Understanding And Making use of The P-Chart: A Complete Information To Management Chart Choice
By admin / October 19, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Understanding and Making use of the P-Chart: A Complete Information to Management Chart Choice
Associated Articles: Understanding and Making use of the P-Chart: A Complete Information to Management Chart Choice
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to Understanding and Making use of the P-Chart: A Complete Information to Management Chart Choice. Let’s weave fascinating data and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Understanding and Making use of the P-Chart: A Complete Information to Management Chart Choice
Management charts are indispensable instruments in statistical course of management (SPC), offering a visible illustration of course of stability and serving to establish potential sources of variation. Among the many numerous forms of management charts, the p-chart holds a singular place, particularly designed for monitoring the proportion of nonconforming items in a pattern. This text delves deep into the p-chart, explaining when it is the suitable alternative, how one can assemble it, and the interpretations that may result in course of enchancment.
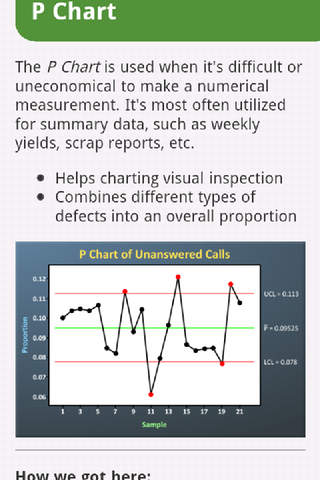
What’s a P-Chart?
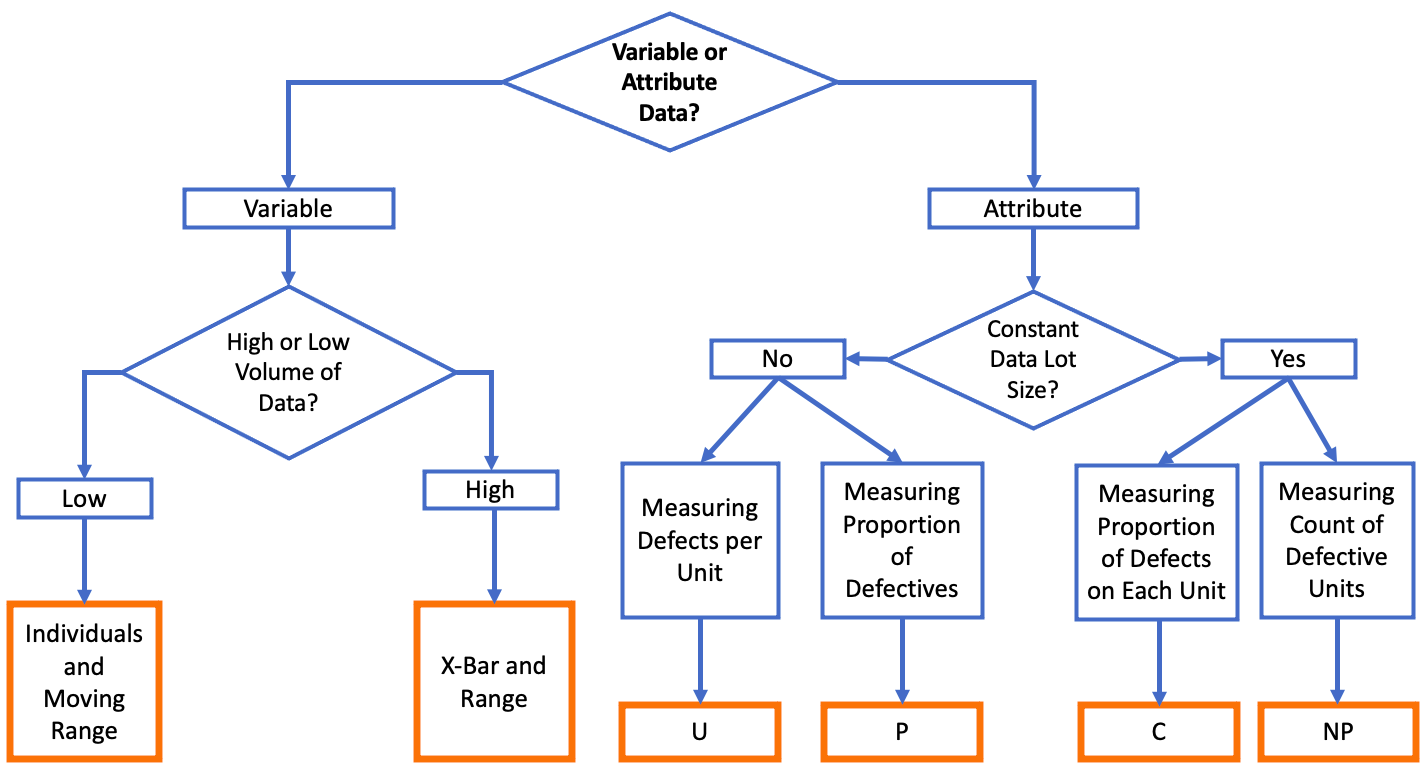
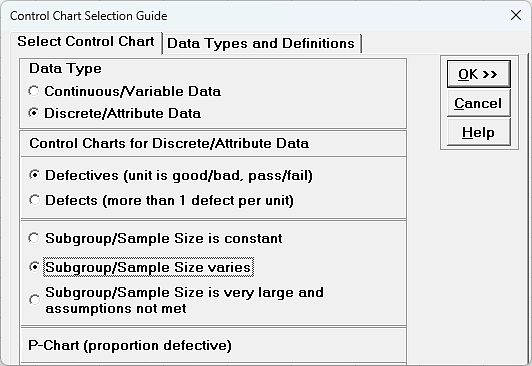
A p-chart, often known as a proportion chart, is a management chart used to watch the proportion (or share) of faulty objects in a pattern. Not like different management charts that observe steady information (like weight or size), the p-chart focuses on attribute information – information that’s categorized as both conforming or nonconforming to a particular specification. This makes it ideally suited for high quality management functions the place the important thing metric is the proportion of defects, quite than the magnitude of the defect.
When to Use a P-Chart:
The choice to make use of a p-chart hinges on a number of vital elements associated to the character of the info and the targets of the method monitoring. This is an in depth breakdown of eventualities the place a p-chart is essentially the most applicable alternative:
