Decoding The Two-Tailed Z-Desk: A Complete Information
By admin / September 26, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Decoding the Two-Tailed Z-Desk: A Complete Information
Associated Articles: Decoding the Two-Tailed Z-Desk: A Complete Information
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we’ll discover the intriguing subject associated to Decoding the Two-Tailed Z-Desk: A Complete Information. Let’s weave fascinating info and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the Two-Tailed Z-Desk: A Complete Information

The Z-table, also called the usual regular desk, is an important software in statistics for figuring out chances related to a normal regular distribution. This distribution, with a imply of 0 and a normal deviation of 1, serves as a basis for a lot of statistical checks and calculations. Whereas typically introduced in its one-tailed kind, understanding the two-tailed Z-table is crucial for a broader vary of functions, significantly in speculation testing involving two-tailed different hypotheses. This text will delve into the intricacies of the two-tailed Z-table, explaining its construction, interpretation, and sensible functions.
Understanding the Customary Regular Distribution and Z-scores
Earlier than diving into the two-tailed Z-table, it is essential to know the idea of the usual regular distribution and Z-scores. The usual regular distribution is a symmetrical bell-shaped curve, the place the imply lies on the middle (Z = 0). The realm below the curve represents likelihood. A Z-score represents the variety of customary deviations a selected knowledge level lies away from the imply. A optimistic Z-score signifies a worth above the imply, whereas a detrimental Z-score signifies a worth beneath the imply.
The Z-score is calculated utilizing the system:
Z = (X – μ) / σ
The place:
- X is the person knowledge level
- μ is the inhabitants imply
- σ is the inhabitants customary deviation
This transformation permits us to standardize any regular distribution into the usual regular distribution, enabling using the Z-table for likelihood calculations whatever the unique distribution’s imply and customary deviation.
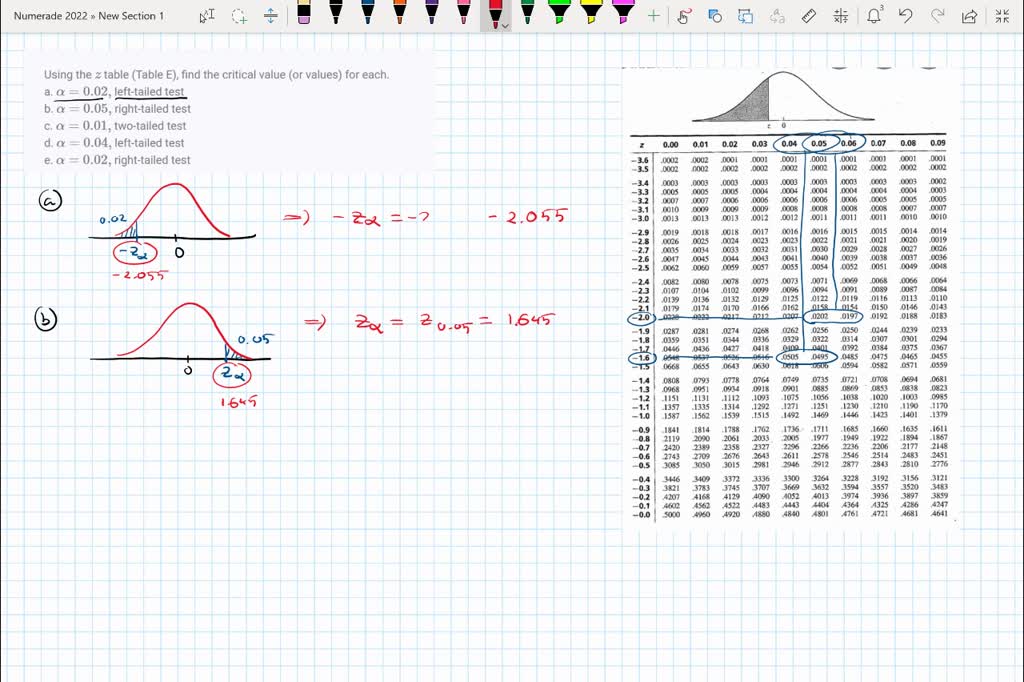
One-Tailed vs. Two-Tailed Exams: A Essential Distinction
The important thing distinction between one-tailed and two-tailed checks lies within the directionality of the speculation. A one-tailed take a look at focuses on whether or not a pattern imply is considerably better than (right-tailed) or lower than (left-tailed) a hypothesized inhabitants imply. A two-tailed take a look at, nevertheless, examines whether or not the pattern imply is considerably completely different from the hypothesized inhabitants imply, whatever the route.
This distinction considerably impacts how we interpret the Z-table. A one-tailed take a look at makes use of just one facet of the distribution to find out the likelihood, whereas a two-tailed take a look at considers each side. It is because a two-tailed take a look at accounts for the potential of the pattern imply being considerably larger or decrease than the hypothesized imply.
