Understanding And Using Burn-Down Charts: A Complete Information With Examples
By admin / August 23, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Understanding and Using Burn-Down Charts: A Complete Information with Examples
Associated Articles: Understanding and Using Burn-Down Charts: A Complete Information with Examples
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to Understanding and Using Burn-Down Charts: A Complete Information with Examples. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Understanding and Using Burn-Down Charts: A Complete Information with Examples
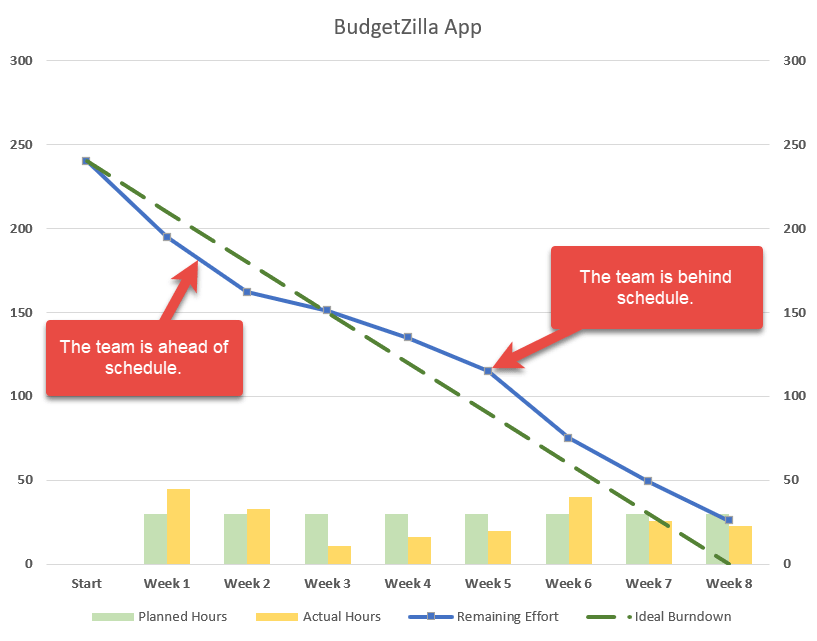
Burn-down charts are highly effective visible instruments utilized in venture administration, significantly inside agile methodologies like Scrum, to trace progress in direction of a venture aim. They supply a transparent and concise illustration of the remaining work, highlighting potential roadblocks and enabling proactive changes to make sure well timed completion. This text delves deep into burn-down charts, exploring their creation, interpretation, differing types, and showcasing sensible examples to solidify understanding.
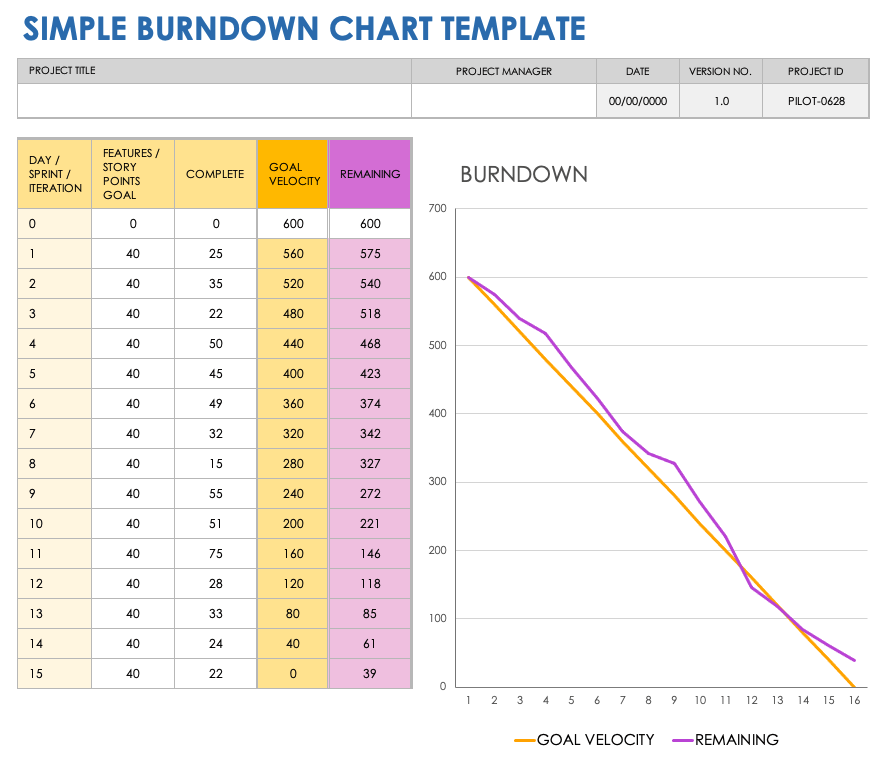
What’s a Burn-Down Chart?
