Understanding And Making use of The I-MR Chart: A Complete Information
By admin / July 13, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Understanding and Making use of the I-MR Chart: A Complete Information
Associated Articles: Understanding and Making use of the I-MR Chart: A Complete Information
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing subject associated to Understanding and Making use of the I-MR Chart: A Complete Information. Let’s weave fascinating info and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Understanding and Making use of the I-MR Chart: A Complete Information

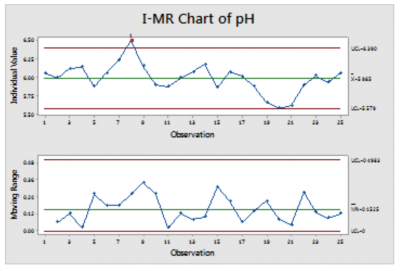
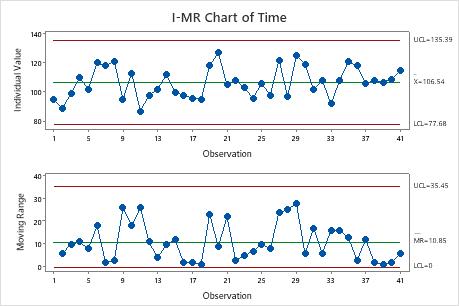
The I-MR chart, often known as the People and Shifting Vary chart, is a robust statistical course of management (SPC) device used to watch the steadiness of a course of the place particular person measurements are taken over time. Not like charts that analyze subgroups of information, the I-MR chart immediately analyzes particular person information factors, making it ultimate for conditions the place amassing subgroups is impractical or inefficient. This text will delve deep into the I-MR chart, exploring its purposes, building, interpretation, and limitations.
When to Use the I-MR Chart:
The I-MR chart is especially efficient when:
-
Particular person measurements are available: The method naturally generates particular person information factors, and amassing subgroups is not possible or fascinating. That is widespread in steady processes the place measurements are taken steadily and robotically. Examples embrace monitoring the temperature of a chemical reactor, the thickness of a sheet of metallic being produced, or the load of things coming off a manufacturing line.
-
Subgroup measurement is impractical: Forming subgroups is perhaps troublesome as a result of nature of the method or the fee concerned. As an illustration, testing a product is perhaps harmful, making it unattainable to create subgroups.
-
Course of variability is comparatively steady: Whereas the I-MR chart can detect shifts within the course of common, it is only when the method variability stays comparatively constant over time. Important modifications in variability would possibly require a unique charting approach.
-
Information are steady: The I-MR chart is designed for steady information (e.g., weight, temperature, size). It is not appropriate for discrete information (e.g., counts, defects).
Setting up the I-MR Chart:
The I-MR chart consists of two separate charts:
-
I-chart (People chart): This chart shows the person measurements over time. It tracks the central tendency of the method.
-
MR-chart (Shifting Vary chart): This chart displays the variability of the method. It plots the transferring vary, which is absolutely the distinction between consecutive particular person measurements.
Steps to Assemble an I-MR Chart:
-
Gather Information: Collect a minimal of 20-25 consecutive particular person measurements from the method. Extra information factors result in higher accuracy and reliability.
-
Calculate Shifting Ranges: Calculate the transferring vary (MR) for every consecutive pair of information factors. The transferring vary for information level i is calculated as |Xi – Xi-1|.
-
Calculate Averages: Calculate the typical of the person measurements (X̄) and the typical of the transferring ranges (MR̄).
-
Decide Management Limits: Management limits are calculated utilizing components primarily based on the variety of information factors. These components account for the variability inherent within the information. Generally used components are:
-
I-chart:
- Higher Management Restrict (UCLI) = X̄ + 3 * (MR̄/d2)
- Decrease Management Restrict (LCLI) = X̄ – 3 * (MR̄/d2)
-
MR-chart:
- Higher Management Restrict (UCLMR) = D4 * MR̄
- Decrease Management Restrict (LCLMR) = D3 * MR̄
The values of d2, D3, and D4 are constants depending on the variety of information factors used to calculate the transferring vary. These constants are available in statistical tables or software program packages. For a pattern measurement of two, d2 ≈ 1.128, D3 = 0, and D4 ≈ 3.267. For bigger pattern sizes, these values change.
-
-
Plot the Information: Plot the person measurements on the I-chart and the transferring ranges on the MR-chart. Draw the middle strains (X̄ and MR̄) and the management limits on each charts.
Decoding the I-MR Chart:
A steady course of is indicated by factors falling throughout the management limits on each charts, with no discernible patterns or traits. Factors outdoors the management limits or patterns throughout the limits counsel potential issues with the method. These patterns can embrace:
-
Factors outdoors the management limits: This means a major shift within the course of common or variability. An investigation is required to establish the foundation trigger.
-
Developments: A constant upward or downward pattern suggests a gradual shift within the course of.
-
Stratification: Clustering of factors above or beneath the middle line suggests a scientific variation within the course of.
-
Cycles: Repeating patterns of excessive and low values point out cyclical variations within the course of.
Benefits of Utilizing I-MR Charts:
-
Simplicity: The I-MR chart is comparatively simple to grasp and assemble, even for people with restricted statistical information.
-
Effectivity: It requires much less information assortment in comparison with subgrouping strategies.
-
Actual-time monitoring: It offers fast suggestions on course of efficiency.
-
Sensitivity: It is delicate to small shifts within the course of common and variability.
Limitations of Utilizing I-MR Charts:
-
Assumption of fixed variability: The I-MR chart assumes that the method variability stays comparatively steady over time. Important modifications in variability can have an effect on the accuracy of the management limits.
-
Sensitivity to outliers: Outliers can considerably affect the calculation of the management limits and result in deceptive interpretations. Strong strategies is perhaps essential to deal with outliers.
-
Restricted info on subgroups: Not like charts that analyze subgroups, the I-MR chart would not present info on the variability inside subgroups.
-
Information necessities: A ample variety of information factors is required for correct management restrict calculations.
Software program and Instruments:
Numerous statistical software program packages (e.g., Minitab, JMP, R) and spreadsheets (e.g., Microsoft Excel) can be utilized to assemble and analyze I-MR charts. These instruments automate the calculations and supply visible representations of the information, simplifying the method.
Case Examine: Monitoring the Weight of a Product
A producing firm produces small digital parts. To observe the load of those parts, they use an I-MR chart. They accumulate 25 consecutive measurements of the load (in grams) of the parts. After calculating the averages and transferring ranges, they decide the management limits. If some extent falls outdoors the management limits, or if a sample emerges throughout the limits, they examine the method to establish and proper the foundation reason behind the variation. This proactive method helps be sure that the parts meet the required weight specs.
Conclusion:
The I-MR chart is a beneficial device for monitoring and controlling processes the place particular person measurements are available. Its simplicity and effectiveness make it a preferred selection in numerous industries. Nonetheless, it is essential to grasp its assumptions and limitations earlier than making use of it. By rigorously amassing information, developing the chart accurately, and deciphering the outcomes precisely, the I-MR chart can present beneficial insights into course of efficiency and assist enhance product high quality and consistency. Keep in mind to all the time think about the particular traits of your course of and select the suitable SPC device accordingly. When unsure, consulting with a statistician or high quality management professional is really useful.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered beneficial insights into Understanding and Making use of the I-MR Chart: A Complete Information. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!