-
Attribute Knowledge: Essentially the most basic requirement is that the info being monitored represents the proportion of nonconforming items. This implies every unit within the pattern is classed as both "faulty" or "non-defective," "cross" or "fail," "conforming" or "nonconforming," and many others. Steady information (e.g., weight, temperature) must be analyzed utilizing totally different management charts like X-bar and R charts or people and transferring vary charts.
-
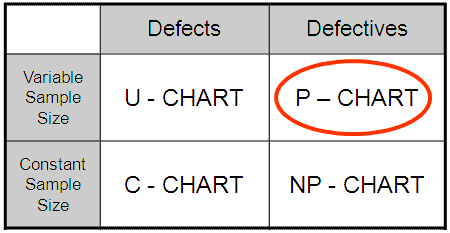
Variable Pattern Dimension: Not like some management charts that require a continuing pattern dimension, the p-chart can successfully deal with variable pattern sizes. This flexibility is essential in conditions the place the pattern dimension would possibly range because of sensible constraints or the character of the method. For instance, a manufacturing line would possibly produce totally different portions of a product all through the day, resulting in variable pattern sizes for inspection.
-
Monitoring Defect Charges: The first objective of a p-chart is to watch the proportion of defects. This makes it significantly helpful in figuring out shifts within the defect price over time. Early detection of a rise within the defect price permits for well timed corrective motion, stopping the manufacturing of huge numbers of faulty items.
-
Course of Functionality Evaluation: Whereas not its main perform, a p-chart could be a priceless software in assessing the aptitude of a course of to fulfill predefined high quality requirements. By analyzing the management limits and the proportion of defects, one can decide whether or not the method is constantly producing inside acceptable limits.
-
Massive Pattern Sizes: Whereas technically relevant to small pattern sizes, p-charts are usually extra dependable and informative when the pattern sizes are fairly massive. It’s because the central restrict theorem ensures that the sampling distribution of the proportion of defects approaches a standard distribution, which is the underlying assumption for the management limits calculation. As a rule of thumb, pattern sizes must be massive sufficient to make sure no less than 5 defects per pattern on common.
