Decoding The Y-Chart: A Deep Dive Into 1-Yr Treasury Invoice Charges And Their Significance
By admin / September 24, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Decoding the Y-Chart: A Deep Dive into 1-Yr Treasury Invoice Charges and Their Significance
Associated Articles: Decoding the Y-Chart: A Deep Dive into 1-Yr Treasury Invoice Charges and Their Significance
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we are going to discover the intriguing matter associated to Decoding the Y-Chart: A Deep Dive into 1-Yr Treasury Invoice Charges and Their Significance. Let’s weave fascinating data and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the Y-Chart: A Deep Dive into 1-Yr Treasury Invoice Charges and Their Significance

The yield curve, typically visualized as a Y-chart, gives an important snapshot of the monetary market’s expectations relating to future rates of interest. A key part of this curve is the 1-year Treasury invoice (T-bill) charge, a benchmark reflecting the market’s evaluation of short-term danger and the Federal Reserve’s financial coverage stance. Understanding its actions and implications is significant for traders, companies, and policymakers alike. This text will delve into the intricacies of the 1-year T-bill charge as depicted on the Y-chart, exploring its determinants, its relationship with different elements of the yield curve, and its broader financial significance.
Understanding the Y-Chart and its Parts
The yield curve, sometimes represented as a Y-chart, plots the yields of presidency bonds in opposition to their maturities. The x-axis represents the time to maturity (starting from a couple of days for T-bills to 30 years for long-term bonds), whereas the y-axis represents the yield or rate of interest. The curve’s form reveals helpful insights into market sentiment and future financial prospects. A traditional yield curve slopes upward, indicating that longer-term bonds supply larger yields to compensate traders for the elevated danger related to longer holding intervals. An inverted yield curve, the place short-term yields exceed long-term yields, is commonly thought-about a recessionary predictor.
The 1-year T-bill charge occupies a pivotal place on this curve. It sits on the shorter finish, representing the market’s expectation for short-term rates of interest over the subsequent yr. Its sensitivity to modifications in financial coverage and financial situations makes it a strong indicator of present and future financial exercise.
Determinants of the 1-Yr T-Invoice Fee
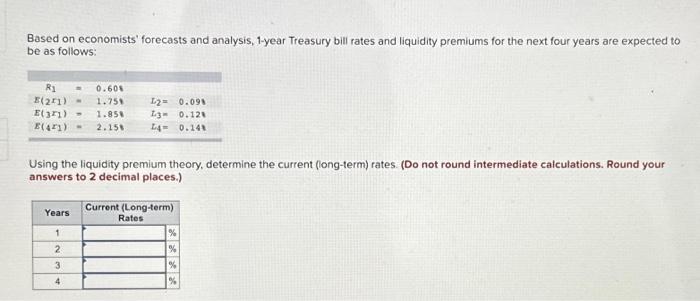
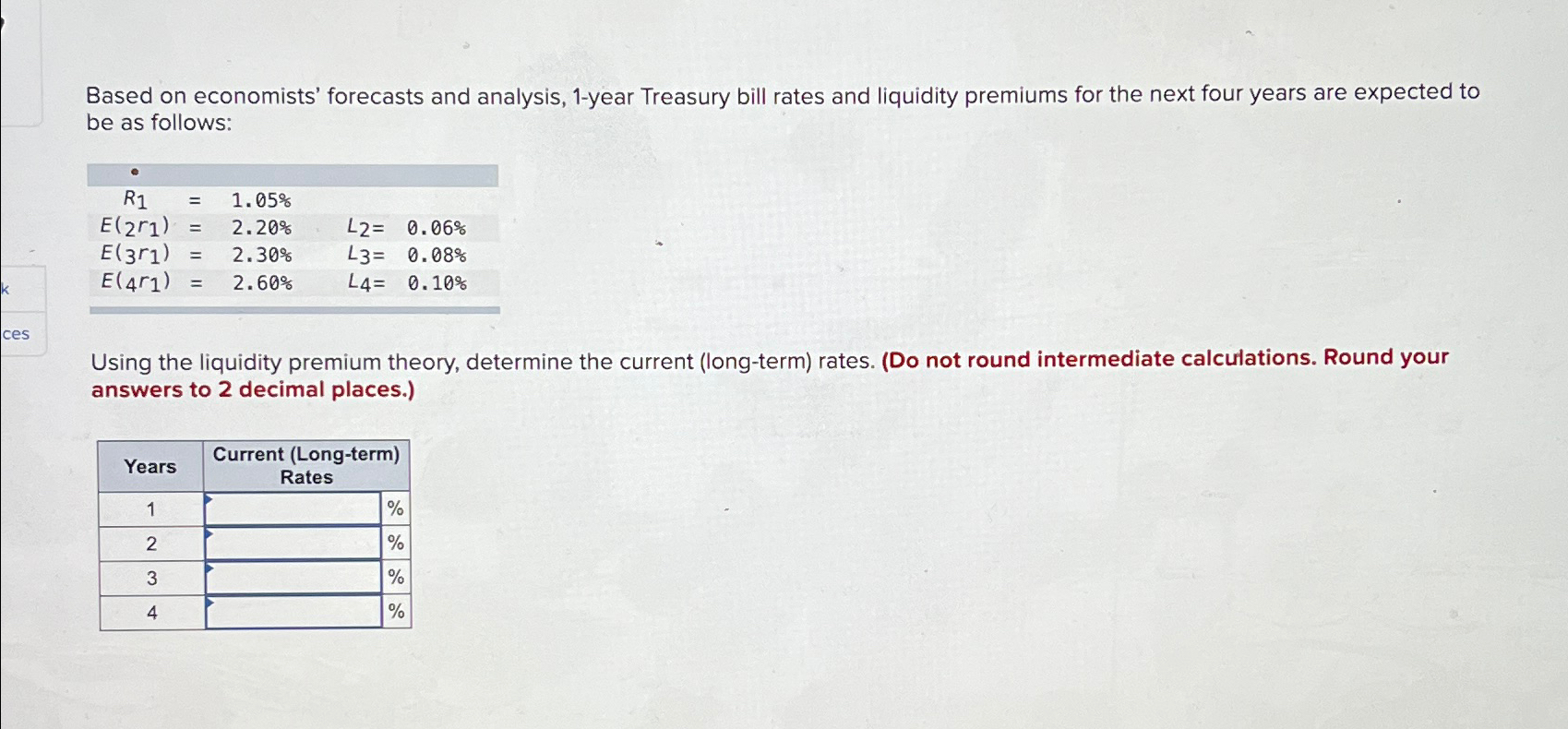
A number of components interaction to find out the 1-year T-bill charge:
-
Federal Reserve Coverage: Probably the most important affect is the Federal Reserve’s financial coverage. The Fed’s actions, primarily by means of the federal funds charge (the goal charge for in a single day lending between banks), instantly influence short-term rates of interest. When the Fed raises the federal funds charge, it usually results in larger yields throughout the yield curve, together with the 1-year T-bill charge. Conversely, decreasing the federal funds charge often ends in decrease T-bill charges.
