Understanding And Using Tables Of Constants For R Charts In Statistical Course of Management
By admin / July 4, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Understanding and Using Tables of Constants for R Charts in Statistical Course of Management
Associated Articles: Understanding and Using Tables of Constants for R Charts in Statistical Course of Management
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we’ll discover the intriguing matter associated to Understanding and Using Tables of Constants for R Charts in Statistical Course of Management. Let’s weave fascinating data and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Understanding and Using Tables of Constants for R Charts in Statistical Course of Management
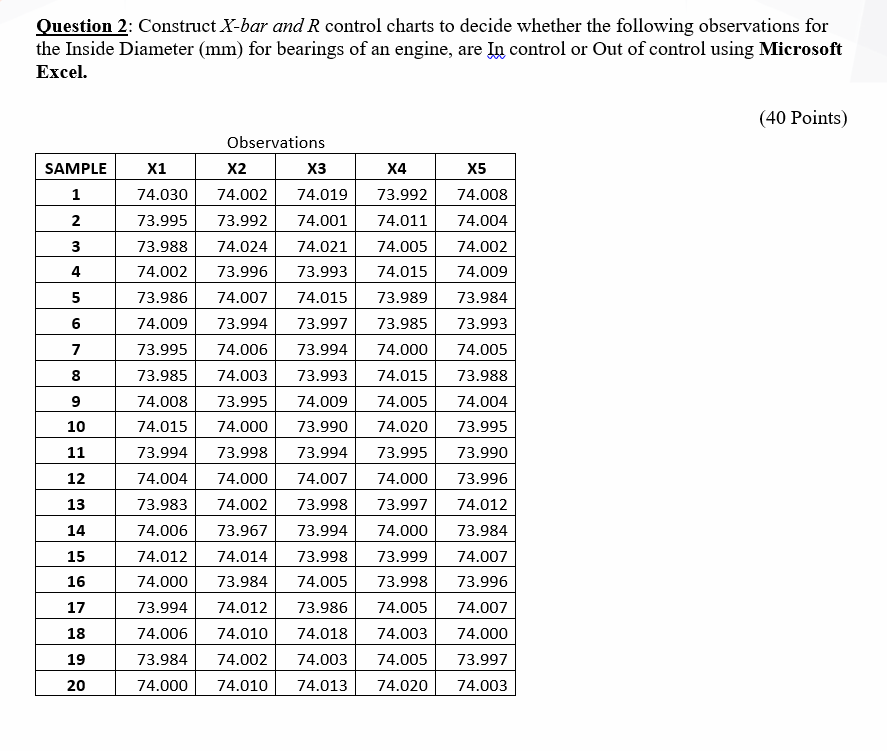
Statistical Course of Management (SPC) is a vital methodology for monitoring and bettering the standard of processes. One of many key instruments inside SPC is the management chart, and amongst these, the R chart performs a significant position in monitoring the variability inside a course of. The R chart, particularly, tracks the vary (R) of subgroups of knowledge, offering insights into the method’s inherent variability. Correct building and interpretation of R charts rely closely on tables of constants, that are important for calculating management limits and assessing course of stability. This text delves into the intricacies of R chart constants, their derivation, software, and the significance of choosing the suitable desk primarily based on subgroup measurement.
