Graph And Chart Distinction
By admin / July 8, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
graph and chart distinction
Associated Articles: graph and chart distinction
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate via the intriguing subject associated to graph and chart distinction. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Unveiling the Variations: Graphs vs. Charts – A Deep Dive into Information Visualization

Information visualization is paramount in in the present day’s data-driven world. It permits us to remodel uncooked numbers into simply digestible and comprehensible data, revealing patterns, developments, and insights that may in any other case stay hidden. Two elementary instruments within the information visualization arsenal are graphs and charts. Whereas typically used interchangeably, they possess distinct traits and are greatest fitted to several types of information and analytical targets. This text delves into the nuances of graphs and charts, exploring their variations, purposes, and optimum utilization situations.
Defining the Phrases: A Foundational Understanding
Earlier than diving into the distinctions, it is essential to determine clear definitions. Whereas a universally accepted, inflexible distinction is not all the time enforced, a normal consensus exists:
-
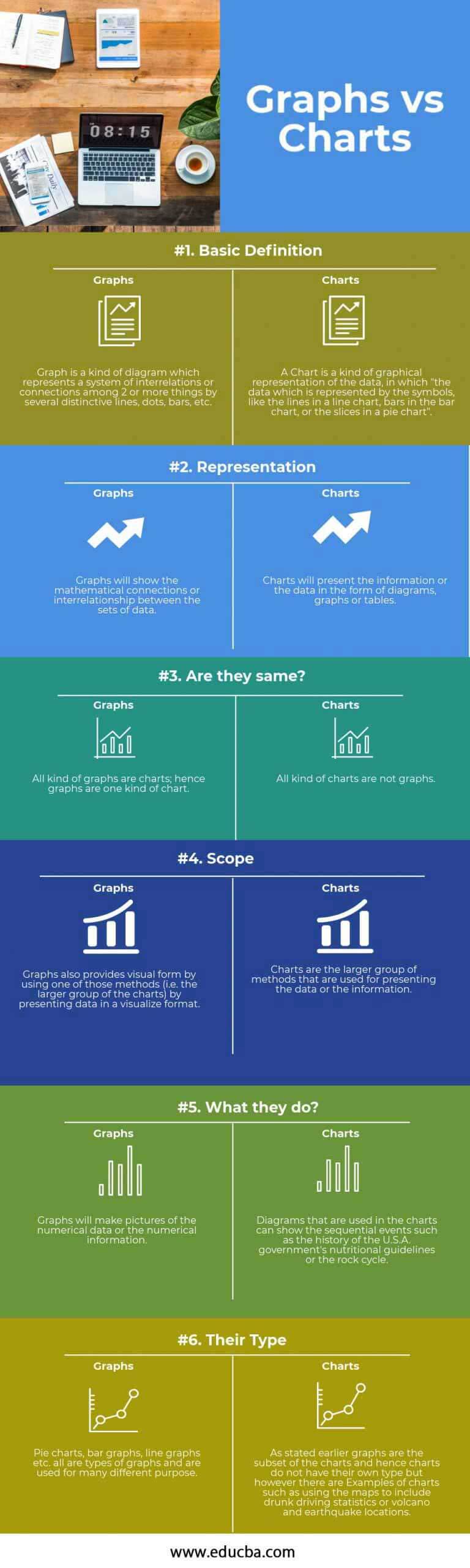
Graphs: Graphs sometimes symbolize information utilizing factors, strains, or curves to indicate relationships between two or extra variables. They emphasize the continual nature of information and the pattern or sample over time or throughout totally different variables. The main target is on the visible depiction of the connection itself, highlighting adjustments and correlations.
-
Charts: Charts are sometimes used to summarize and examine information utilizing bars, slices, or different visible parts. They typically deal with discrete information factors or classes and their relative magnitudes. The emphasis is on evaluating totally different classes or teams, highlighting variations in measurement, proportion, or frequency.
This elementary distinction – steady vs. discrete information – kinds the bedrock of their distinct purposes. Nonetheless, the road between graphs and charts can generally blur, significantly with hybrid visualizations that incorporate parts of each.
