Displaying Two Information Sequence: A Complete Information To Chart Choice And Efficient Visualization
By admin / September 27, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Displaying Two Information Sequence: A Complete Information to Chart Choice and Efficient Visualization
Associated Articles: Displaying Two Information Sequence: A Complete Information to Chart Choice and Efficient Visualization
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to Displaying Two Information Sequence: A Complete Information to Chart Choice and Efficient Visualization. Let’s weave fascinating data and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Displaying Two Information Sequence: A Complete Information to Chart Choice and Efficient Visualization
Visualizing information successfully is essential for conveying insights and facilitating understanding. When coping with two information sequence, the selection of chart kind considerably impacts the readability and interpretability of your presentation. This text explores varied chart varieties appropriate for displaying two information sequence, highlighting their strengths, weaknesses, and acceptable use circumstances. We’ll delve into the nuances of every possibility, offering sensible steerage on making knowledgeable selections based mostly in your particular information and analytical objectives.
Understanding Your Information: The Basis of Efficient Visualization
Earlier than diving into chart varieties, it is important to know the character of your two information sequence. Take into account the next:
- Sort of Information: Are your information sequence steady (e.g., temperature, weight) or categorical (e.g., gender, product kind)? The kind of information dictates which chart varieties are most acceptable.
- Relationship between Information Sequence: Are the 2 sequence unbiased, correlated, or causally associated? Understanding the connection helps you select a chart that successfully highlights the interplay between the sequence.
- Purpose of Visualization: What story are you attempting to inform? Are you aiming to point out traits, comparisons, correlations, or distributions? Your goal will information your chart choice.
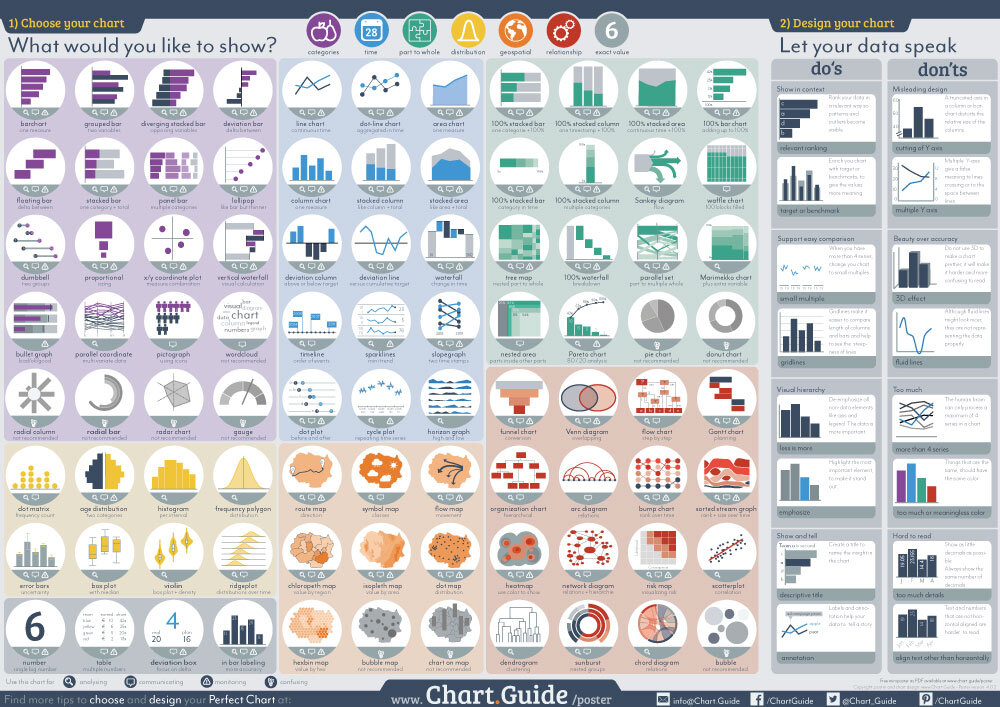
Chart Sorts for Displaying Two Information Sequence:
A number of chart varieties are well-suited for visualizing two information sequence. We’ll study the most typical and efficient choices:
1. Line Charts:
Line charts are glorious for displaying traits over time or throughout a steady variable. When visualizing two information sequence, every sequence is represented by a definite line. This permits for straightforward comparability of traits and identification of intersections or divergences.