The R Chart: A Basis of Course of Variability Monitoring
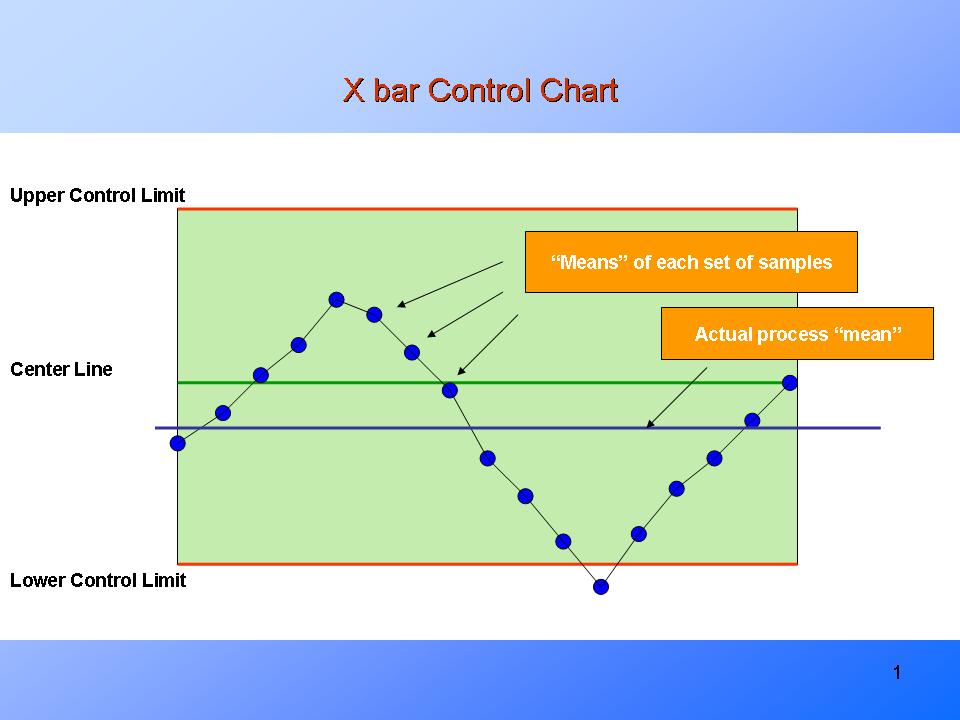
The R chart focuses on the vary, which is the distinction between the biggest and smallest values inside a subgroup. By plotting the vary of every subgroup over time, the R chart visually represents the method’s variability. A secure course of will exhibit ranges that fall inside predictable limits, whereas an unstable course of will present ranges that exceed these limits, indicating a possible drawback requiring investigation.
The important thing to developing an correct R chart lies within the correct calculation of the management limits. These limits should not arbitrarily chosen however are derived utilizing statistical strategies and rely on the subgroup measurement (n). That is the place tables of constants come into play.
Tables of Constants: The Spine of R Chart Calculations
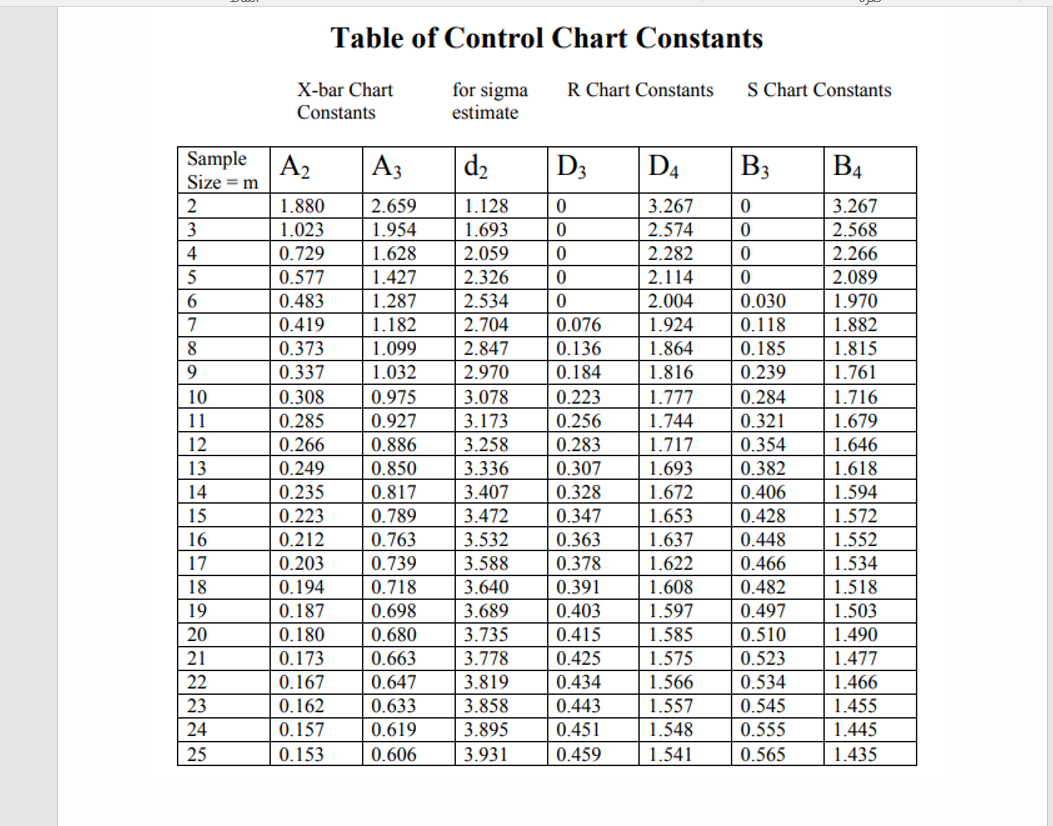
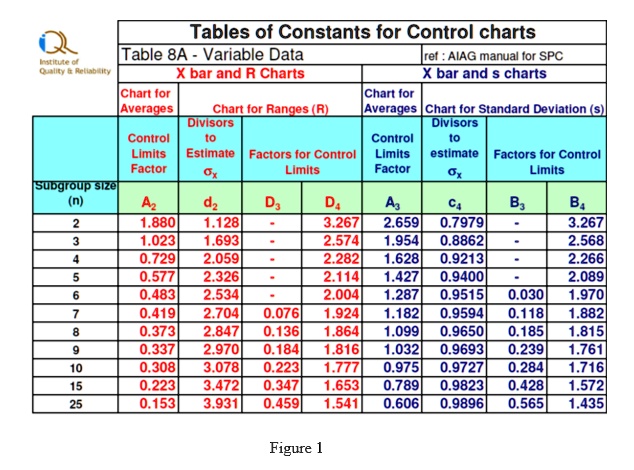
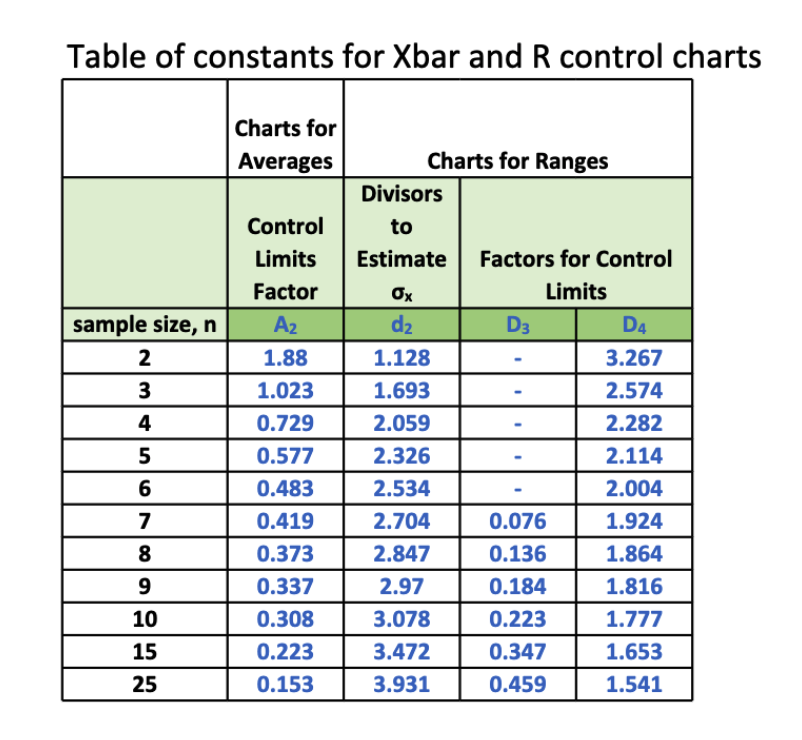
Tables of constants for R charts present the mandatory elements for calculating the central line and management limits. These tables are primarily based on the sampling distribution of the vary for various subgroup sizes. Probably the most generally used constants are:
-
d₂ (d-two): This fixed is used to calculate the central line of the R chart. The central line represents the common vary of the subgroups and is calculated as:
Central Line = R-bar = ΣR / okay, the place R-bar is the common vary and okay is the variety of subgroups. The worth of d₂ is then used to estimate the common vary if the underlying distribution is regular. -
D₃ (D-three): This fixed is used to calculate the decrease management restrict (LCL) of the R chart. The LCL is calculated as:
LCL = D₃ * R-bar. It is necessary to notice that D₃ is usually equal to zero, particularly for smaller subgroup sizes (n ≤ 5). This means that the decrease management restrict is successfully zero, implying that the vary can’t be unfavorable. -
D₄ (D-four): This fixed is used to calculate the higher management restrict (UCL) of the R chart. The UCL is calculated as:
UCL = D₄ * R-bar. The UCL represents the utmost acceptable vary for a secure course of.
