Mastering The R Chart In Minitab: A Complete Information To Course of Variation Management
By admin / August 27, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Mastering the R Chart in Minitab: A Complete Information to Course of Variation Management
Associated Articles: Mastering the R Chart in Minitab: A Complete Information to Course of Variation Management
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by means of the intriguing matter associated to Mastering the R Chart in Minitab: A Complete Information to Course of Variation Management. Let’s weave fascinating info and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Mastering the R Chart in Minitab: A Complete Information to Course of Variation Management
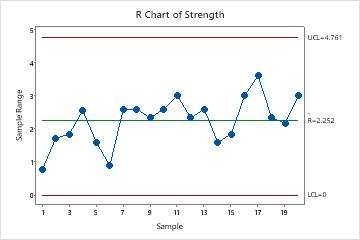
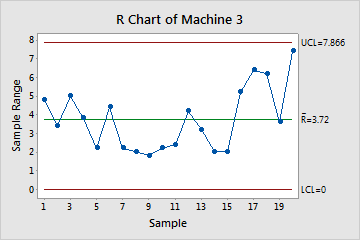
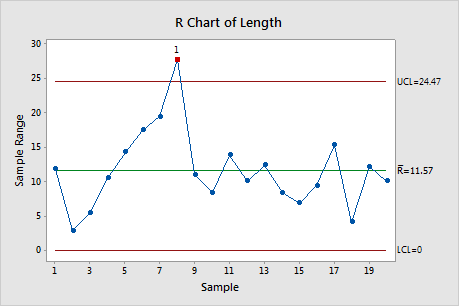
The R chart, a cornerstone of Statistical Course of Management (SPC), is a strong instrument for monitoring the variability inside subgroups of a course of. In contrast to the X-bar chart which focuses on the typical, the R chart particularly tracks the vary – the distinction between the best and lowest values – inside every subgroup. This makes it invaluable for figuring out shifts in course of dispersion, even when the typical stays comparatively steady. Minitab, a number one statistical software program bundle, offers a user-friendly interface for creating and deciphering R charts, making them accessible even to customers with restricted statistical experience. This text delves into the intricacies of R charts inside Minitab, masking their creation, interpretation, and sensible functions, together with superior issues and troubleshooting.
Understanding the Ideas of R Charts
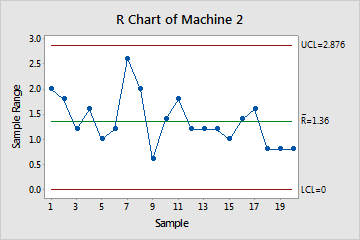
Earlier than diving into Minitab’s functionalities, let’s set up a agency understanding of the underlying statistical rules. The R chart depends on the idea that the info being analyzed comes from a usually distributed inhabitants. Whereas slight deviations from normality do not severely influence the chart’s effectiveness, important departures can have an effect on its accuracy. The chart’s management limits are calculated based mostly on the typical vary (R-bar) throughout all subgroups. These limits outline the anticipated vary of variation beneath steady course of circumstances. Observations falling outdoors these limits sign potential issues with course of variability.
The important thing elements of an R chart are:
- Middle Line (R-bar): The typical vary calculated from all subgroups. This represents the standard course of variation.
- Higher Management Restrict (UCL): The higher boundary past which an noticed vary signifies extreme variability.
- Decrease Management Restrict (LCL): The decrease boundary beneath which an noticed vary suggests unusually low variability (although generally the LCL is omitted for ranges, significantly for smaller subgroup sizes).
These limits are usually calculated utilizing components derived from the distribution of ranges. Minitab mechanically calculates these components based mostly on the subgroup measurement. The formulation concerned are based mostly on the distribution of the pattern vary, which is intently associated to the traditional distribution.
Creating an R Chart in Minitab
Minitab streamlines the method of producing R charts. The steps concerned are simple:
-
Information Entry: Start by getting into your knowledge into Minitab. The info ought to be organized with every column representing a subgroup and every row representing an statement inside that subgroup. Make sure that your knowledge are accurately formatted; any errors in knowledge entry will straight have an effect on the accuracy of the chart.
-
Choosing the ‘Management Charts’ Menu: Navigate to the ‘Stat’ menu, then choose ‘Management Charts,’ and at last select ‘Variables Charts for Subgroups.’
-
Selecting the ‘R Chart’ Possibility: Within the subsequent dialog field, choose ‘R’ because the chart kind. You may must specify the columns containing your subgroup knowledge. Minitab permits for a number of columns to be chosen concurrently, enabling the creation of a number of R charts for comparability or completely different features of the method.