A burn-down chart is a line graph that plots the quantity of labor remaining towards time. The "burn-down" refers back to the gradual discount within the remaining work because the venture progresses. The horizontal axis represents time (often days or sprints), whereas the vertical axis represents the quantity of labor remaining, typically measured in story factors, process hours, or just the variety of duties. The best burn-down chart exhibits a gentle, downward pattern, indicating constant progress in direction of the venture aim.
Key Parts of a Burn-Down Chart:
- X-axis (Time): Represents the venture timeline, usually damaged down into days, sprints, or iterations.
- Y-axis (Work Remaining): Represents the quantity of labor but to be accomplished. The models used rely upon the venture’s methodology and complexity.
- Baseline: A straight line representing the perfect burn-down charge. This line connects the preliminary quantity of labor to zero on the venture deadline. Deviations from this line point out potential points.
- Precise Progress Line: A line that plots the precise remaining work every day or dash. This line’s trajectory supplies insights into the venture’s precise progress.
- Knowledge Factors: Every level on the precise progress line represents the remaining work at a particular cut-off date.
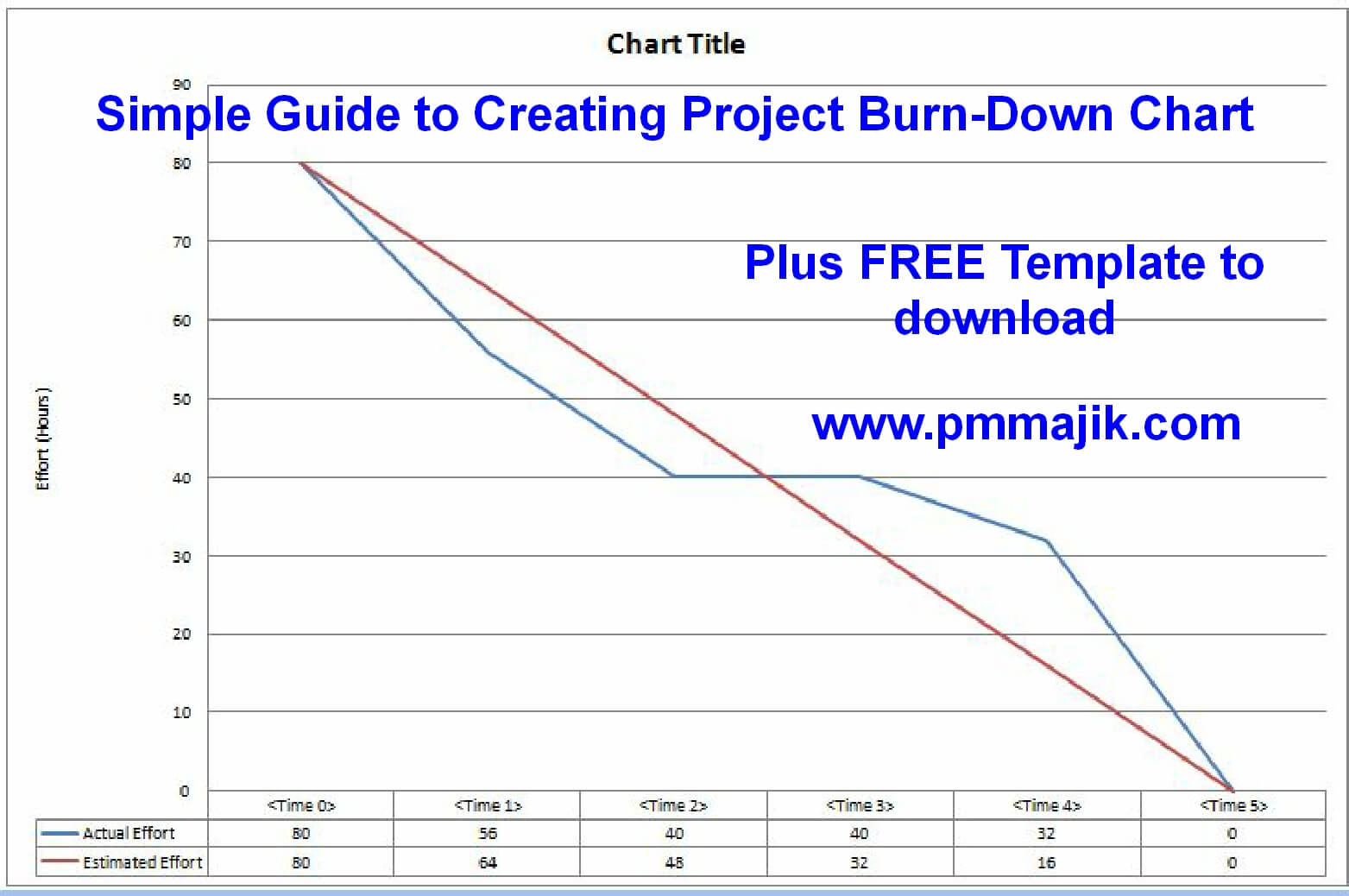
Making a Burn-Down Chart: A Step-by-Step Information
-
Outline the Scope: Clearly outline the venture scope and the work concerned. Break down the venture into smaller, manageable duties or person tales.