Key Variations: A Comparative Evaluation
A number of key traits differentiate graphs and charts:
| Function | Graph | Chart |
|---|---|---|
| Information Kind | Primarily steady information, exhibiting developments | Primarily discrete information, evaluating classes |
| Visible Parts | Strains, curves, factors, scatter plots | Bars, slices, pictograms, tables |
| Emphasis | Relationships, developments, adjustments over time | Comparisons, proportions, frequencies |
| Axes | Usually makes use of x and y axes (or extra) | Could or might not use axes, relying on sort |
| Complexity | Can vary from easy to extremely advanced | Can vary from easy to reasonably advanced |
| Finest Suited For | Displaying correlations, forecasting, time sequence | Evaluating teams, exhibiting proportions, rankings |
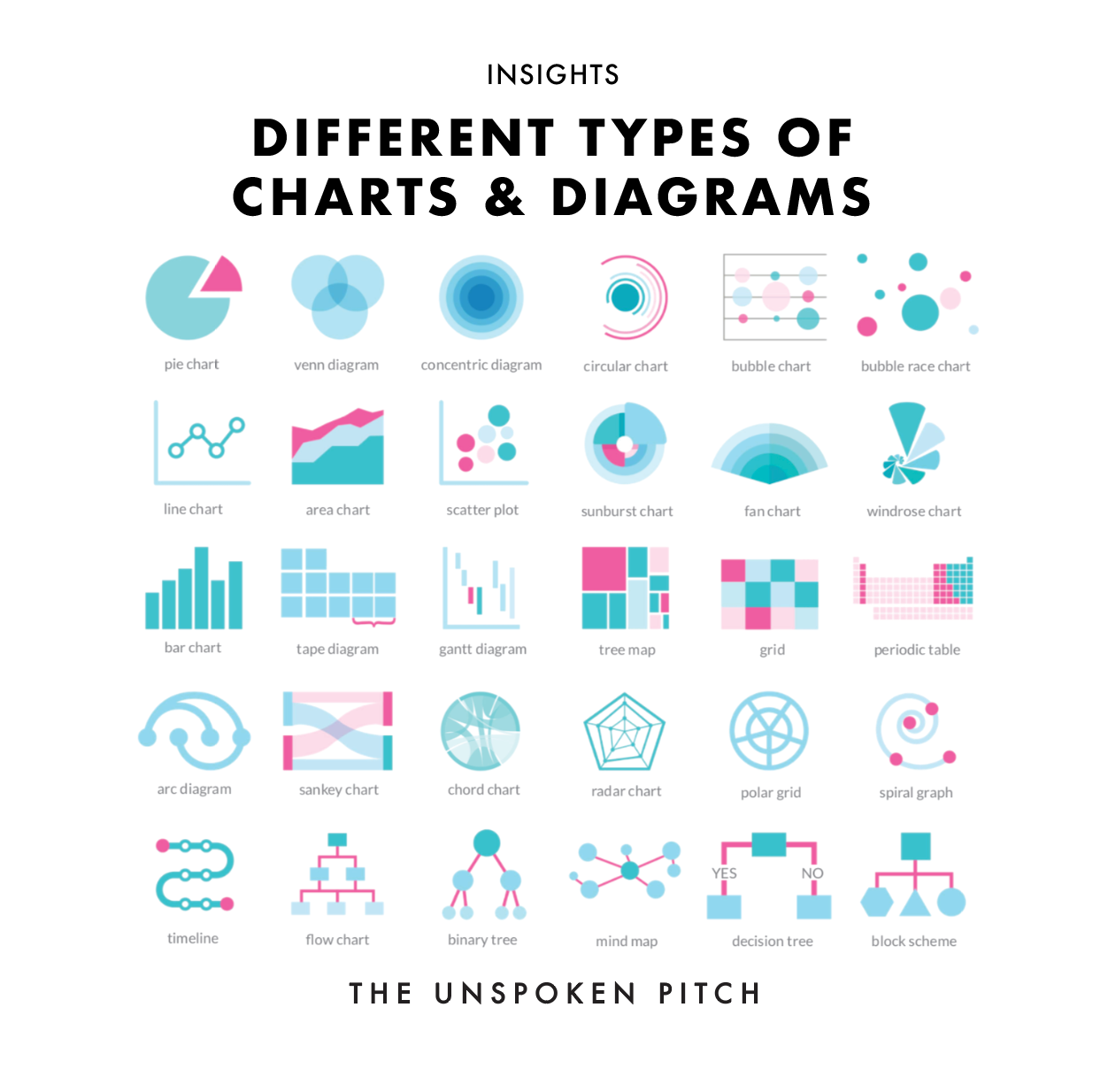
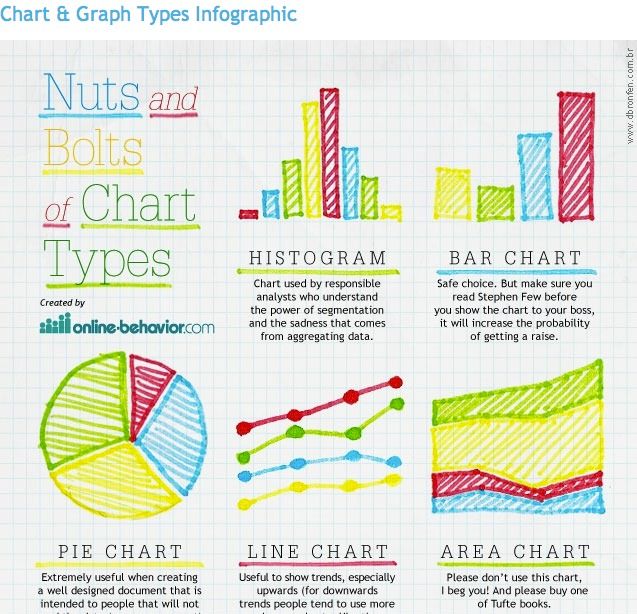
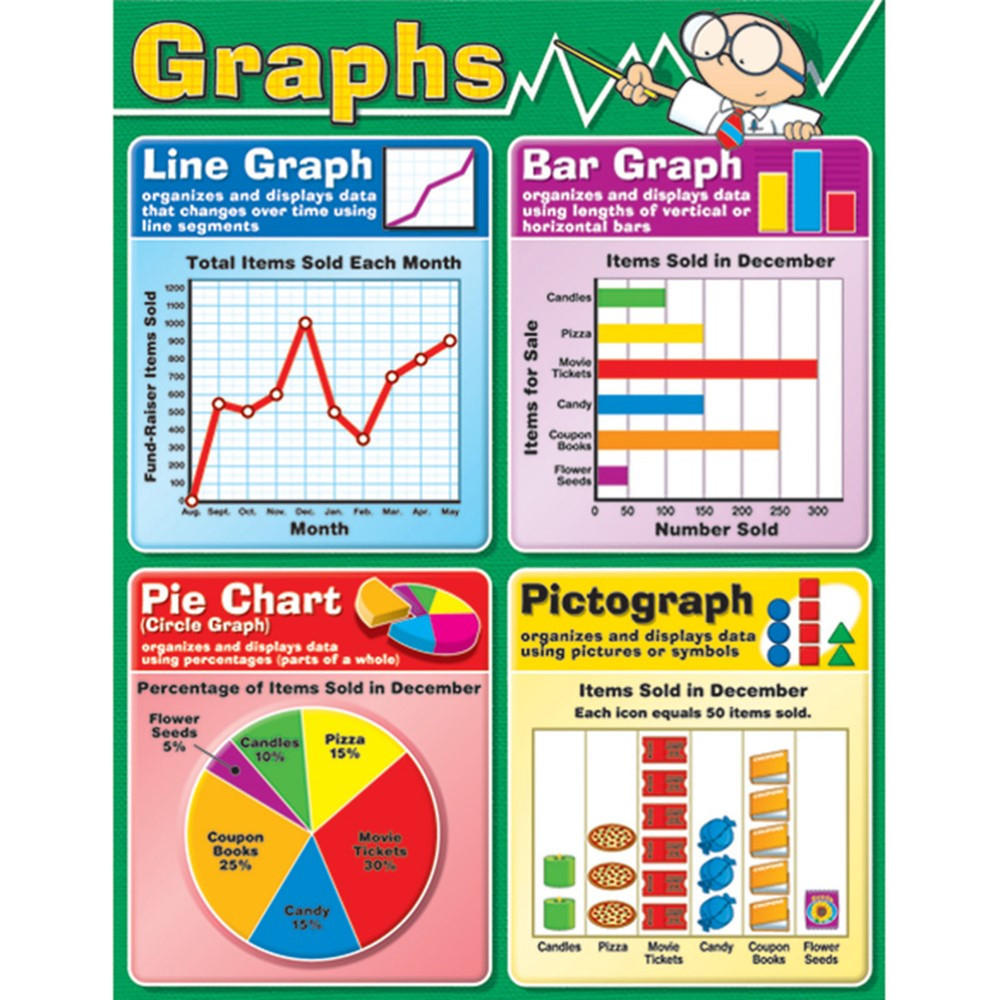
Varieties of Graphs and Their Purposes:
A number of sorts of graphs cater to totally different information visualization wants:
-
Line Graphs: Excellent for displaying developments over time. They successfully present the development of a variable, making them appropriate for analyzing gross sales figures, inventory costs, or temperature adjustments over a interval.
