The Artwork And Science Of Chart Shade Codes: A Complete Information
By admin / October 6, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
The Artwork and Science of Chart Shade Codes: A Complete Information
Associated Articles: The Artwork and Science of Chart Shade Codes: A Complete Information
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we’ll discover the intriguing matter associated to The Artwork and Science of Chart Shade Codes: A Complete Information. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
The Artwork and Science of Chart Shade Codes: A Complete Information
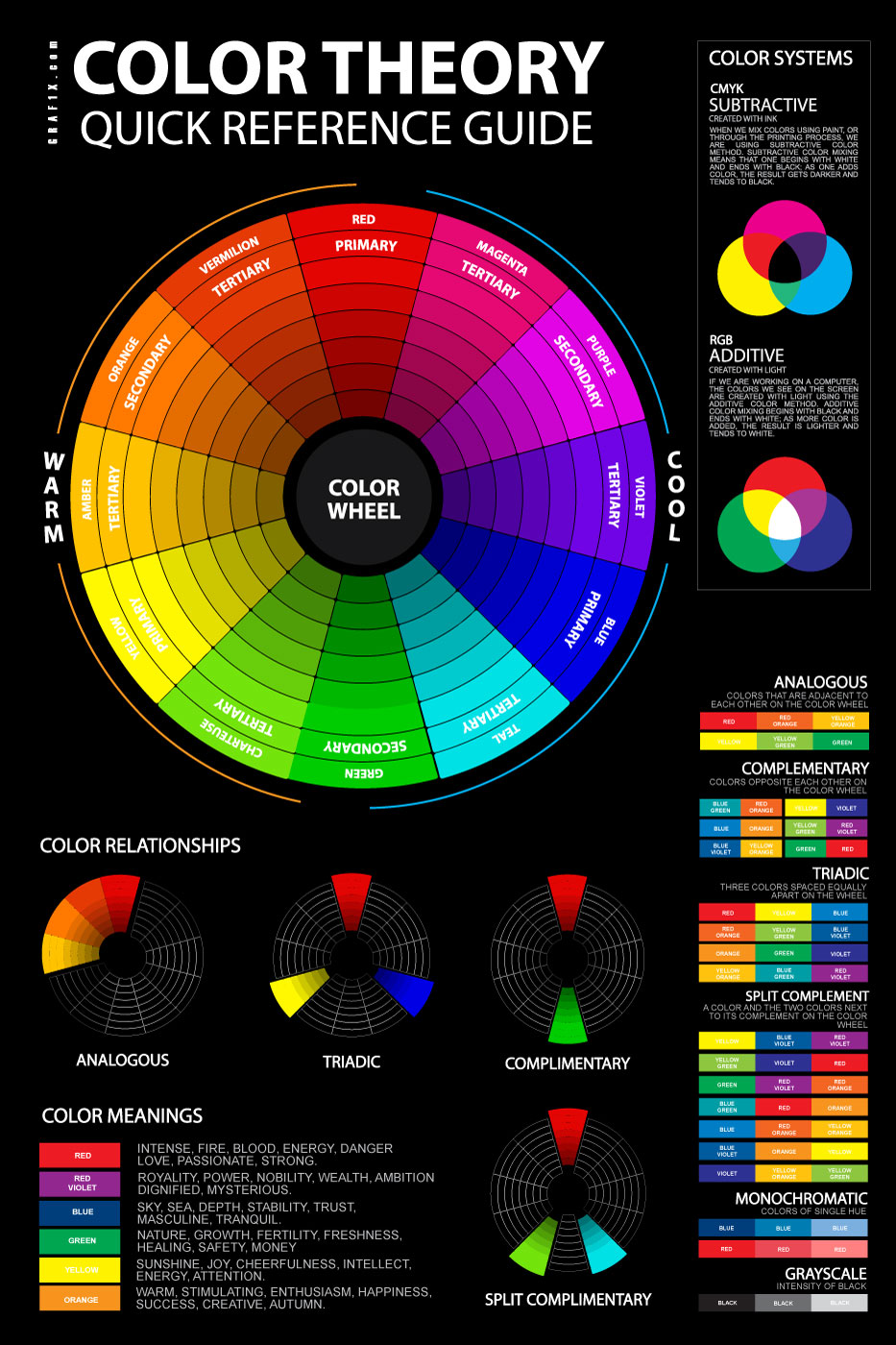
Charts and graphs are the visible language of information, conveying complicated info concisely and successfully. Nevertheless, the influence of a chart hinges not simply on the info it presents, but in addition on its visible presentation. A vital ingredient of this presentation is coloration. Selecting the best coloration code for a chart is not arbitrary; it is a mix of artwork and science, impacting readability, accessibility, and the general message conveyed. This text delves deep into the nuances of chart coloration codes, exploring greatest practices, widespread pitfalls, and the instruments accessible to create visually compelling and informative information visualizations.
I. The Psychology of Shade in Chart Design:
Shade is extra than simply aesthetics; it evokes feelings, influences perceptions, and guides the viewer’s eye. Understanding coloration psychology is paramount when choosing a coloration palette on your charts. Completely different colours carry totally different connotations:
- Pink: Typically related to urgency, hazard, or significance. Overuse might be overwhelming. Greatest used sparingly to spotlight crucial information factors.
- Orange: Conveys enthusiasm, creativity, and vitality. Good for representing optimistic developments or highlighting secondary info.
- Yellow: Represents happiness, optimism, and warning. Will be troublesome to learn on display, particularly for people with coloration imaginative and prescient deficiencies.
- Inexperienced: Typically related to progress, nature, and concord. Typically used to signify optimistic developments or profitable outcomes.