-
Estimate Work: Estimate the hassle required for every process. This may be in hours, story factors, or every other related unit. Consistency in estimation is essential for correct interpretation.
-
Calculate Preliminary Work: Sum the estimated effort for all duties to find out the preliminary quantity of labor remaining. This kinds the start line on the Y-axis of your chart.
-
Set up a Timeline: Outline the venture’s length and divide it into acceptable intervals (days or sprints). This kinds the X-axis of your chart.
-
Observe Progress: Usually monitor the completion of duties and replace the remaining work accordingly. This entails subtracting the finished work from the full remaining work at every interval.
-
Plot the Knowledge: Plot the remaining work towards the corresponding time intervals on the chart. Join the information factors to create the precise progress line.
-
Draw the Baseline: Draw a straight line connecting the preliminary quantity of labor on the Y-axis to zero on the venture deadline. This represents the perfect burn-down charge.
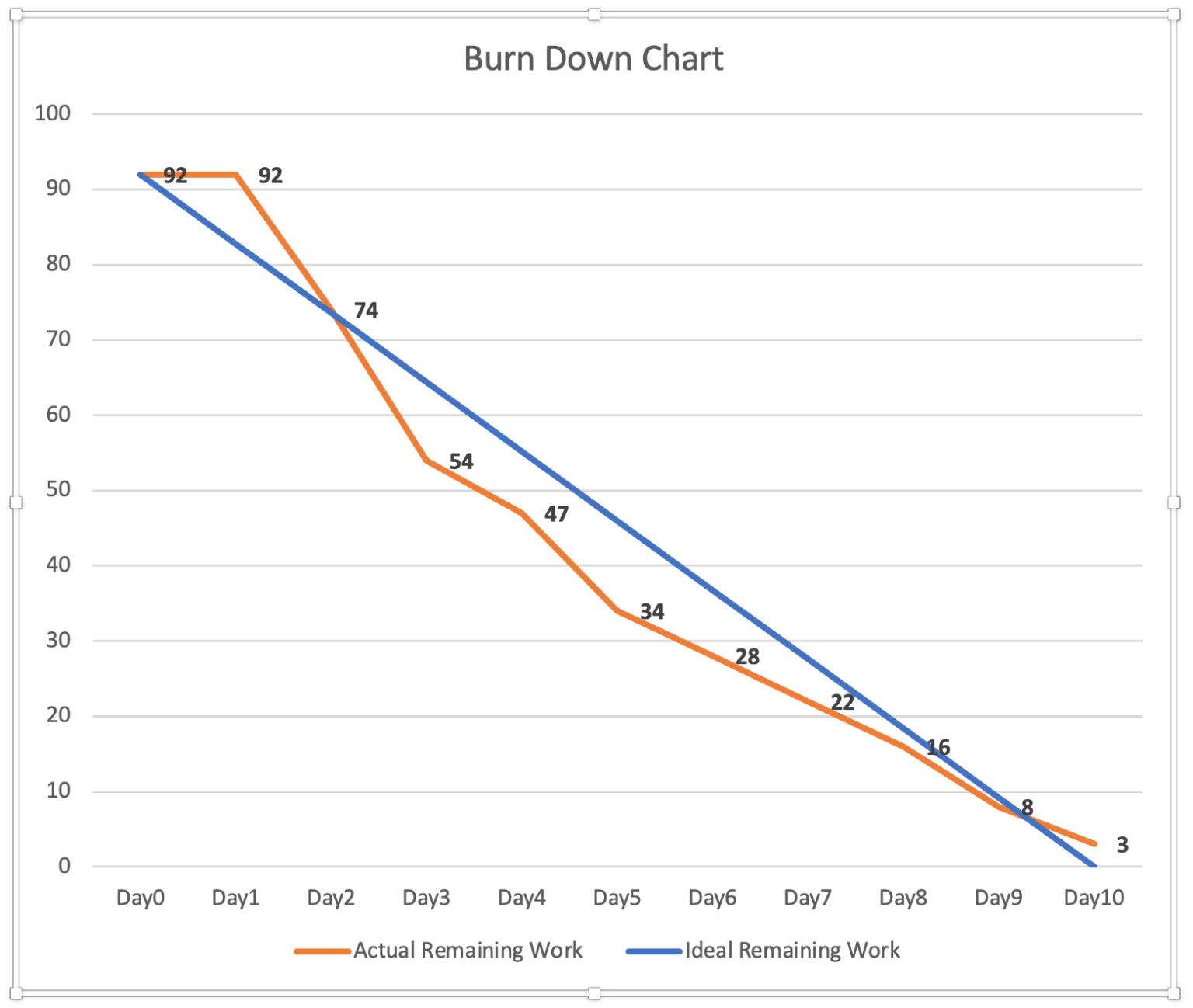
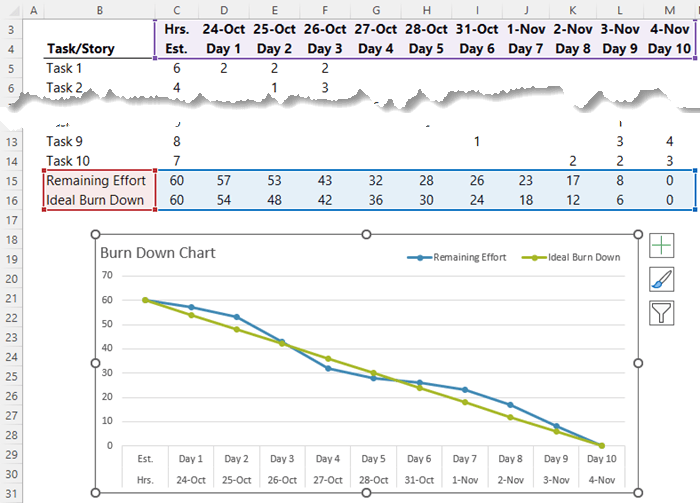
Instance Situation: Software program Improvement Mission
Let’s think about a software program growth venture with a dash length of two weeks (10 working days). The workforce initially estimated 50 story factors of labor. The next desk exhibits the remaining story factors on the finish of every day:
| Day | Remaining Story Factors |
|---|---|
| 0 | 50 |
| 1 | 45 |
| 2 | 40 |
| 3 | 38 |
| 4 | 32 |
| 5 | 28 |
| 6 | 25 |
| 7 | 20 |
| 8 | 15 |
| 9 | 10 |
| 10 | 0 |
