Unveiling The Variations: Histograms, Bar Graphs, And Pie Charts
By admin / August 25, 2024 / No Comments / 2025
Unveiling the Variations: Histograms, Bar Graphs, and Pie Charts
Associated Articles: Unveiling the Variations: Histograms, Bar Graphs, and Pie Charts
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate via the intriguing matter associated to Unveiling the Variations: Histograms, Bar Graphs, and Pie Charts. Let’s weave fascinating data and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Unveiling the Variations: Histograms, Bar Graphs, and Pie Charts
![[통계학원론 with R] (자료의 기술) 4. 자료의 시각적 해석 : 네이버 블로그](https://www.investopedia.com/thmb/ilebTtfvaQER39ue8gEkMIpP6MY=/1500x0/filters:no_upscale():max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Histogram1-92513160f945482e95c1afc81cb5901e.png)
Knowledge visualization is paramount in successfully speaking insights derived from information evaluation. Selecting the best chart kind is essential for conveying data clearly and precisely. Three generally used chart sorts – histograms, bar graphs, and pie charts – every serve distinct functions and are greatest suited to completely different varieties of knowledge. Whereas they might seem related at first look, understanding their elementary variations is significant for creating compelling and informative visualizations. This text will delve into the specifics of every chart kind, outlining their purposes, strengths, and limitations.
1. Histograms: Unveiling the Distribution of Steady Knowledge
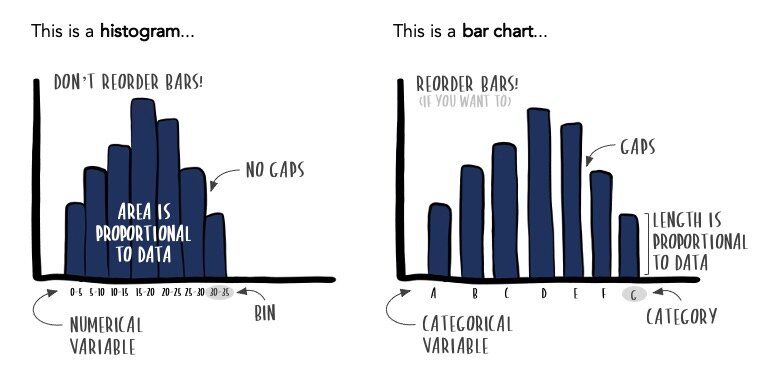
Histograms are a robust software for visualizing the distribution of steady information. Not like bar graphs, which signify categorical information, histograms showcase the frequency distribution of numerical information that falls inside particular intervals or bins. The horizontal axis represents the vary of the continual variable, divided into equally sized intervals (bins), whereas the vertical axis represents the frequency (depend) or relative frequency (proportion) of knowledge factors falling inside every bin.
Key Traits of Histograms:
- Steady Knowledge: Histograms are completely used for steady information, equivalent to peak, weight, temperature, or revenue. Discrete information with numerous values will also be successfully represented utilizing histograms.
- Bins: The information is grouped into bins or intervals, creating a visible illustration of the info’s density. The width of the bins can affect the looks of the histogram, and selecting an acceptable bin width is essential for correct interpretation. Too few bins would possibly obscure essential particulars, whereas too many bins would possibly create a jagged and uninformative graph.
- No Gaps Between Bars: A defining function of histograms is the absence of gaps between the bars. The bars are contiguous, emphasizing the continual nature of the info. The world of every bar represents the frequency or relative frequency of the info factors inside that bin.
- Form of the Distribution: Histograms reveal the form of the info distribution, permitting for the identification of patterns like symmetry, skewness, and modality (variety of peaks). This data is essential for understanding the underlying information traits and making knowledgeable inferences.
Purposes of Histograms:
- Understanding Knowledge Distribution: Histograms are invaluable for exploring the distribution of a steady variable, revealing its central tendency, unfold, and potential outliers.
- Figuring out Outliers: Outliers, information factors considerably completely different from the remainder, are simply noticed in histograms as remoted bars or gaps within the distribution.
- Evaluating Distributions: A number of histograms can be utilized to match the distributions of the identical variable throughout completely different teams or populations.
- High quality Management: In manufacturing and different industries, histograms are used to observe the standard of merchandise or processes by visualizing the distribution of key traits.
Limitations of Histograms:
- Bin Width Sensitivity: The selection of bin width can considerably influence the looks and interpretation of the histogram. Completely different bin widths can result in completely different interpretations of the info.
- Lack of Particular person Knowledge Factors: Histograms group information into bins, resulting in a lack of particular person information level data.