Decoding the Two-Tailed Z-Desk
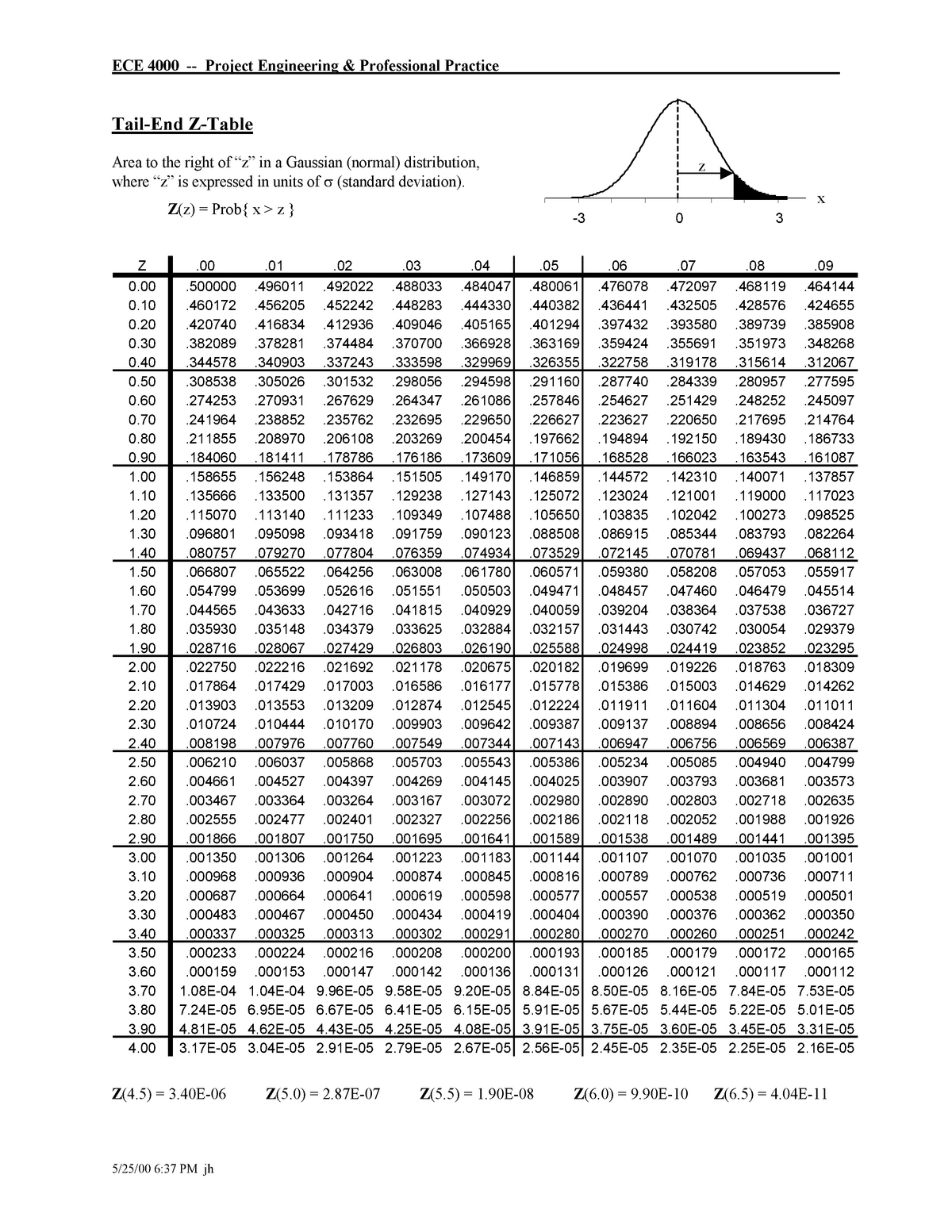
The 2-tailed Z-table would not exist as a separate desk; as an alternative, we make the most of the usual one-tailed Z-table to calculate chances for two-tailed checks. The method includes just a few key steps:
-
Discovering the Z-score: Calculate the Z-score utilizing the system talked about above. Keep in mind to think about the signal of the Z-score, because it signifies the route relative to the imply.
