Unveiling The Circle: A Complete Exploration Of Pie Charts
By admin / November 8, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Unveiling the Circle: A Complete Exploration of Pie Charts
Associated Articles: Unveiling the Circle: A Complete Exploration of Pie Charts
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate via the intriguing matter associated to Unveiling the Circle: A Complete Exploration of Pie Charts. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Unveiling the Circle: A Complete Exploration of Pie Charts
The pie chart, a ubiquitous visible illustration of information, affords a easy but highly effective approach to convey proportions and percentages inside an entire. Its round format, divided into slices, intuitively communicates the relative sizes of various classes, making it a invaluable device for knowledge visualization throughout numerous fields, from enterprise shows and scientific studies to instructional supplies and on a regular basis infographics. This text delves deep into the definition, building, purposes, benefits, limitations, and finest practices related to pie charts, offering a complete understanding of this basic knowledge visualization method.
Definition and Primary Development:
At its core, a pie chart is a round statistical graphic that represents numerical proportions as slices of a circle. Your complete circle represents the entire worth of the dataset, whereas every slice corresponds to a particular class or section inside that dataset. The scale of every slice is instantly proportional to the proportion or proportion it represents; a bigger slice signifies the next share, and a smaller slice represents a decrease share. The sum of all of the slices’ angles at all times equals 360 levels, reflecting the totality of the dataset.
The development of a pie chart entails a number of key steps:
-
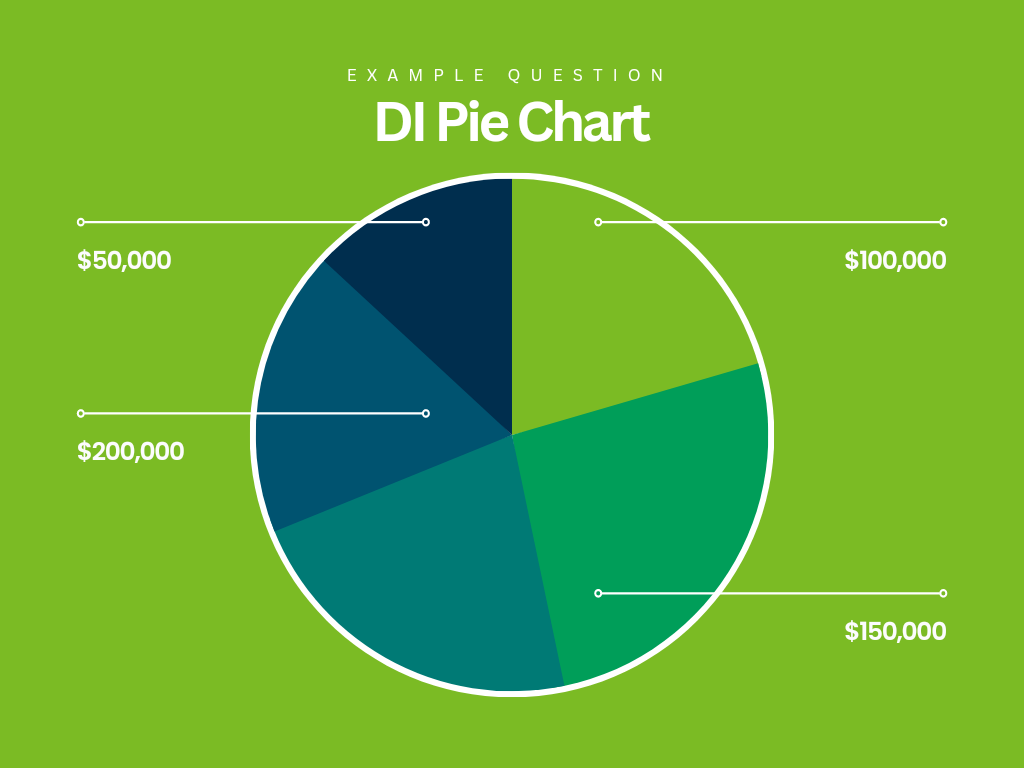
Knowledge Assortment and Preparation: The method begins with gathering the related knowledge. This knowledge must be categorical, that means it represents distinct classes or teams. The information must also be quantitative, with numerical values assigned to every class. For instance, a pie chart may signify the distribution of gross sales throughout completely different product strains, the place every product line is a class and its gross sales determine is the quantitative worth.