- Strengths: Clearly reveals traits, highlights adjustments over time or a steady variable, simple to interpret.
- Weaknesses: Can change into cluttered with many information factors or sequence, much less efficient for evaluating discrete classes.
- Finest Use Circumstances: Displaying adjustments in gross sales over time for 2 totally different merchandise, monitoring inventory costs of two competing corporations, visualizing temperature fluctuations for 2 totally different areas.
Instance: A line chart might successfully show the month-to-month gross sales figures for 2 totally different product strains over a 12 months. Every line represents a product line, and the viewer can simply evaluate their gross sales efficiency all year long.
2. Bar Charts (and variations):
Bar charts are perfect for evaluating discrete classes. When coping with two information sequence, you should utilize grouped bar charts or stacked bar charts.
- Grouped Bar Charts: Every class has two bars side-by-side, one for every information sequence. This permits for straightforward comparability inside every class.
- Stacked Bar Charts: The bars for every information sequence are stacked on high of one another inside every class. This reveals the contribution of every sequence to the whole for every class.
- Strengths: Straightforward to check classes and sequence, visually interesting, efficient for categorical information.
- Weaknesses: Much less efficient for displaying traits over time, can change into cluttered with many classes or sequence.
- Finest Use Circumstances: Evaluating gross sales figures for 2 merchandise throughout totally different areas, displaying the distribution of genders in two totally different age teams, visualizing the composition of various supplies in two totally different merchandise.
Instance: A grouped bar chart might evaluate the typical buyer satisfaction scores for 2 totally different service suppliers throughout a number of key efficiency indicators (KPIs).
3. Space Charts:
Space charts are much like line charts, however the space beneath the road is crammed with coloration. This emphasizes the magnitude of the information and may be notably efficient when displaying proportions or cumulative values. When utilizing space charts with two information sequence, the areas for every sequence may be stacked or positioned side-by-side.
- Strengths: Exhibits traits and magnitudes concurrently, helpful for visualizing proportions or cumulative values.
- Weaknesses: Could be troublesome to learn with many sequence or complicated information, much less efficient for exact comparisons of particular person information factors.
- Finest Use Circumstances: Visualizing market share for 2 competing corporations over time, displaying the contribution of various income streams to complete income, displaying cumulative gross sales figures for 2 product strains.
Instance: An space chart might illustrate the altering market share of two main working techniques for cellular gadgets over a five-year interval.
4. Scatter Plots:
Scatter plots are glorious for exploring the connection between two steady variables. When displaying two information sequence, every sequence may be represented by a special set of factors on the plot. This permits for the identification of correlations or patterns between the sequence.
- Strengths: Exhibits relationships between two steady variables, identifies correlations, permits for the inclusion of a 3rd variable utilizing coloration or measurement.
- Weaknesses: Not efficient for displaying traits over time or for categorical information, may be troublesome to interpret with massive datasets.
- Finest Use Circumstances: Investigating the connection between promoting spend and gross sales income, exploring the correlation between temperature and power consumption, visualizing the connection between two totally different financial indicators.
Instance: A scatter plot might visualize the connection between a pupil’s hours of examine and their examination scores, with totally different colours representing totally different examine strategies.
5. Mixture Charts:
Mixture charts mix parts of various chart varieties to current a number of features of the information concurrently. As an example, a line chart could possibly be mixed with a bar chart to point out traits and particular person information factors.
- Strengths: Permits for the presentation of a number of views on the information, gives a richer understanding of the relationships between sequence.
- Weaknesses: Can change into complicated and troublesome to interpret if not designed rigorously, requires cautious consideration of the chart parts.
- Finest Use Circumstances: Displaying traits alongside particular person information factors, combining categorical and steady information, visualizing the connection between totally different variables over time.
Instance: A mixture chart might show the typical month-to-month temperature (line chart) alongside the month-to-month rainfall (bar chart) for a specific area.