When NOT to Use a P-Chart:
Regardless of its versatility, a p-chart shouldn’t be all the time your best option. Contemplate these eventualities the place different management charts is likely to be extra applicable:
-
Steady Knowledge: As talked about, p-charts will not be appropriate for steady information. For steady measurements, X-bar and R charts (for subgroups) or people and transferring vary charts (for particular person observations) are extra applicable.
-
Small Pattern Sizes with Few Defects: If pattern sizes are constantly small and the variety of defects is rare, the p-chart would possibly lack sensitivity and produce unreliable management limits. In such instances, the u-chart, which displays the variety of defects per unit, is likely to be a greater choice.
-
A number of Defect Sorts: If a number of forms of defects are current and have to be monitored concurrently, a separate p-chart for every defect kind is critical. Nevertheless, if the main target is on the overall variety of defects no matter kind, the c-chart (for rely of defects) or u-chart (for defects per unit) is likely to be extra environment friendly.
-
Non-Random Knowledge: The p-chart assumes that the info are impartial and randomly sampled. If there’s proof of autocorrelation (information factors are correlated over time) or different types of non-randomness, the management limits is likely to be deceptive. In such instances, extra superior statistical methods is likely to be essential.
Establishing a P-Chart:
The development of a p-chart includes a number of steps:
-
Acquire Knowledge: Collect information on the variety of nonconforming items in every pattern. File each the variety of nonconforming items and the pattern dimension for every pattern.
-
Calculate the Pattern Proportions: For every pattern, calculate the proportion of nonconforming items (pᵢ) by dividing the variety of nonconforming items by the pattern dimension.
-
Calculate the Total Proportion: Calculate the typical proportion of nonconforming items (p̄) throughout all samples. That is the central tendency of the method.
-
Calculate the Management Limits: The management limits are calculated utilizing the next formulation:
- Heart Line (CL): p̄
- Higher Management Restrict (UCL): p̄ + 3√[(p̄(1-p̄))/n̄]
- Decrease Management Restrict (LCL): p̄ – 3√[(p̄(1-p̄))/n̄]
The place n̄ is the typical pattern dimension. Observe that if the LCL falls beneath zero, it’s usually set to zero.
-
Plot the Knowledge: Plot the pattern proportions (pᵢ) on a graph with time or pattern quantity on the x-axis and the proportion on the y-axis. Draw the middle line and management limits on the identical graph.
-
Interpret the Outcomes: Analyze the chart to establish any factors that fall exterior the management limits or any patterns that counsel instability within the course of.
Decoding the P-Chart:
A p-chart offers priceless insights into course of stability. This is how one can interpret the outcomes:
-
Factors Outdoors Management Limits: Factors constantly falling exterior the management limits point out that the method is uncontrolled. This means a major shift within the proportion of nonconforming items and warrants rapid investigation to establish the basis trigger.
-
Patterns Inside Management Limits: Even when all factors fall inside the management limits, patterns like developments (constant upward or downward motion), cycles (repeating patterns), or stratification (clustering of factors) can point out underlying course of instability. These patterns must be investigated to establish and tackle potential issues.
-
Steady Course of: If the factors are randomly distributed inside the management limits and no patterns are noticed, it signifies that the method is statistically secure and predictable.
Conclusion:
The p-chart is a robust software for monitoring the proportion of nonconforming items in a course of. By fastidiously contemplating the character of the info and the targets of the evaluation, practitioners can successfully make the most of the p-chart to establish sources of variation, enhance course of functionality, and improve product high quality. Nevertheless, it is essential to grasp the constraints of the p-chart and select the suitable management chart based mostly on the precise traits of the info and the method being monitored. Correct understanding and utility of the p-chart, coupled with thorough investigation of out-of-control alerts, can considerably contribute to steady course of enchancment and enhanced general high quality.



Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied priceless insights into Understanding and Making use of the P-Chart: A Complete Information to Management Chart Choice. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!