- Tough to Examine A number of Variables: Whereas evaluating distributions of a single variable throughout completely different teams is feasible, evaluating a number of variables concurrently is difficult utilizing histograms.
2. Bar Graphs: Categorical Knowledge Visualization
Bar graphs, not like histograms, are used to signify categorical information. They show the frequencies or proportions of various classes of a variable. The horizontal axis represents the classes, and the vertical axis represents the frequency or proportion of every class. The bars are separated, emphasizing the discrete nature of the explicit information.
Key Traits of Bar Graphs:
- Categorical Knowledge: Bar graphs are designed for categorical information, equivalent to gender, colour, kind of automobile, or nation.
- Separated Bars: A vital distinction from histograms is the separation between bars. This visible separation highlights the distinct nature of the classes.
- Frequency or Proportion: The peak of every bar represents the frequency (depend) or proportion (proportion) of observations in every class.
- Straightforward Comparability: Bar graphs facilitate straightforward comparability of frequencies or proportions throughout completely different classes.
Purposes of Bar Graphs:
- Evaluating Classes: Bar graphs are wonderful for evaluating the frequencies or proportions of various classes.
- Displaying Traits Over Time: When the classes signify time intervals (e.g., years, months), bar graphs can successfully present traits over time.
- Presenting Survey Outcomes: Bar graphs are generally used to current the outcomes of surveys and polls, exhibiting the distribution of responses throughout completely different classes.
- Illustrating Categorical Knowledge Relationships: Bar graphs can be utilized for example the connection between two categorical variables, typically utilizing grouped or stacked bar charts.
Limitations of Bar Graphs:
- Not Appropriate for Steady Knowledge: Bar graphs usually are not acceptable for representing steady information.
- Order of Classes: The order of classes on the horizontal axis can affect the visible interpretation of the info.
- Restricted Data on Distribution: Bar graphs don’t present detailed details about the distribution of knowledge inside every class.
3. Pie Charts: Proportional Illustration of Components of a Entire
Pie charts are used to signify the proportion of various classes relative to the entire. Every slice of the pie represents a class, and the scale of the slice is proportional to the class’s proportion of the full.
Key Traits of Pie Charts:
- Proportional Illustration: Pie charts visually signify the proportion of every class as a slice of a circle. The scale of every slice is immediately proportional to its proportion of the full.
- Straightforward Understanding: Pie charts are usually straightforward to grasp and interpret, particularly when the variety of classes is small.
- Restricted Variety of Classes: Pie charts are handiest when the variety of classes is comparatively small (sometimes lower than 7). Too many classes could make the chart cluttered and tough to interpret.
- Emphasis on Proportions: Pie charts emphasize the relative proportions of various classes somewhat than their absolute frequencies.
Purposes of Pie Charts:
- Displaying Composition: Pie charts are perfect for exhibiting the composition of a complete, such because the market share of various corporations or the distribution of age teams in a inhabitants.
- Easy Proportions: When the main target is on demonstrating the proportion of every class relative to the full, pie charts present a transparent and concise visualization.
- Presenting Funds Allocation: Pie charts can successfully illustrate how a price range is allotted throughout completely different areas.
Limitations of Pie Charts:
- Tough to Examine Slices: Exact comparability of slice sizes might be difficult, particularly when the slices are related in dimension.
- Restricted Variety of Classes: Pie charts develop into cluttered and tough to interpret when the variety of classes is giant.
- Doesn’t Present Absolute Values: Pie charts solely present proportions; they don’t show absolutely the frequencies or values of every class.
- Deceptive with Unequal Slices: When slices are shut in dimension, it turns into tough to evaluate their relative proportions precisely.
Selecting the Proper Chart Kind:
The selection of chart kind depends upon the kind of information and the message you need to convey. This is a abstract that can assist you resolve:
- Steady Knowledge, Distribution Focus: Use a histogram.
- Categorical Knowledge, Comparability Focus: Use a bar graph.
- Categorical Knowledge, Proportion Focus: Use a pie chart.
By understanding the strengths and limitations of histograms, bar graphs, and pie charts, you’ll be able to choose probably the most acceptable chart kind to successfully visualize your information and talk your findings clearly and precisely. Do not forget that efficient information visualization is not only about choosing the proper chart, but additionally about cautious design, clear labeling, and acceptable context. Utilizing these instruments correctly will considerably improve your potential to extract that means from information and share your insights with others.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered beneficial insights into Unveiling the Variations: Histograms, Bar Graphs, and Pie Charts. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!