Navigating The Microscopic World: A Complete Information To The M, Cm, Mm, µm, And Nm Chart
By admin / September 20, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Navigating the Microscopic World: A Complete Information to the m, cm, mm, µm, and nm Chart
Associated Articles: Navigating the Microscopic World: A Complete Information to the m, cm, mm, µm, and nm Chart
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by means of the intriguing matter associated to Navigating the Microscopic World: A Complete Information to the m, cm, mm, µm, and nm Chart. Let’s weave fascinating data and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Navigating the Microscopic World: A Complete Information to the m, cm, mm, µm, and nm Chart
The world round us exists on an unlimited scale, from the immensity of galaxies to the intricacies of the atom. Understanding this scale requires familiarity with the models used to measure size, notably within the realm of the microscopic. This text gives a complete exploration of the metric prefixes used to signify size, specializing in meters (m), centimeters (cm), millimeters (mm), micrometers (µm), and nanometers (nm), presenting them in a transparent, accessible chart and delving into their functions throughout numerous scientific fields.
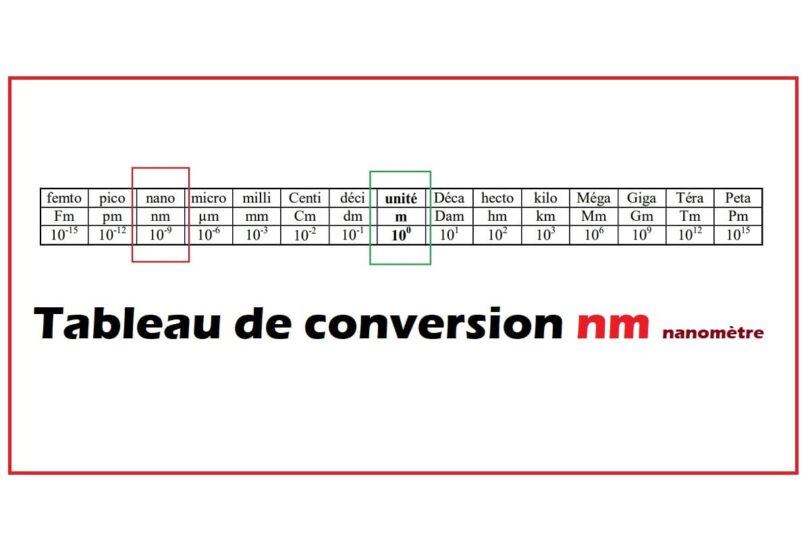
Understanding the Metric System:
The metric system, often known as the Worldwide System of Models (SI), is a decimal system based mostly on powers of ten. This makes conversions between models extremely easy. The bottom unit for size within the SI system is the meter (m). All different models of size are derived from the meter by multiplying or dividing by powers of ten. This inherent simplicity contrasts with imperial methods, such because the US customary system, which require extra advanced conversion elements.
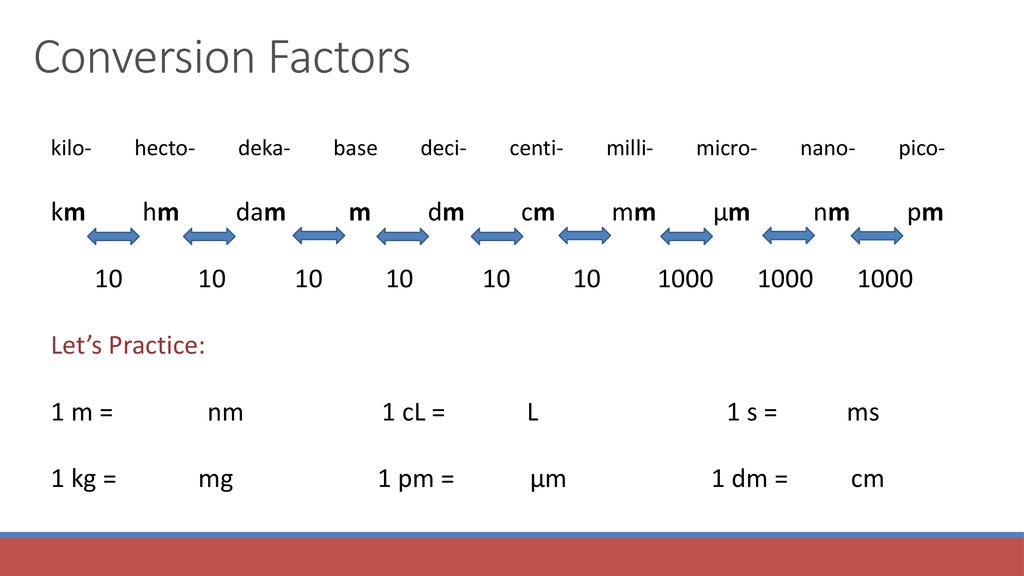
The m, cm, mm, µm, and nm Chart:
The next chart summarizes the relationships between meters (m), centimeters (cm), millimeters (mm), micrometers (µm), and nanometers (nm):
| Unit | Abbreviation | Worth in Meters (m) | Relative Measurement to Meter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Meter | m | 1 | 1 |
| Centimeter | cm | 0.01 (10⁻²) | 1/100 |
| Millimeter | mm | 0.001 (10⁻³) | 1/1000 |
| Micrometer | µm | 0.000001 (10⁻⁶) | 1/1,000,000 |
| Nanometer | nm | 0.000000001 (10⁻⁹) | 1/1,000,000,000 |
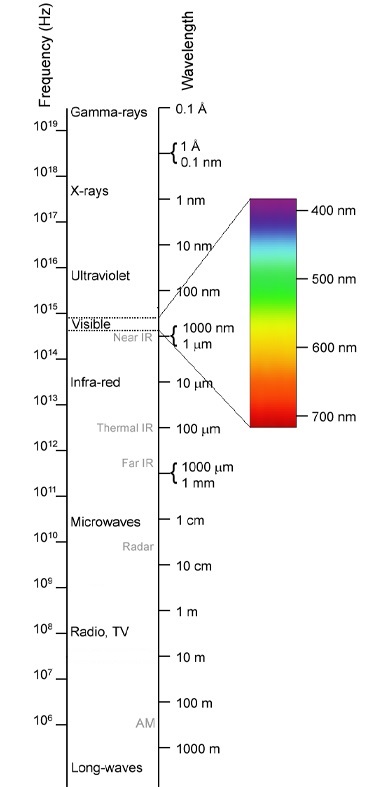
Visualizing the Scale:
To really grasp the variations between these models, take into account these analogies:
- Meter (m): A typical human top is roughly 1.7 meters.
