Creating A Three-Sigma R Chart: A Complete Information
By admin / November 9, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Creating a Three-Sigma R Chart: A Complete Information
Associated Articles: Creating a Three-Sigma R Chart: A Complete Information
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate via the intriguing subject associated to Creating a Three-Sigma R Chart: A Complete Information. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Creating a Three-Sigma R Chart: A Complete Information
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ThreeSigmaLimits_final-3e323eac8e104e09a15fb5ca9e8b264a.png)
Statistical Course of Management (SPC) is a strong instrument for monitoring and enhancing course of efficiency. A key part of SPC is the management chart, which visually shows course of information over time, permitting for the identification of tendencies, shifts, and particular causes of variation. Among the many varied management charts, the R chart, particularly the three-sigma R chart, holds a big place in monitoring course of variability. This text delves into the intricacies of creating a strong three-sigma R chart, protecting its objective, methodology, interpretation, and limitations.
Understanding the R Chart and its Objective
The R chart, or vary chart, is a sort of management chart used to watch the variability inside subgroups of knowledge. Not like the X-bar chart which screens the typical of subgroups, the R chart focuses solely on the vary, which is the distinction between the most important and smallest values inside a subgroup. The R chart is especially helpful when:
- The method imply is comparatively secure: Whereas the R chart can be utilized independently, its effectiveness is maximized when paired with an X-bar chart. A secure imply ensures that variations within the vary actually mirror adjustments in course of variability, reasonably than shifts within the common.
- Subgroup sizes are small and constant: The R chart is only with small subgroups (sometimes 2-10 observations). Bigger subgroups can result in much less delicate detection of variability adjustments. Constant subgroup sizes are essential for correct calculation and interpretation of the management limits.
- Knowledge is often distributed (roughly): Whereas the R chart is comparatively strong to deviations from normality, the accuracy of the management limits improves with information nearer to a traditional distribution.
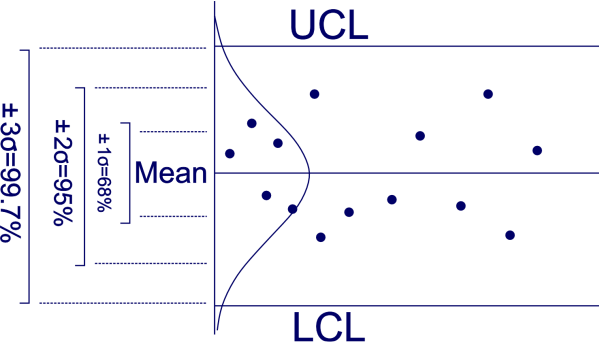
The Three-Sigma Management Limits
The three-sigma limits on an R chart outline the vary inside which the method vary is taken into account to be in statistical management. These limits are calculated primarily based on the typical vary (R-bar) of the subgroups and the management chart constants (d2, D3, and D4) particular to the subgroup measurement. These constants are derived from the sampling distribution of the vary and account for the inherent variability within the vary statistic.
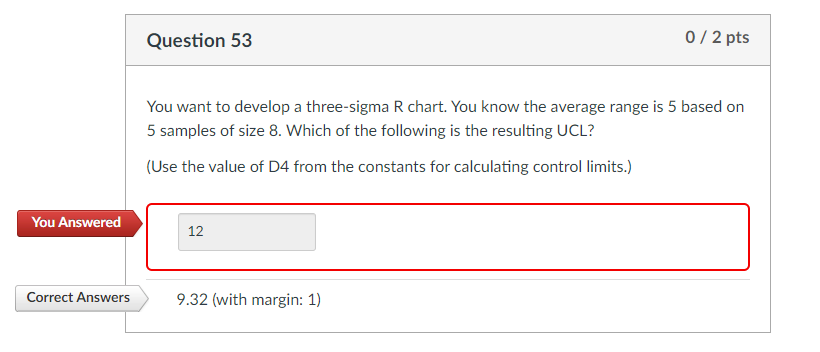
The formulation for the three-sigma management limits are:
- *Higher Management Restrict (UCL): D4 R-bar**
- Heart Line (CL): R-bar
- *Decrease Management Restrict (LCL): D3 R-bar**
The place:
- R-bar: The typical of the ranges of all subgroups. Calculated by summing the ranges of all subgroups and dividing by the variety of subgroups.
- D3 and D4: Management chart constants that rely on the subgroup measurement (n). These constants are available in statistical tables or software program packages. For small subgroup sizes, D3 might be zero, indicating that the LCL is zero.
Creating a Three-Sigma R Chart: A Step-by-Step Information
Let’s illustrate the method of creating a three-sigma R chart with a hypothetical instance. Suppose we’re monitoring the diameter of a manufactured half, gathering information in subgroups of measurement 5 (n=5). We accumulate information from 25 subgroups.