-
Scatter Plots: Used as an instance the connection between two variables. They reveal correlations, clusters, and outliers. Scatter plots are precious in figuring out potential causal relationships or just understanding the co-variation of information factors.
-
Bar Graphs: Whereas technically a chart, bar graphs can be thought of a hybrid. They symbolize discrete information utilizing bars of various heights, making them appropriate for evaluating classes or teams. Nonetheless, when used to symbolize steady information over time, they transition in direction of a graph-like illustration.
-
Space Graphs: Much like line graphs, however the space below the road is stuffed, highlighting the cumulative impact over time. They’re appropriate for exhibiting progress or decline over time, significantly when the magnitude of change is vital.
-
Pie Charts: Whereas a chart, it may be used to symbolize a steady distribution. If the distribution is represented as a frequency distribution, then it turns into discrete.
-
Bubble Charts: Prolong scatter plots by including a 3rd dimension represented by the dimensions of the bubbles. They’re helpful for exhibiting the connection between three variables concurrently.
Varieties of Charts and Their Purposes:
A number of sorts of charts serve numerous information visualization functions:
-
Bar Charts: As talked about earlier, these are used for evaluating discrete classes. They are often horizontal or vertical and are efficient for showcasing variations in magnitude between teams.
-
Pie Charts: Present the proportion of various classes inside an entire. They are perfect for illustrating percentages or market share. Nonetheless, they turn into much less efficient with many classes.
-
Column Charts: Much like bar charts, however the bars are oriented vertically. They’re typically used interchangeably with bar charts.
-
Pictograms: Use photographs or icons to symbolize information, making them visually partaking and simply comprehensible, significantly for non-technical audiences.
-
Flowcharts: Illustrate processes or workflows, exhibiting the sequence of steps and choice factors. They’re generally utilized in enterprise course of modeling and software program growth.
-
Gantt Charts: Particularly designed to visualise mission schedules, exhibiting duties, durations, and dependencies. They’re essential for mission administration and planning.
-
Histograms: Symbolize the frequency distribution of a steady variable, exhibiting the variety of information factors falling inside particular ranges or bins. They’re helpful for understanding the information distribution and figuring out potential outliers.
Selecting the Proper Visualization: Context Issues
The selection between a graph and a chart relies upon closely on the kind of information, the message to be conveyed, and the viewers. Think about the next:
-
Information Kind: Steady information (e.g., temperature over time) is greatest represented by graphs, whereas discrete information (e.g., gross sales by area) is best fitted to charts.
-
Goal: If the aim is to indicate developments and relationships, a graph is extra applicable. If the aim is to match classes or present proportions, a chart is a better option.
-
Viewers: For a technical viewers, advanced graphs is perhaps appropriate. For a non-technical viewers, easier charts or pictograms is perhaps more practical.
-
Information Quantity: Giant datasets may require extra subtle graphs or interactive visualizations, whereas smaller datasets could be successfully represented by easier charts.
Hybrid Visualizations: Mixing the Better of Each Worlds
The excellence between graphs and charts is not all the time absolute. Many visualizations mix parts of each, leveraging the strengths of every strategy. For instance, a mixture chart may use a line graph to indicate a pattern over time alongside a bar chart to match totally different classes inside every time interval. These hybrid visualizations typically present a extra complete and insightful illustration of the information.
Conclusion: A Highly effective Partnership
Graphs and charts are highly effective instruments for information visualization, every serving a novel objective. Understanding their variations and deciding on the suitable visualization is essential for successfully speaking information insights. By mastering the artwork of selecting between graphs and charts, information analysts and communicators can unlock the complete potential of information to tell selections, drive innovation, and inform compelling tales. The important thing lies in rigorously contemplating the information, the message, and the viewers to create visualizations that aren’t solely informative but in addition partaking and simply understood. The synergy between graphs and charts, and the artistic use of hybrid visualizations, finally enhances the facility of information visualization in a world more and more reliant on data-driven insights.


Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied precious insights into graph and chart distinction. We recognize your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!