- Centimeter (cm): The width of a fingernail is roughly 1 centimeter.
- Millimeter (mm): The thickness of a dime is about 1 millimeter.
- Micrometer (µm): A single human hair is roughly 50-100 micrometers in diameter. Micro organism are sometimes measured in micrometers.
- Nanometer (nm): Atoms have diameters starting from 0.1 to 0.5 nanometers. DNA’s width is about 2 nanometers.
These comparisons spotlight the dramatic lower in dimension as we transfer from meters to nanometers. The dimensions is exponential, with every unit being one-tenth the dimensions of the previous one.
Purposes Throughout Scientific Disciplines:
The selection of unit relies upon closely on the dimensions of the item or phenomenon being measured. This is a breakdown of functions for every unit:
-
Meter (m): Used for measuring macroscopic objects, distances, and large-scale phenomena like constructing heights, highway lengths, and astronomical distances (although kilometers (km) are extra sensible for giant distances).
-
Centimeter (cm): Generally utilized in on a regular basis measurements, resembling clothes sizes, paper dimensions, and smaller objects. It is also prevalent in sure scientific contexts, like measuring plant development or animal anatomy.
-
Millimeter (mm): Continuously utilized in engineering, manufacturing, and precision measurements. Examples embrace the thickness of supplies, the size of digital parts, and the calibration of devices.
-
Micrometer (µm): Important in microscopy, cell biology, and supplies science. It is used to measure the dimensions of cells, microorganisms, and the options of supplies on the microscopic degree. Purposes embrace analyzing blood cell counts, learning tissue samples, and characterizing floor textures.
-
Nanometer (nm): The realm of nanotechnology, the place manipulating supplies on the atomic and molecular degree is essential. It is used to characterize nanoparticles, measure the thickness of skinny movies, research the construction of proteins and DNA, and develop superior supplies with novel properties. Nanomaterials are discovering functions in drugs (drug supply), electronics (smaller and quicker transistors), and vitality (photo voltaic cells).
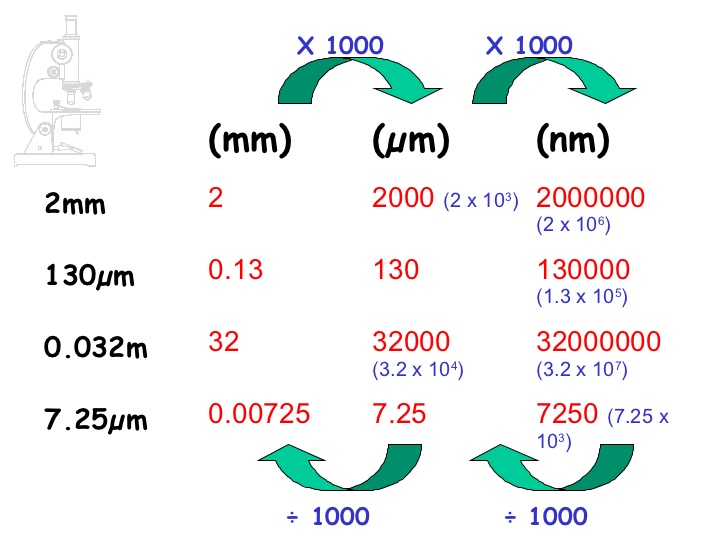
Conversions and Calculations:
Changing between these models is simple because of the decimal nature of the metric system. To transform from a bigger unit to a smaller unit, multiply by the suitable energy of ten. To transform from a smaller unit to a bigger unit, divide by the suitable energy of ten.
For instance:
- To transform 2 meters to centimeters: 2 m * 100 cm/m = 200 cm
- To transform 500 millimeters to meters: 500 mm / 1000 mm/m = 0.5 m
- To transform 10 micrometers to nanometers: 10 µm * 1000 nm/µm = 10,000 nm
Conclusion:
Understanding the connection between meters, centimeters, millimeters, micrometers, and nanometers is essential for navigating the huge spectrum of scales within the bodily world. From the on a regular basis measurements we make to the cutting-edge analysis in nanotechnology, these models present a elementary framework for quantifying size and enabling scientific developments throughout quite a few disciplines. The simplicity of the metric system and the clear relationships between these models make them invaluable instruments for scientists, engineers, and anybody in search of to grasp the world round them, from the macroscopic to the nanoscopic. This chart and the accompanying explanations function a helpful useful resource for anybody in search of a deeper understanding of those elementary models of measurement.




Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered helpful insights into Navigating the Microscopic World: A Complete Information to the m, cm, mm, µm, and nm Chart. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!