Derivation of Constants: A Glimpse into Statistical Idea
The constants d₂, D₃, and D₄ are derived from the sampling distribution of the vary. This distribution depends on the underlying distribution of the information. For usually distributed information, the constants are derived utilizing the next ideas:
-
Anticipated Worth of the Vary: The anticipated worth of the vary (E[R]) for a pattern of measurement n from a traditional distribution is a operate of the inhabitants commonplace deviation (σ) and is proportional to d₂σ. This relationship permits for the estimation of σ from the common vary R-bar.
-
Distribution of the Vary: The distribution of the vary is just not regular, however its properties are well-established. The constants D₃ and D₄ are derived from the percentiles of the vary distribution, defining the boundaries inside which the vary is predicted to fall with a excessive likelihood (sometimes 99.73% for 3-sigma limits).
The derivation includes advanced mathematical procedures using the likelihood density operate of the vary and integration strategies. These calculations are sometimes carried out utilizing statistical software program or pre-computed tables.
Using Tables of Constants: A Sensible Information
Utilizing tables of constants is simple. As soon as the subgroup measurement (n) is decided, find the corresponding values of d₂, D₃, and D₄ within the desk. Then, calculate the central line and management limits utilizing the formulation talked about earlier.
For instance, if we now have subgroups of measurement n=5, a typical desk would supply the next constants:
- d₂ ≈ 2.326
- D₃ ≈ 0
- D₄ ≈ 2.115
For example we now have collected information from 20 subgroups, and the common vary (R-bar) is 5. The management limits could be calculated as follows:
- Central Line = R-bar = 5
- LCL = D₃ R-bar = 0 5 = 0
- UCL = D₄ R-bar = 2.115 5 = 10.575
These values would then be used to assemble the R chart.
Significance of Subgroup Measurement Choice
The selection of subgroup measurement (n) is essential and influences the effectiveness of the R chart. A smaller subgroup measurement (e.g., n=2 or n=3) could also be extra delicate to smaller shifts in variability however might also be extra inclined to noise. Bigger subgroup sizes (e.g., n=10 or n=20) could also be much less delicate to small shifts however can present a extra secure estimate of the method variability. The optimum subgroup measurement relies on the particular software and course of traits. It is necessary to contemplate elements reminiscent of the associated fee and time concerned in accumulating information and the specified sensitivity of the chart.
Past Regular Distribution: Issues for Non-Regular Information
The constants in commonplace tables are primarily based on the belief of a usually distributed course of. Nonetheless, many real-world processes don’t completely comply with a traditional distribution. If the information deviates considerably from normality, the accuracy of the management limits calculated utilizing commonplace tables could also be compromised. In such circumstances, different strategies, reminiscent of utilizing non-parametric management charts or bootstrapping strategies, could also be extra acceptable.
Software program and Instruments for R Chart Development
Quite a few software program packages and instruments can be found to simplify the development and evaluation of R charts. Statistical software program like Minitab, JMP, and R present built-in features for calculating constants, developing charts, and performing statistical exams. These instruments automate the calculations and supply visible representations of the information, making the method extra environment friendly and fewer susceptible to errors.
Conclusion: The Important Function of Tables of Constants in R Chart Implementation
Tables of constants are indispensable instruments for developing and deciphering R charts successfully. They supply the mandatory elements for calculating management limits, that are essential for monitoring course of variability and figuring out potential issues. Understanding the derivation and software of those constants is crucial for anybody concerned in high quality management and course of enchancment. By deciding on the suitable desk primarily based on subgroup measurement and contemplating the underlying distribution of the information, practitioners can make sure the correct and dependable software of R charts of their high quality administration efforts. The usage of acceptable software program can additional streamline the method, making certain environment friendly and correct evaluation of course of variability. The continued use and understanding of R charts and their related constants stay important for sustaining and bettering the standard of processes throughout numerous industries.



Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered priceless insights into Understanding and Using Tables of Constants for R Charts in Statistical Course of Management. We hope you discover this text informative and helpful. See you in our subsequent article!