-
Calculating Percentages: As soon as the information is collected, every class’s share of the entire is calculated. This entails dividing the worth of every class by the entire worth and multiplying by 100. As an example, if the entire gross sales are $100,000 and one product line generated $25,000 in gross sales, its share could be (25,000/100,000) * 100 = 25%.
-
Figuring out Slice Angles: The share of every class is then transformed into an angle utilizing the next method: Angle = (Share/100) 360 levels. In our instance, the 25% product line would correspond to an angle of (25/100) 360 = 90 levels.
-
Creating the Chart: Utilizing a software program program (like Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets, or specialised knowledge visualization instruments), or manually with a compass and protractor, a circle is drawn. Every slice is then constructed utilizing the calculated angles, making certain that the slices precisely signify the proportions of the classes.
-
Labeling and Formatting: Lastly, every slice is labeled with its corresponding class identify and share. Applicable colours and a transparent title are added to boost readability and comprehension. A legend may be included to make clear the color-category mapping, significantly when coping with many classes.
Functions of Pie Charts:
The flexibility of pie charts makes them relevant throughout a variety of fields:
-
Enterprise and Finance: Analyzing market share, buyer demographics, gross sales efficiency, price range allocation, and funding portfolios.
-
Advertising and Promoting: Understanding shopper preferences, marketing campaign effectiveness, and model consciousness.
-
Healthcare: Illustrating illness prevalence, affected person demographics, remedy outcomes, and useful resource allocation.
-
Schooling: Representing scholar demographics, topic efficiency, and useful resource distribution inside faculties.
-
Science and Analysis: Visualizing experimental outcomes, survey knowledge, and inhabitants distributions.
-
Authorities and Public Coverage: Presenting demographic knowledge, price range breakdowns, and coverage affect assessments.
Benefits of Pie Charts:
Pie charts possess a number of benefits that contribute to their widespread use:
-
Intuitive Understanding: Their visible simplicity makes them simply comprehensible, even for people with restricted statistical data. The proportional illustration of information is instantly obvious.
-
Efficient Communication: They successfully talk relative proportions and percentages, permitting for fast comparisons between classes.
-
Conciseness: They current complicated knowledge in a compact and visually interesting format.
-
Broad Software program Assist: Most spreadsheet and knowledge visualization software program packages readily create pie charts.
-
Versatile Software: Their applicability spans numerous disciplines and knowledge varieties.
Limitations of Pie Charts:
Regardless of their benefits, pie charts even have limitations that ought to be thought-about:
-
Restricted Class Capability: Pie charts turn into tough to interpret after they include too many classes (usually greater than 6-8). The slices turn into too small and tough to differentiate, rendering the chart ineffective.
-
Problem in Evaluating Small Variations: It is difficult to precisely evaluate the sizes of slices that signify small share variations. The visible distinction could be negligible, making exact comparisons tough.
-
Deceptive Visible Notion: The human eye is not at all times correct at judging angles and areas, probably resulting in misinterpretations of the information.
-
Lack of ability to Present Adjustments Over Time: Pie charts are static; they do not successfully signify modifications in proportions over time. For time-series knowledge, different chart varieties like line charts or bar charts are extra appropriate.
-
Lack of Exact Numerical Knowledge: Whereas percentages are sometimes displayed, the precise numerical values usually are not at all times readily obvious.
Finest Practices for Creating Efficient Pie Charts:
To maximise the effectiveness of a pie chart, adhere to those finest practices:
-
Restrict the Variety of Classes: Hold the variety of classes to a manageable stage (6-8 at most) to stop visible litter and confusion.
-
Begin with the Largest Slice: Start with the biggest slice on the 12 o’clock place for higher visible movement and simpler comparability.
-
Use Clear and Concise Labels: Label every slice with its class identify and share. Keep away from overly lengthy or complicated labels.
-
Select Applicable Colours: Use contrasting colours which can be straightforward to differentiate. Think about using a coloration palette constant along with your branding or the general report model.
-
**Present a Clear



![Electricity Pie Chart [Sample IELTS Essay] - TED IELTS](https://ted-ielts.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/Learn-How-to-Describe-Pie-Charts-for-IELTS.png)

Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied invaluable insights into Unveiling the Circle: A Complete Exploration of Pie Charts. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!