-
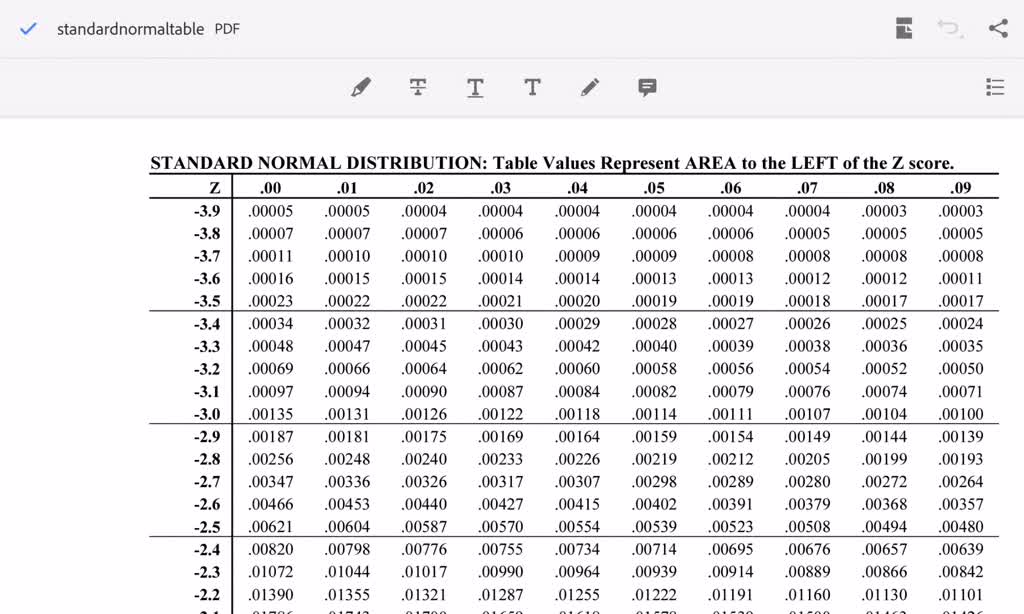
Utilizing the One-Tailed Z-Desk: Find the Z-score (or the closest approximation) within the one-tailed Z-table. The desk supplies the world below the curve to the left of the Z-score. This represents the likelihood of observing a worth lower than or equal to the Z-score.
-
Calculating the Two-Tailed Likelihood: For a two-tailed take a look at, we have to contemplate each tails of the distribution. The likelihood present in step 2 represents the likelihood of 1 tail. To search out the two-tailed likelihood, we double this worth (offered the Z-score is optimistic). If the Z-score is detrimental, absolutely the worth is used earlier than doubling. It is because the usual regular distribution is symmetric.
Instance: A Two-Tailed Speculation Check
Let’s illustrate the method with an instance. Suppose we’re testing a speculation that the typical top of grownup ladies is 165 cm. We acquire a pattern of 100 ladies and discover the pattern imply to be 167 cm with a normal deviation of 5 cm. Our speculation take a look at is two-tailed, that means we need to see if the pattern imply is considerably completely different from 165 cm, both larger or decrease.
- Calculate the Z-score:
Z = (167 – 165) / (5 / √100) = 4
-
Seek the advice of the One-Tailed Z-Desk: Trying up a Z-score of 4 in a one-tailed Z-table offers a likelihood of roughly 0.99997. This represents the world below the curve to the left of Z = 4.
-
Calculate the Two-Tailed Likelihood: Since this can be a two-tailed take a look at, we double the one-tailed likelihood:
2 * (1 – 0.99997) ≈ 0.00006
This extraordinarily small likelihood suggests robust proof to reject the null speculation that the typical top is 165 cm. The extraordinarily low p-value (0.00006) signifies that the noticed distinction is very unlikely to have occurred by probability alone.
Significance Degree and p-values
The idea of a significance stage (alpha) is vital in speculation testing. The importance stage is the likelihood of rejecting the null speculation when it’s truly true (Sort I error). Frequent significance ranges are 0.05 (5%) and 0.01 (1%).
The p-value is the likelihood of observing a outcome as excessive as, or extra excessive than, the one obtained, assuming the null speculation is true. If the p-value is lower than the importance stage, we reject the null speculation. In our instance, the p-value (0.00006) is way lower than 0.05 or 0.01, resulting in the rejection of the null speculation.
Limitations and Issues
Whereas the Z-table is a robust software, it has limitations:
- Massive Pattern Measurement Assumption: The Z-test assumes a big pattern measurement (usually n ≥ 30). For smaller samples, the t-test is extra acceptable.
- Inhabitants Customary Deviation: The Z-test requires figuring out the inhabitants customary deviation. If that is unknown, the pattern customary deviation is used, and the t-test is most popular.
- Normality Assumption: The Z-test assumes that the information is generally distributed. If this assumption is violated, non-parametric checks must be thought-about.
Conclusion
The 2-tailed Z-table, although not a separate desk, is a vital part of statistical evaluation, significantly for speculation testing involving two-tailed different hypotheses. By understanding the connection between one-tailed and two-tailed chances and making use of the proper interpretation, researchers can precisely assess the importance of their findings. Keep in mind to all the time contemplate the assumptions of the Z-test and select the suitable statistical take a look at primarily based on the traits of the information. Mastering using the Z-table is key to a powerful understanding of statistical inference and speculation testing. This detailed rationalization supplies a sturdy basis for navigating the complexities of two-tailed Z-tests and deciphering the outcomes with confidence. Additional exploration into statistical software program packages can streamline the calculation course of, permitting for a extra environment friendly evaluation of knowledge.




Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered invaluable insights into Decoding the Two-Tailed Z-Desk: A Complete Information. We respect your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!