-
Inflation Expectations: Inflation performs an important position. Traders demand larger yields to compensate for the erosion of buying energy brought on by inflation. Rising inflation expectations push T-bill charges upward, as traders search to guard their investments from inflation’s influence. Conversely, declining inflation expectations can result in decrease T-bill charges.
-
Financial Progress: The tempo of financial progress considerably influences T-bill charges. Sturdy financial progress typically results in elevated demand for credit score, driving up rates of interest, together with the 1-year T-bill charge. Conversely, weak financial progress can dampen demand for credit score, leading to decrease T-bill charges.
-
Provide and Demand for Treasury Securities: The provision of T-bills and the general demand for presidency debt affect their yields. Elevated authorities borrowing to finance deficits can enhance the availability of T-bills, probably placing downward stress on their costs and upward stress on their yields. Conversely, sturdy demand for safe-haven belongings throughout occasions of uncertainty can drive up T-bill costs and decrease their yields.
-
International Financial Situations: International financial components, resembling worldwide rates of interest and foreign money fluctuations, may have an effect on the 1-year T-bill charge. As an illustration, larger rates of interest in different nations may appeal to traders away from U.S. T-bills, probably growing their yields.
The 1-Yr T-Invoice Fee and the Broader Yield Curve
The 1-year T-bill charge’s place on the yield curve gives insights into the general form and slope of the curve. Its relationship with longer-term charges helps predict future financial developments:
-
Regular Yield Curve: A traditional upward-sloping curve means that traders anticipate larger rates of interest sooner or later. This suggests confidence in financial progress and the expectation of future inflation. The 1-year T-bill charge on this state of affairs is decrease than longer-term charges.
-
Inverted Yield Curve: An inverted yield curve, the place short-term charges (just like the 1-year T-bill charge) exceed long-term charges, is commonly interpreted as a recessionary sign. Traders could anticipate future financial slowdown or deflation, main them to demand larger yields on short-term securities as a secure haven.
-
Flat Yield Curve: A flat yield curve, the place short-term and long-term charges are comparatively shut, suggests uncertainty about future financial prospects. Traders are not sure about future inflation and financial progress, resulting in a scarcity of great distinction in yields throughout maturities.
Financial Significance and Implications
The 1-year T-bill charge holds important financial implications:
-
Financial Coverage Steering: The speed serves as a key indicator of the effectiveness of the Federal Reserve’s financial coverage. Modifications within the charge replicate the influence of the Fed’s actions on short-term rates of interest.
-
Enterprise Funding: Companies use the 1-year T-bill charge as a benchmark for borrowing prices when making funding choices. Increased charges can discourage funding, whereas decrease charges can stimulate funding.
-
Client Spending: Modifications within the charge can affect shopper spending by means of their influence on borrowing prices for mortgages, auto loans, and bank cards.
-
Inflation Hedging: Traders use T-bills as a safe-haven asset and a hedge in opposition to inflation, particularly in periods of uncertainty.
-
Predicting Financial Recessions: The connection between the 1-year T-bill charge and different elements of the yield curve, notably the inversion of the yield curve, has been traditionally related to elevated chance of future financial recessions.
Conclusion
The 1-year Treasury invoice charge, as depicted on the Y-chart, is a strong barometer of the monetary market’s sentiment and a key indicator of financial well being. Its sensitivity to financial coverage, inflation expectations, financial progress, and world financial situations makes it an important information level for traders, companies, and policymakers. Understanding its determinants, its relationship with the broader yield curve, and its financial implications is essential for navigating the complexities of the monetary markets and anticipating future financial developments. By fastidiously analyzing the 1-year T-bill charge and its actions throughout the context of the general yield curve, stakeholders can acquire helpful insights into the present financial panorama and make knowledgeable choices. Steady monitoring of this charge, alongside different financial indicators, is important for efficient monetary planning and strategic decision-making.

Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered helpful insights into Decoding the Y-Chart: A Deep Dive into 1-Yr Treasury Invoice Charges and Their Significance. We hope you discover this text informative and useful. See you in our subsequent article!