-
Subgroup Dimension Specification: Point out the subgroup measurement (the variety of observations in every subgroup). That is essential for correct calculation of the management limits. Inconsistent subgroup sizes can result in inaccurate outcomes.
-
Non-obligatory Settings: Minitab provides a number of elective settings, together with:
- Checks for Particular Causes: Minitab can mechanically carry out exams for particular causes of variation, equivalent to factors outdoors the management limits, runs of factors above or beneath the middle line, and different patterns indicative of instability. These exams assist determine potential issues throughout the course of.
- Historic Information: When you’ve got historic knowledge, you may incorporate it into the evaluation to enhance the accuracy of the management limits and improve the sensitivity of the chart.
- Customized Management Limits: In sure conditions, you may need to use customized management limits based mostly on particular necessities or prior data. Minitab permits for this customization.
-
Chart Output: As soon as you’ve got specified all the required parameters, click on ‘OK’ to generate the R chart. Minitab will show the chart, together with the middle line, management limits, and any knowledge factors that exceed these limits.
Decoding the R Chart
Decoding an R chart entails assessing the soundness of the method variability. The next factors are essential:
-
Factors Outdoors Management Limits: Any factors that fall outdoors the higher or decrease management limits point out extreme or unusually low variability, respectively. This implies a possible drawback within the course of that wants investigation. The reason for this variation ought to be recognized and corrected.
-
Patterns Inside Management Limits: Even when all factors stay throughout the management limits, sure patterns may sign underlying points. These patterns embody:
- Tendencies: A constant upward or downward development suggests a gradual shift in course of variability.
- Cycles: Recurring patterns of excessive and low variability point out periodic influences on the method.
- Stratification: Clustering of factors round sure values may point out the presence of subgroups with completely different variability traits.
-
Run Charts: Analyzing a run chart alongside the R chart can present further insights into the method’s stability. Run charts illustrate the sequence of knowledge factors, making it simpler to determine traits and patterns that is perhaps missed within the R chart alone.
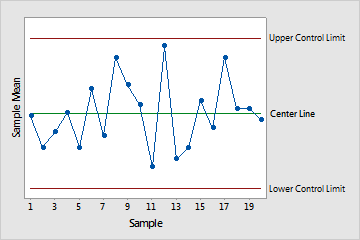
Utilizing R Charts with X-bar Charts
R charts are sometimes used along with X-bar charts (which observe the typical of every subgroup). This mixture offers a complete evaluation of each the central tendency and the variability of the method. By analyzing each charts concurrently, you may acquire a clearer understanding of the general course of stability and determine the basis causes of any noticed variations. Minitab simplifies this course of by permitting you to create each charts concurrently.
Superior Concerns and Troubleshooting
A number of superior issues and potential troubleshooting steps are essential for efficient R chart utilization:
-
Non-normality: In case your knowledge considerably deviates from normality, transformations equivalent to logarithmic or sq. root transformations is perhaps vital to enhance the accuracy of the R chart. Minitab provides instruments for assessing normality and making use of transformations.
-
Subgroup Dimension: The selection of subgroup measurement is essential. Smaller subgroups are extra delicate to small variations however may result in extra false alarms. Bigger subgroups are much less delicate however present a extra steady estimate of the method variability. The optimum subgroup measurement is dependent upon the precise course of and the specified sensitivity.
-
Information Outliers: Outliers can considerably affect the calculation of the management limits. Cautious examination and potential elimination (with justification) of outliers is perhaps vital earlier than producing the R chart.
-
Decoding Uncommon Patterns: Understanding the potential causes of surprising patterns, equivalent to traits, cycles, and stratification, is significant for efficient course of enchancment. This usually requires an intensive investigation into the method itself and potential contributing components.
-
False Alarms: Whereas R charts are extremely efficient, there’s at all times a risk of false alarms – factors outdoors the management limits that do not signify true course of instability. Cautious investigation is required to distinguish between true alerts and false alarms.
Conclusion
The R chart, readily applied and interpreted inside Minitab, serves as an important instrument for monitoring and controlling course of variability. By understanding its rules, mastering its creation inside Minitab, and accurately deciphering its output, customers can considerably improve their means to determine and handle sources of variation, resulting in improved course of effectivity and product high quality. The mixture of the R chart with the X-bar chart offers a complete strategy to course of management, permitting for a deeper understanding of course of habits and enabling more practical decision-making. By leveraging the superior options and troubleshooting capabilities of Minitab, customers can confidently apply R charts to a variety of functions, contributing to steady course of enchancment and total organizational success.



Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied beneficial insights into Mastering the R Chart in Minitab: A Complete Information to Course of Variation Management. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!