By plotting this information on a chart, we will visualize the progress. The baseline could be a straight line from (0, 50) to (10, 0). The precise progress line will observe the information factors, doubtlessly deviating from the baseline. A major deviation would possibly point out a necessity for investigation.
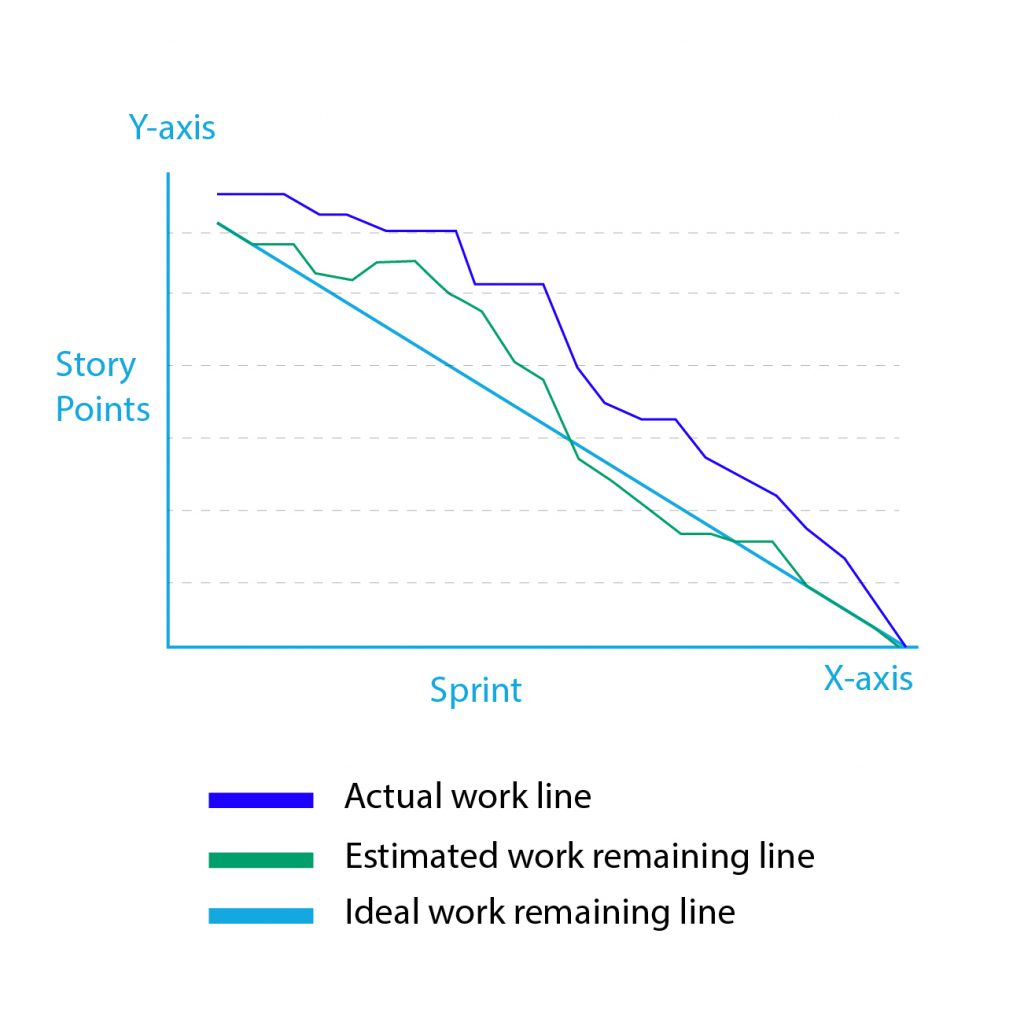
Decoding a Burn-Down Chart:
-
Best Progress: A line intently following the baseline signifies regular progress and a excessive probability of on-time completion.
-
Falling Behind: A line persistently under the baseline suggests the workforce is falling not on time. This requires figuring out bottlenecks and taking corrective actions.
-
Sudden Drops: Unexpectedly steep drops would possibly point out inaccurate preliminary estimations or the invention and backbone of great points.
-
Gradual Progress: A flat or slowly declining line signifies sluggish progress. This could possibly be on account of unexpected complexities, useful resource constraints, or scope creep.
-
Spikes: Sudden will increase in remaining work counsel new duties or points have emerged, requiring consideration and re-planning.
Forms of Burn-Down Charts:
-
Dash Burn-Down Chart: Tracks the progress of a single dash, exhibiting the remaining work inside that iteration.
-
Launch Burn-Down Chart: Tracks the progress of a whole launch, encompassing a number of sprints. It supplies a higher-level view of the venture’s total progress.
-
Cumulative Stream Diagram: Whereas not strictly a burn-down chart, it is a associated visible instrument that tracks the stream of labor by totally different phases of the event course of. It affords a extra complete view of workflow bottlenecks.
Past the Fundamentals: Enhancing Burn-Down Charts
-
Including impediments: Notice important impediments or roadblocks on the chart to offer context for deviations from the baseline.
-
A number of Baselines: For initiatives with a number of groups or workstreams, use a number of baselines to match progress throughout totally different areas.
-
Totally different Metrics: Experiment with totally different metrics for the Y-axis, equivalent to hours, story factors, or process counts, relying on the venture’s wants and complexity.
-
Common Updates: Common updates are essential for sustaining the accuracy and usefulness of the chart. Every day or weekly updates are widespread practices.
Conclusion:
Burn-down charts are invaluable instruments for visualizing venture progress, figuring out potential issues early, and facilitating proactive changes. Whereas seemingly easy, their efficient use requires cautious planning, correct estimation, and constant monitoring. By understanding their parts, interpretation, and variations, venture managers can leverage burn-down charts to boost workforce collaboration, enhance venture predictability, and in the end improve the probability of profitable venture supply. The examples supplied illustrate the sensible software of burn-down charts and spotlight their significance in agile venture administration. Keep in mind to adapt the chart and its metrics to greatest go well with the precise wants of your venture and workforce.



Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied beneficial insights into Understanding and Using Burn-Down Charts: A Complete Information with Examples. We recognize your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!