Step 1: Knowledge Assortment and Subgrouping
Step one is to gather information in subgroups of a constant measurement. In our instance, we’ve 25 subgroups, every containing 5 measurements of the half diameter. This information would possibly appear to be this (simplified instance):
| Subgroup | Measurement 1 | Measurement 2 | Measurement 3 | Measurement 4 | Measurement 5 | Vary (R) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10.1 | 10.2 | 10.0 | 10.3 | 10.1 | 0.3 |
| 2 | 10.0 | 10.1 | 9.9 | 10.2 | 10.0 | 0.3 |
| 3 | 10.2 | 10.1 | 10.3 | 10.0 | 10.2 | 0.3 |
| … | … | … | … | … | … | … |
| 25 | 9.9 | 10.0 | 10.1 | 10.2 | 10.0 | 0.3 |
Step 2: Calculate the Vary for Every Subgroup
For every subgroup, calculate the vary (R) by subtracting the smallest measurement from the most important measurement. This has been included within the desk above.
Step 3: Calculate the Common Vary (R-bar)
Sum the ranges of all 25 subgroups and divide by the variety of subgroups (25). This offers us R-bar. For instance, if the sum of all ranges is 7.5, then R-bar = 7.5 / 25 = 0.3.
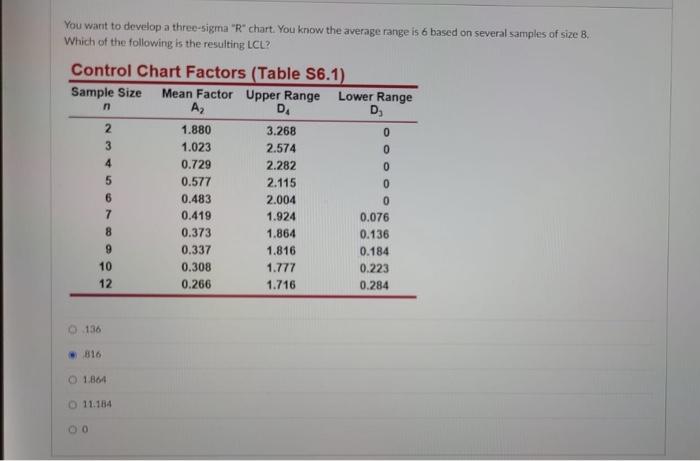
Step 4: Decide the Management Chart Constants (D3 and D4)
For a subgroup measurement of n=5, we seek the advice of a management chart constants desk (simply discovered on-line or in statistical textbooks). For n=5, we discover D3 ≈ 0 and D4 ≈ 2.114.
Step 5: Calculate the Management Limits
Utilizing the formulation from earlier:
- UCL = D4 R-bar = 2.114 0.3 ≈ 0.634
- CL = R-bar = 0.3
- LCL = D3 R-bar = 0 0.3 = 0
Step 6: Assemble the R Chart
Plot the vary (R) for every subgroup on the vertical axis in opposition to the subgroup quantity on the horizontal axis. Draw horizontal strains representing the UCL, CL, and LCL.
Step 7: Interpret the Chart
Look at the chart for any factors exterior the management limits or patterns that recommend the method is uncontrolled. Factors exterior the management limits point out potential particular causes of variation that require investigation. Patterns comparable to tendencies, cycles, or runs additionally recommend potential issues.
Software program for R Chart Creation
A number of software program packages can automate the creation and evaluation of R charts. In style choices embrace:
- Minitab: A extensively used statistical software program bundle with in depth SPC capabilities.
- JMP: One other highly effective statistical software program with strong management chart options.
- R (with packages like
qcc): A free and open-source statistical programming language with packages particularly designed for management chart evaluation. - Excel: Whereas much less refined, Excel can be utilized to create fundamental R charts utilizing its charting instruments and statistical features.
Limitations of the R Chart
Whereas the R chart is a worthwhile instrument, it has sure limitations:
- Sensitivity to outliers: Excessive values inside a subgroup can considerably inflate the vary, probably masking different variations.
- Assumption of normality (roughly): Whereas comparatively strong, vital deviations from normality can have an effect on the accuracy of the management limits.
- Data loss: The R chart solely considers the vary and ignores different details about the info distribution inside subgroups.
Conclusion
The three-sigma R chart is a basic instrument for monitoring course of variability. By systematically gathering information, calculating management limits, and deciphering the chart, we are able to successfully determine and tackle particular causes of variation, resulting in improved course of stability and high quality. Nonetheless, it’s essential to recollect the restrictions of the R chart and to make use of it along with different SPC instruments and methods for a complete understanding of course of efficiency. The usage of statistical software program considerably simplifies the method and enhances accuracy, making it a really helpful strategy for creating and analyzing R charts in real-world functions. Do not forget that a radical understanding of the underlying course of and information is important for correct interpretation and efficient use of the R chart.


Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied worthwhile insights into Creating a Three-Sigma R Chart: A Complete Information. We hope you discover this text informative and useful. See you in our subsequent article!