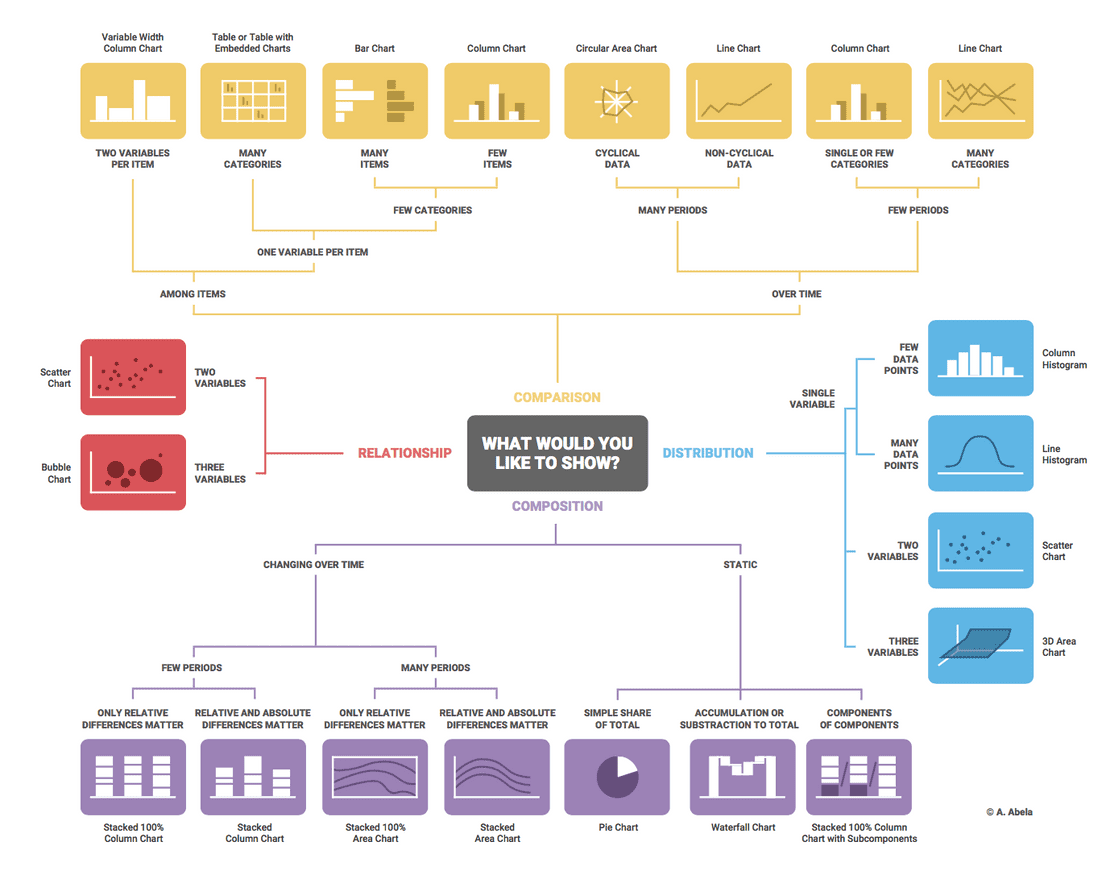
Selecting the Proper Chart: A Sensible Information
Choosing the suitable chart kind is dependent upon a number of components:
- Information Sort: Categorical information is finest represented by bar charts, whereas steady information is best fitted to line charts, space charts, and scatter plots.
- Relationship between Sequence: If you wish to spotlight the connection between two sequence, a scatter plot is an effective selection. If you wish to evaluate traits, line charts or space charts are extra acceptable.
- Viewers and Context: Take into account the viewers’s familiarity with totally different chart varieties and the general context of your presentation. Simplicity and readability are key.
- Information Quantity: For big datasets, think about using interactive charts or strategies like aggregation to keep away from cluttering the visualization.
Past Chart Sort: Enhancing Information Visualization
Choosing the fitting chart kind is simply step one. To create actually efficient visualizations, think about the next:
- Clear Labeling: Use clear and concise labels for axes, legends, and information factors.
- Applicable Scaling: Select acceptable scales to your axes to keep away from deceptive interpretations.
- Coloration Palette: Use a constant and visually interesting coloration palette.
- Information Annotations: Spotlight key information factors or traits with annotations.
- Contextual Info: Present ample context to assist the viewers perceive the information and its implications.
By rigorously contemplating the character of your information, your analytical objectives, and the ideas of efficient visualization, you’ll be able to create compelling charts that successfully talk insights out of your two information sequence. Keep in mind that the last word objective is to current your information in a transparent, concise, and simply comprehensible method, enabling your viewers to know the important thing takeaways shortly and effectively.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered useful insights into Displaying Two Information Sequence: A Complete Information to Chart Choice and Efficient Visualization. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!