- Blue: Tasks calmness, belief, and stability. Appropriate for representing impartial or steady information.
- Purple: Can signify luxurious, royalty, or creativity. Use judiciously to keep away from showing overly flamboyant.
- Brown: Conveys earthiness, reliability, and ease. Will be much less visually stimulating than different colours.
- Grey/Black: Impartial colours, typically used for backgrounds or to de-emphasize much less vital information. Black might be harsh in giant portions.
- White: Represents purity, simplicity, and cleanliness. Typically used as a background coloration.
These are common associations; cultural contexts can affect coloration notion. What’s optimistic in a single tradition could also be unfavourable in one other. Think about your target market when making coloration selections.
II. Selecting a Shade Palette for Information Visualization:
The effectiveness of your chart relies upon closely on the chosen coloration palette. A number of key issues information this choice:
-
Information Sort and Relationships: The kind of information and the relationships between information factors affect coloration selections. For categorical information (e.g., totally different product classes), distinct, simply distinguishable colours are essential. For steady information (e.g., temperature adjustments), a sequential coloration palette (e.g., shades of blue from gentle to darkish) can successfully signify gradual adjustments. Diverging palettes (e.g., starting from blue to pink by a impartial midpoint) are perfect for highlighting deviations from a central worth.
-
Shade Blindness Concerns: Roughly 8% of males and 0.5% of girls expertise some type of coloration imaginative and prescient deficiency. Designing charts which might be accessible to all requires cautious consideration to paint selections. Keep away from utilizing red-green combos, as these are the commonest problematic pairings. Instruments and assets can be found to simulate coloration blindness and examine for accessibility (extra on this later).
-
Distinction and Readability: Ample distinction between information factors and the background is crucial for readability. Use instruments to measure distinction ratios (WCAG pointers suggest a minimal ratio of 4.5:1 for textual content and three:1 for big textual content). Be sure that textual content labels and information factors are clearly seen in opposition to the chosen background and coloration scheme.
-
Visible Hierarchy: Shade can be utilized to create visible hierarchy, guiding the viewer’s eye to a very powerful info. Use brighter, extra saturated colours for key information factors and fewer saturated colours for secondary info.
-
Consistency: Preserve consistency all through your chart and throughout a number of charts inside a presentation or report. Utilizing the identical coloration to signify the identical information level throughout totally different visualizations enhances understanding and reduces confusion.
III. Forms of Shade Palettes:
A number of established coloration palette sorts cater to totally different information visualization wants:
-
Sequential Palettes: These palettes use shades of a single coloration, progressing from gentle to darkish (or vice versa) to signify a steady variable. They’re best for displaying gradients, rankings, or magnitudes.
-
Diverging Palettes: These palettes use two distinct colours, typically with a impartial midpoint, to point out deviations from a central worth. They’re efficient for visualizing variations or contrasts.
-
Qualitative Palettes: These palettes use distinct, unrelated colours to signify totally different classes. The purpose is to maximise visible distinction between classes, to not indicate any order or magnitude.
-
Categorical Palettes: Just like qualitative palettes, these use distinct colours to signify classes. Nevertheless, they’re typically designed with coloration blindness in thoughts, providing larger accessibility.
-
Monochromatic Palettes: These palettes use varied shades and tints of a single coloration, offering a cohesive and chic look. They are often much less efficient for charts with many information factors.
IV. Instruments and Sources for Selecting Chart Shade Codes:
A number of instruments simplify the method of choosing applicable coloration palettes:
-
Shade Brewer: A preferred on-line software that gives palettes optimized for coloration blindness and cartographic visualization. It means that you can choose the kind of palette (sequential, diverging, and many others.) and the variety of colours wanted.
-
Adobe Shade: Adobe’s coloration software affords a variety of options, together with coloration palette era, coloration concord exploration, and coloration theme saving.
-
Coolors: A user-friendly software for producing and exploring coloration palettes. It permits for real-time changes and palette saving.
-
Paletton: A complete coloration scheme generator that means that you can outline colours primarily based on totally different coloration fashions (e.g., RGB, HSL) and discover varied coloration harmonies.
These instruments might help guarantee your coloration selections are accessible, visually interesting, and successfully talk your information.
V. Widespread Pitfalls to Keep away from:
-
Overusing Shade: Too many colours can overwhelm the viewer and make the chart troublesome to interpret. Follow a restricted palette that enhances readability.
-
Poor Distinction: Inadequate distinction between information factors and the background makes the chart troublesome to learn, notably for people with visible impairments.
-
Ignoring Shade Blindness: Failing to think about coloration blindness can render your chart inaccessible to a good portion of the inhabitants.
-
Utilizing Arbitrary Colours: Selecting colours with out contemplating their psychological influence can result in misinterpretations of the info.
-
Inconsistent Shade Use: Utilizing totally different colours to signify the identical information level throughout totally different charts creates confusion.
VI. Conclusion:
The selection of chart coloration code is a crucial side of efficient information visualization. By understanding the psychology of coloration, choosing applicable palettes, using accessible instruments, and avoiding widespread pitfalls, you’ll be able to create charts that aren’t solely visually interesting but in addition clear, accessible, and successfully talk your information insights. Keep in mind, the purpose is to information the viewer’s understanding, to not overwhelm or confuse them. A well-chosen coloration palette is an funding in clear communication and efficient information storytelling. The cautious collection of colours transforms information factors right into a compelling narrative, guaranteeing your message resonates together with your viewers.








Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered invaluable insights into The Artwork and Science of Chart Shade Codes: A Complete Information. We hope you discover this text informative and useful. See you in our subsequent article!