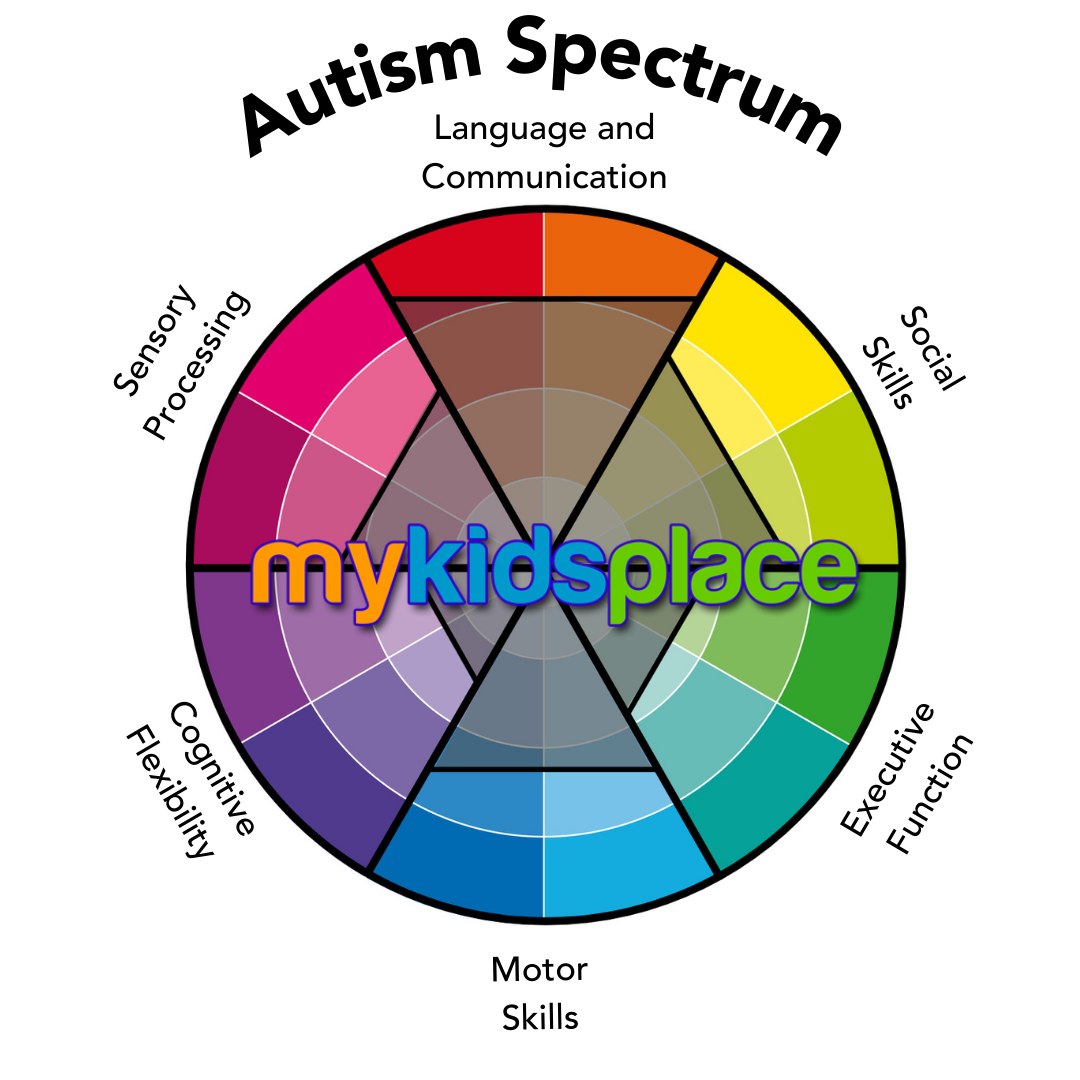
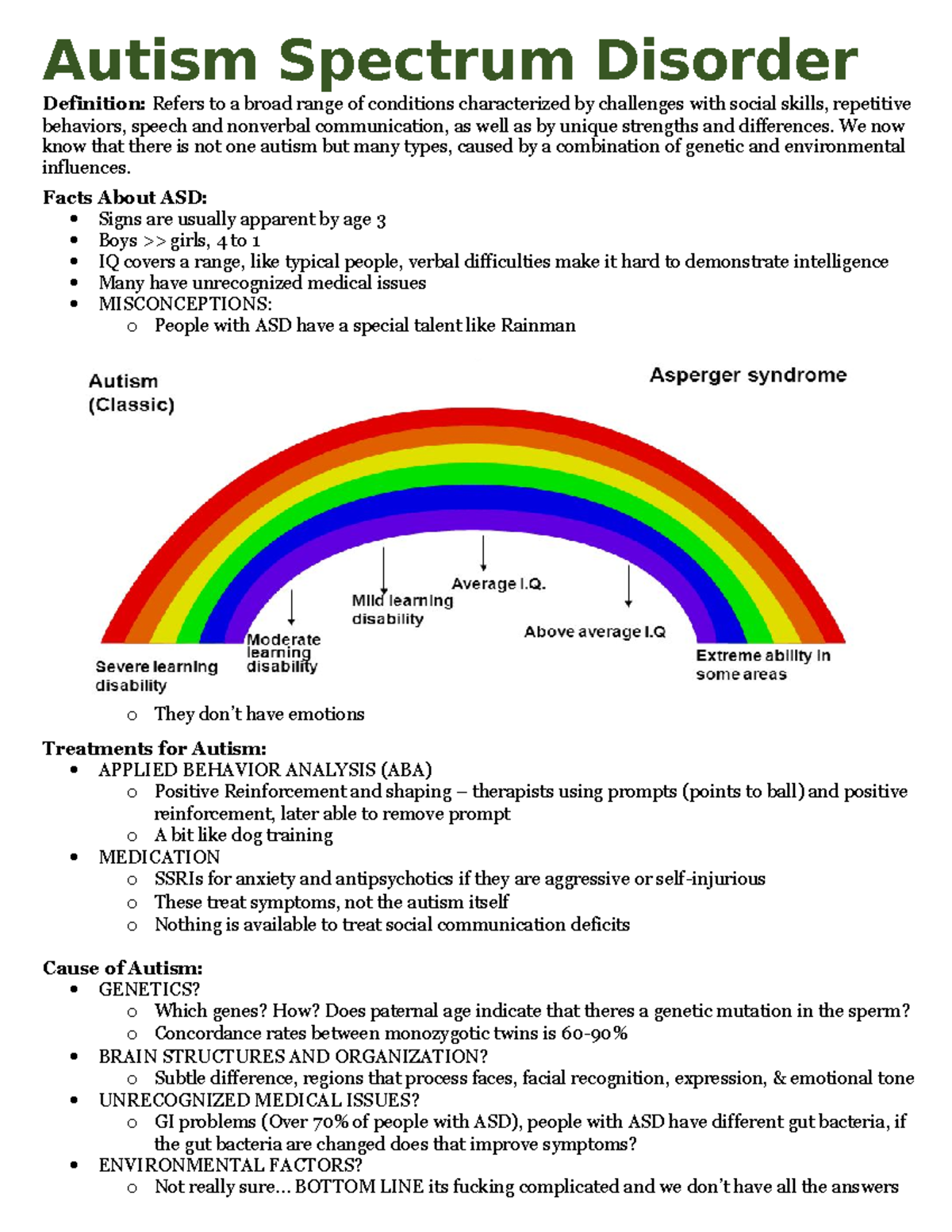
Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered invaluable insights into Decoding the Spectrum: A Complete Information to Autism Spectrum Chart Checks and Their Limitations. We admire your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!